动机
为了逼近现实生活中的最短路径,例如地图,可能存在许多障碍的游戏。
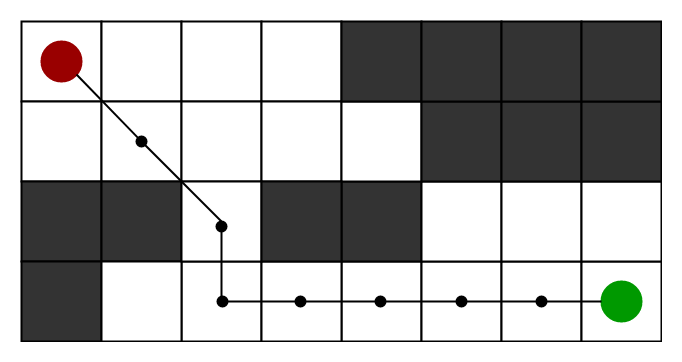
我们可以考虑一个有多个障碍的2D网格,我们从源单元格(下面的红色)开始向目标单元格(下面的绿色)开始
什么是A *搜索算法?
A *搜索算法是在路径查找和图形遍历中使用的最佳且流行的技术之一。
为什么要使用A *搜索算法?
非正式地说,A *搜索算法与其他遍历技术不同,它具有“大脑”。这意味着它确实是一种智能算法,可将其与其他常规算法区分开。以下各节将详细说明这一事实。
而且值得一提的是,许多游戏和基于Web的地图都使用此算法非常有效地找到最短路径(近似值)。
解释
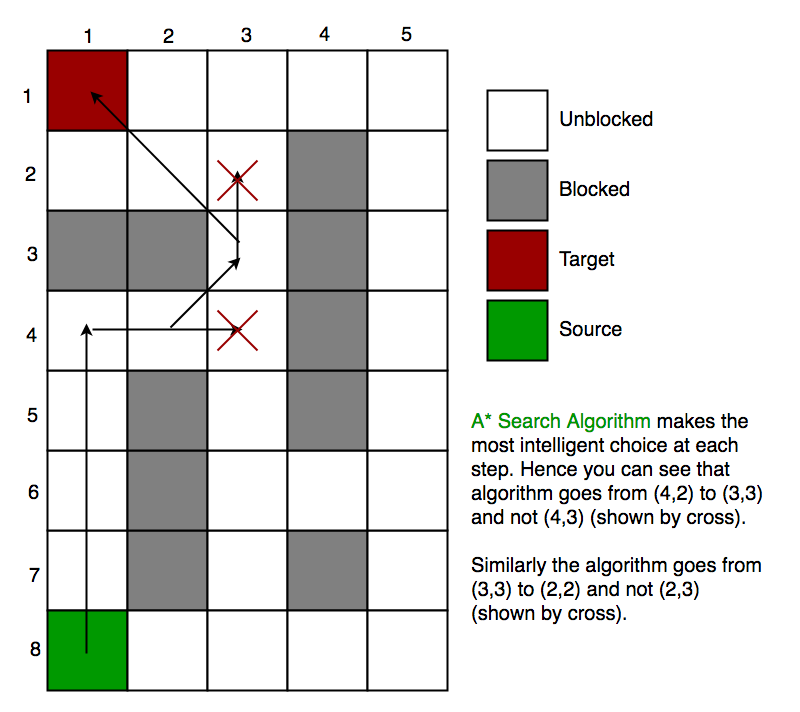
考虑一个有许多障碍的正方形网格,我们得到了一个起始单元和一个目标单元。我们希望尽快从起始单元格到达目标单元格。在这里,A *搜索算法可以解决问题。
A *搜索算法的作用是,在每个步骤中,它都根据值“ f ”来选择节点,该值“ f”等于两个其他参数“ g ”和“ h ”之和。在每个步骤中,它选择具有最低“ f ”的节点/单元,并处理该节点/单元。
我们在下面尽可能简单地定义“ g ”和“ h”
g =从起点到网格上给定正方形的移动成本,遵循生成到该路径的路径。
h =从网格上给定正方形移动到最终目的地的估计移动成本。这通常被称为启发式,这不过是一种明智的猜测。在找到路径之前,我们真的不知道实际距离,因为各种各样的东西都可能挡住道路(墙壁,水等)。可以使用许多方法来计算此“ h”,这将在后面的部分中进行讨论。
算法
我们创建两个列表–打开列表和关闭列表(就像Dijkstra算法一样)
// A* Search Algorithm
1. Initialize the open list
2. Initialize the closed list
put the starting node on the open
list (you can leave its f at zero)
3. while the open list is not empty
a) find the node with the least f on
the open list, call it "q"
b) pop q off the open list
c) generate q's 8 successors and set their
parents to q
d) for each successor
i) if successor is the goal, stop search
successor.g = q.g + distance between
successor and q
successor.h = distance from goal to
successor (This can be done using many
ways, we will discuss three heuristics-
Manhattan, Diagonal and Euclidean
Heuristics)
successor.f = successor.g + successor.h
ii) if a node with the same position as
successor is in the OPEN list which has a
lower f than successor, skip this successor
iii) if a node with the same position as
successor is in the CLOSED list which has
a lower f than successor, skip this successor
otherwise, add the node to the open list
end (for loop)
e) push q on the closed list
end (while loop)因此,假设如下图所示,如果我们想从源像元到达目标像元,则A * Search算法将遵循如下所示的路径。请注意,下图是通过将欧几里德距离作为启发式方法得出的。
启发式
我们可以计算g,但是如何计算h呢?
我们可以做的事。
A)要么计算h的确切值(这肯定很耗时)。
或者
B)使用一些启发法(较少的时间消耗)来近似估计h的值。
我们将讨论这两种方法。
A)精确启发式–
我们可以找到h的确切值,但这通常非常耗时。
以下是一些计算h确切值的方法。
1)在运行A *搜索算法之前,预先计算每对像元之间的距离。
2)如果没有阻塞的单元格/障碍物,那么我们可以使用距离公式/欧几里得距离来找到h的确切值而无需任何预先计算
B)近似启发式–
通常,可以使用三种近似试探法来计算h –
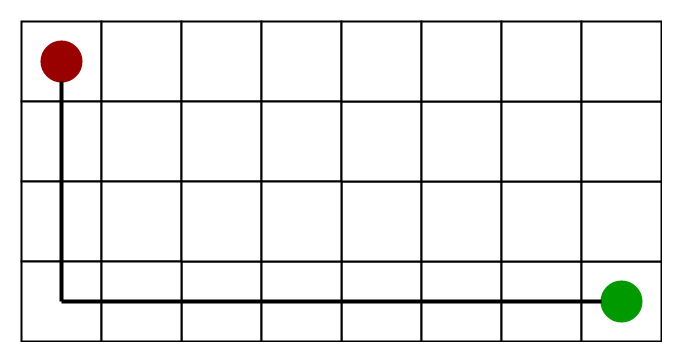
1)曼哈顿距离–
- 它不过是目标的x和y坐标与当前单元格的x和y坐标之差的绝对值之和,即
h = abs (current_cell.x – goal.x) +
abs (current_cell.y – goal.y)- 什么时候使用这种启发式? –仅允许我们在四个方向(右,左,上,下)移动时
下图显示了曼哈顿距离启发法(假设红色斑点作为源单元格,绿色斑点作为目标单元格)。
2)对角线距离
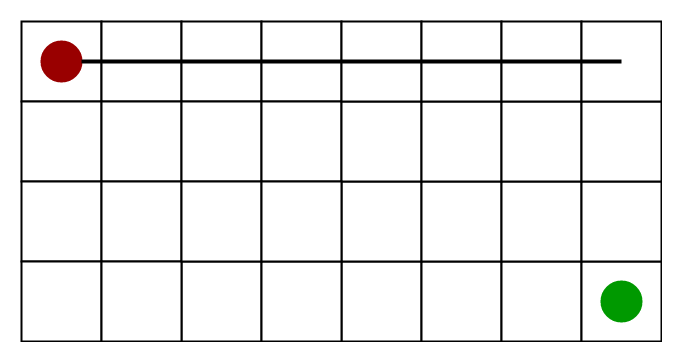
- 仅仅是目标的x和y坐标与当前单元格的x和y坐标之差的绝对值的最大值,即
h = max { abs(current_cell.x – goal.x),
abs(current_cell.y – goal.y) }- 什么时候使用这种启发式? –当我们只被允许在八个方向上移动时(类似于国际象棋中国王的移动)
下图显示了对角距离启发法(假设红色斑点作为源单元格,绿色斑点作为目标单元格)。
3)欧几里德距离-
- 从其名称可以清楚地看出,它只是使用距离公式的当前像元与目标像元之间的距离
h = sqrt ( (current_cell.x – goal.x)2 +
(current_cell.y – goal.y)2 )- 什么时候使用这种启发式? –当我们被允许向任何方向移动时。
下图显示了欧几里得距离启发法(假设红色斑点为源单元格,绿色斑点为目标单元格)。
与其他算法的关系(相似性和差异)
Dijkstra是A *搜索算法的特例,其中所有节点的h = 0。
执行
我们可以使用任何数据结构来实现打开列表和关闭列表,但是为了获得最佳性能,我们使用C++ STL的一组数据结构(实现为Red-Black Tree)和一个布尔哈希表来关闭列表。
实现类似于Dijsktra的算法。如果我们使用Fibonacci堆而不是二进制堆/自平衡树来实现打开列表,则性能会更好(因为Fibonacci堆平均需要O(1)的时间才能插入打开列表并减少键)
为了减少计算g所花费的时间,我们将使用动态编程。
CPP
// A C++ Program to implement A* Search Algorithm
#include
using namespace std;
#define ROW 9
#define COL 10
// Creating a shortcut for int, int pair type
typedef pair Pair;
// Creating a shortcut for pair> type
typedef pair > pPair;
// A structure to hold the neccesary parameters
struct cell {
// Row and Column index of its parent
// Note that 0 <= i <= ROW-1 & 0 <= j <= COL-1
int parent_i, parent_j;
// f = g + h
double f, g, h;
};
// A Utility Function to check whether given cell (row, col)
// is a valid cell or not.
bool isValid(int row, int col)
{
// Returns true if row number and column number
// is in range
return (row >= 0) && (row < ROW) && (col >= 0)
&& (col < COL);
}
// A Utility Function to check whether the given cell is
// blocked or not
bool isUnBlocked(int grid[][COL], int row, int col)
{
// Returns true if the cell is not blocked else false
if (grid[row][col] == 1)
return (true);
else
return (false);
}
// A Utility Function to check whether destination cell has
// been reached or not
bool isDestination(int row, int col, Pair dest)
{
if (row == dest.first && col == dest.second)
return (true);
else
return (false);
}
// A Utility Function to calculate the 'h' heuristics.
double calculateHValue(int row, int col, Pair dest)
{
// Return using the distance formula
return ((double)sqrt(
(row - dest.first) * (row - dest.first)
+ (col - dest.second) * (col - dest.second)));
}
// A Utility Function to trace the path from the source
// to destination
void tracePath(cell cellDetails[][COL], Pair dest)
{
printf("\nThe Path is ");
int row = dest.first;
int col = dest.second;
stack Path;
while (!(cellDetails[row][col].parent_i == row
&& cellDetails[row][col].parent_j == col)) {
Path.push(make_pair(row, col));
int temp_row = cellDetails[row][col].parent_i;
int temp_col = cellDetails[row][col].parent_j;
row = temp_row;
col = temp_col;
}
Path.push(make_pair(row, col));
while (!Path.empty()) {
pair p = Path.top();
Path.pop();
printf("-> (%d,%d) ", p.first, p.second);
}
return;
}
// A Function to find the shortest path between
// a given source cell to a destination cell according
// to A* Search Algorithm
void aStarSearch(int grid[][COL], Pair src, Pair dest)
{
// If the source is out of range
if (isValid(src.first, src.second) == false) {
printf("Source is invalid\n");
return;
}
// If the destination is out of range
if (isValid(dest.first, dest.second) == false) {
printf("Destination is invalid\n");
return;
}
// Either the source or the destination is blocked
if (isUnBlocked(grid, src.first, src.second) == false
|| isUnBlocked(grid, dest.first, dest.second)
== false) {
printf("Source or the destination is blocked\n");
return;
}
// If the destination cell is the same as source cell
if (isDestination(src.first, src.second, dest)
== true) {
printf("We are already at the destination\n");
return;
}
// Create a closed list and initialise it to false which
// means that no cell has been included yet This closed
// list is implemented as a boolean 2D array
bool closedList[ROW][COL];
memset(closedList, false, sizeof(closedList));
// Declare a 2D array of structure to hold the details
// of that cell
cell cellDetails[ROW][COL];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < COL; j++) {
cellDetails[i][j].f = FLT_MAX;
cellDetails[i][j].g = FLT_MAX;
cellDetails[i][j].h = FLT_MAX;
cellDetails[i][j].parent_i = -1;
cellDetails[i][j].parent_j = -1;
}
}
// Initialising the parameters of the starting node
i = src.first, j = src.second;
cellDetails[i][j].f = 0.0;
cellDetails[i][j].g = 0.0;
cellDetails[i][j].h = 0.0;
cellDetails[i][j].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i][j].parent_j = j;
/*
Create an open list having information as-
>
where f = g + h,
and i, j are the row and column index of that cell
Note that 0 <= i <= ROW-1 & 0 <= j <= COL-1
This open list is implenented as a set of pair of
pair.*/
set openList;
// Put the starting cell on the open list and set its
// 'f' as 0
openList.insert(make_pair(0.0, make_pair(i, j)));
// We set this boolean value as false as initially
// the destination is not reached.
bool foundDest = false;
while (!openList.empty()) {
pPair p = *openList.begin();
// Remove this vertex from the open list
openList.erase(openList.begin());
// Add this vertex to the closed list
i = p.second.first;
j = p.second.second;
closedList[i][j] = true;
/*
Generating all the 8 successor of this cell
N.W N N.E
\ | /
\ | /
W----Cell----E
/ | \
/ | \
S.W S S.E
Cell-->Popped Cell (i, j)
N --> North (i-1, j)
S --> South (i+1, j)
E --> East (i, j+1)
W --> West (i, j-1)
N.E--> North-East (i-1, j+1)
N.W--> North-West (i-1, j-1)
S.E--> South-East (i+1, j+1)
S.W--> South-West (i+1, j-1)*/
// To store the 'g', 'h' and 'f' of the 8 successors
double gNew, hNew, fNew;
//----------- 1st Successor (North) ------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i - 1, j) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i - 1, j, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i - 1][j].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i - 1][j].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i - 1][j] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i - 1, j)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.0;
hNew = calculateHValue(i - 1, j, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i - 1][j].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i - 1][j].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i - 1, j)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i - 1][j].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i - 1][j].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 2nd Successor (South) ------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i + 1, j) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i + 1, j, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i + 1][j].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i + 1][j].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i + 1][j] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i + 1, j)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.0;
hNew = calculateHValue(i + 1, j, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i + 1][j].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i + 1][j].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i + 1, j)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i + 1][j].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i + 1][j].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 3rd Successor (East) ------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i, j + 1) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i, j + 1, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i][j + 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i][j + 1].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i][j + 1] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i, j + 1)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.0;
hNew = calculateHValue(i, j + 1, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i][j + 1].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i][j + 1].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i, j + 1)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i][j + 1].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i][j + 1].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i][j + 1].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i][j + 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i][j + 1].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 4th Successor (West) ------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i, j - 1) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i, j - 1, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i][j - 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i][j - 1].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i][j - 1] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i, j - 1)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.0;
hNew = calculateHValue(i, j - 1, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i][j - 1].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i][j - 1].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i, j - 1)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i][j - 1].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i][j - 1].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i][j - 1].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i][j - 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i][j - 1].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 5th Successor (North-East)
//------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i - 1, j + 1) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i - 1, j + 1, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i - 1][j + 1] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i - 1, j + 1)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.414;
hNew = calculateHValue(i - 1, j + 1, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i - 1, j + 1)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i - 1][j + 1].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 6th Successor (North-West)
//------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i - 1, j - 1) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i - 1, j - 1, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i - 1][j - 1] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i - 1, j - 1)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.414;
hNew = calculateHValue(i - 1, j - 1, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i - 1, j - 1)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i - 1][j - 1].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 7th Successor (South-East)
//------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i + 1, j + 1) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i + 1, j + 1, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i + 1][j + 1] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i + 1, j + 1)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.414;
hNew = calculateHValue(i + 1, j + 1, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i + 1, j + 1)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i + 1][j + 1].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
//----------- 8th Successor (South-West)
//------------
// Only process this cell if this is a valid one
if (isValid(i + 1, j - 1) == true) {
// If the destination cell is the same as the
// current successor
if (isDestination(i + 1, j - 1, dest) == true) {
// Set the Parent of the destination cell
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].parent_j = j;
printf("The destination cell is found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
foundDest = true;
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the closed
// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.
// Else do the following
else if (closedList[i + 1][j - 1] == false
&& isUnBlocked(grid, i + 1, j - 1)
== true) {
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.414;
hNew = calculateHValue(i + 1, j - 1, dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to
// the open list. Make the current square
// the parent of this square. Record the
// f, g, and h costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list already, check
// to see if this path to that square is
// better, using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].f == FLT_MAX
|| cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].f > fNew) {
openList.insert(make_pair(
fNew, make_pair(i + 1, j - 1)));
// Update the details of this cell
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].f = fNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].g = gNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].h = hNew;
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].parent_i = i;
cellDetails[i + 1][j - 1].parent_j = j;
}
}
}
}
// When the destination cell is not found and the open
// list is empty, then we conclude that we failed to
// reach the destiantion cell. This may happen when the
// there is no way to destination cell (due to
// blockages)
if (foundDest == false)
printf("Failed to find the Destination Cell\n");
return;
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
/* Description of the Grid-
1--> The cell is not blocked
0--> The cell is blocked */
int grid[ROW][COL]
= { { 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1 } };
// Source is the left-most bottom-most corner
Pair src = make_pair(8, 0);
// Destination is the left-most top-most corner
Pair dest = make_pair(0, 0);
aStarSearch(grid, src, dest);
return (0);
} C++14
// A C++ Program to implement A* Search Algorithm
#include "math.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Creating a shortcut for int, int pair type
typedef pair Pair;
// Creating a shortcut for tuple type
typedef tuple Tuple;
// A structure to hold the neccesary parameters
struct cell {
// Row and Column index of its parent
Pair parent;
// f = g + h
double f, g, h;
cell()
: parent(-1, -1)
, f(-1)
, g(-1)
, h(-1)
{
}
};
// A Utility Function to check whether given cell (row, col)
// is a valid cell or not.
template
bool isValid(const array, ROW>& grid,
const Pair& point)
{ // Returns true if row number and column number is in
// range
if (ROW > 0 && COL > 0)
return (point.first >= 0) && (point.first < ROW)
&& (point.second >= 0)
&& (point.second < COL);
return false;
}
// A Utility Function to check whether the given cell is
// blocked or not
template
bool isUnBlocked(const array, ROW>& grid,
const Pair& point)
{
// Returns true if the cell is not blocked else false
return isValid(grid, point)
&& grid[point.first][point.second] == 1;
}
// A Utility Function to check whether destination cell has
// been reached or not
bool isDestination(const Pair& position, const Pair& dest)
{
return position == dest;
}
// A Utility Function to calculate the 'h' heuristics.
double calculateHValue(const Pair& src, const Pair& dest)
{
// h is estimated with the two points distance formula
return sqrt(pow((src.first - dest.first), 2.0)
+ pow((src.second - dest.second), 2.0));
}
// A Utility Function to trace the path from the source to
// destination
template
void tracePath(
const array, ROW>& cellDetails,
const Pair& dest)
{
printf("\nThe Path is ");
stack Path;
int row = dest.second;
int col = dest.second;
Pair next_node = cellDetails[row][col].parent;
do {
Path.push(next_node);
next_node = cellDetails[row][col].parent;
row = next_node.first;
col = next_node.second;
} while (cellDetails[row][col].parent != next_node);
Path.emplace(row, col);
while (!Path.empty()) {
Pair p = Path.top();
Path.pop();
printf("-> (%d,%d) ", p.first, p.second);
}
}
// A Function to find the shortest path between a given
// source cell to a destination cell according to A* Search
// Algorithm
template
void aStarSearch(const array, ROW>& grid,
const Pair& src, const Pair& dest)
{
// If the source is out of range
if (!isValid(grid, src)) {
printf("Source is invalid\n");
return;
}
// If the destination is out of range
if (!isValid(grid, dest)) {
printf("Destination is invalid\n");
return;
}
// Either the source or the destination is blocked
if (!isUnBlocked(grid, src)
|| !isUnBlocked(grid, dest)) {
printf("Source or the destination is blocked\n");
return;
}
// If the destination cell is the same as source cell
if (isDestination(src, dest)) {
printf("We are already at the destination\n");
return;
}
// Create a closed list and initialise it to false which
// means that no cell has been included yet This closed
// list is implemented as a boolean 2D array
bool closedList[ROW][COL];
memset(closedList, false, sizeof(closedList));
// Declare a 2D array of structure to hold the details
// of that cell
array, ROW> cellDetails;
int i, j;
// Initialising the parameters of the starting node
i = src.first, j = src.second;
cellDetails[i][j].f = 0.0;
cellDetails[i][j].g = 0.0;
cellDetails[i][j].h = 0.0;
cellDetails[i][j].parent = { i, j };
/*
Create an open list having information as-
>
where f = g + h,
and i, j are the row and column index of that cell
Note that 0 <= i <= ROW-1 & 0 <= j <= COL-1
This open list is implenented as a set of tuple.*/
std::priority_queue,
std::greater >
openList;
// Put the starting cell on the open list and set its
// 'f' as 0
openList.emplace(0.0, i, j);
// We set this boolean value as false as initially
// the destination is not reached.
while (!openList.empty()) {
const Tuple& p = openList.top();
// Add this vertex to the closed list
i = get<1>(p); // second element of tupla
j = get<2>(p); // third element of tupla
// Remove this vertex from the open list
openList.pop();
closedList[i][j] = true;
/*
Generating all the 8 successor of this cell
N.W N N.E
\ | /
\ | /
W----Cell----E
/ | \
/ | \
S.W S S.E
Cell-->Popped Cell (i, j)
N --> North (i-1, j)
S --> South (i+1, j)
E --> East (i, j+1)
W --> West (i, j-1)
N.E--> North-East (i-1, j+1)
N.W--> North-West (i-1, j-1)
S.E--> South-East (i+1, j+1)
S.W--> South-West (i+1, j-1)
*/
for (int add_x = -1; add_x <= 1; add_x++) {
for (int add_y = -1; add_y <= 1; add_y++) {
Pair neighbour(i + add_x, j + add_y);
// Only process this cell if this is a valid
// one
if (isValid(grid, neighbour)) {
// If the destination cell is the same
// as the current successor
if (isDestination(
neighbour,
dest)) { // Set the Parent of
// the destination cell
cellDetails[neighbour.first]
[neighbour.second]
.parent
= { i, j };
printf("The destination cell is "
"found\n");
tracePath(cellDetails, dest);
return;
}
// If the successor is already on the
// closed list or if it is blocked, then
// ignore it. Else do the following
else if (!closedList[neighbour.first]
[neighbour.second]
&& isUnBlocked(grid,
neighbour)) {
double gNew, hNew, fNew;
gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.0;
hNew = calculateHValue(neighbour,
dest);
fNew = gNew + hNew;
// If it isn’t on the open list, add
// it to the open list. Make the
// current square the parent of this
// square. Record the f, g, and h
// costs of the square cell
// OR
// If it is on the open list
// already, check to see if this
// path to that square is better,
// using 'f' cost as the measure.
if (cellDetails[neighbour.first]
[neighbour.second]
.f
== -1
|| cellDetails[neighbour.first]
[neighbour.second]
.f
> fNew) {
openList.emplace(
fNew, neighbour.first,
neighbour.second);
// Update the details of this
// cell
cellDetails[neighbour.first]
[neighbour.second]
.g
= gNew;
cellDetails[neighbour.first]
[neighbour.second]
.h
= hNew;
cellDetails[neighbour.first]
[neighbour.second]
.f
= fNew;
cellDetails[neighbour.first]
[neighbour.second]
.parent
= { i, j };
}
}
}
}
}
}
// When the destination cell is not found and the open
// list is empty, then we conclude that we failed to
// reach the destiantion cell. This may happen when the
// there is no way to destination cell (due to
// blockages)
printf("Failed to find the Destination Cell\n");
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
/* Description of the Grid-
1--> The cell is not blocked
0--> The cell is blocked */
array, 9> grid{
{ { { 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 } },
{ { 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1 } },
{ { 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 } },
{ { 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 } },
{ { 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0 } },
{ { 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 } },
{ { 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1 } },
{ { 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 } },
{ { 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1 } } }
};
// Source is the left-most bottom-most corner
Pair src(8, 0);
// Destination is the left-most top-most corner
Pair dest(0, 0);
aStarSearch(grid, src, dest);
return 0;
} 局限性
尽管A *搜索算法是周围最好的寻路算法,但它并非总是产生最短的路径,因为它严重依赖于启发式/近似法来计算– h
应用领域
这是A *搜索算法中最有趣的部分。它们用于游戏中!但是如何?
曾经玩过塔防游戏吗?
塔防是一种战略视频游戏,其目标是通过阻碍敌方攻击者来保卫玩家的领土或财产,通常是通过在其攻击路径上或沿其攻击路径放置防御结构来实现的。
A *搜索算法通常用于查找从一个点到另一点的最短路径。您可以将其用于每个敌人,以找到通往目标的路径。
其中一个例子是非常受欢迎的游戏《魔兽争霸III》
如果搜索空间不是网格而是图形,该怎么办?
相同的规则也适用于此。网格的示例是为了简化理解。因此,我们可以使用此A *搜索算法在图中找到源节点和目标节点之间的最短路径,就像我们对2D网格所做的一样。
时间复杂度
考虑一个图,可能需要我们从源单元行进所有的边缘以到达目标单元[例如,考虑一个图,其中源节点和目标节点通过一系列边连接,例如– 0(source)–> 1 –> 2 –> 3(目标)
因此,最糟糕的情况是时间复杂度为O(E),其中E是图中的边数
辅助空间在最坏的情况下,我们可以将所有边都包含在开放列表中,因此,在最坏的情况下,所需的辅助空间为O(V),其中V是顶点的总数。
练习给读者-
有没有想过如何制作像《吃豆人》这样的游戏,那里有很多这样的障碍。我们可以使用A *搜索算法找到正确的方法吗?
认为这是一个有趣的练习。
感兴趣的读者的文章
在我们的程序中,障碍是固定的。如果障碍在移动,该怎么办?有兴趣的读者可能会在这里看到有关此主题的精彩讨论。
概括
那么,何时在A *上使用DFS,何时在A *上使用Dijkstra找到最短路径?
我们可以总结如下:
1)一个来源和一个目的地-
→使用A *搜索算法(适用于未加权以及加权图)
2)一个来源,所有目的地–
→使用BFS(用于未加权图)
→使用Dijkstra(用于没有负权重的加权图)
→使用Bellman Ford(用于负权重的加权图)
3)在每对节点之间-
→弗洛伊德·沃歇尔(Floyd-Warshall)
→约翰逊算法