给定一棵具有N个节点和N-1个边的树,当树中的任何节点被视为树的根时,找出树的最大高度。

上图表示一棵具有11个节点和10条边的树,以及当将节点1视为根时给出最大高度的路径。最大高度为3。
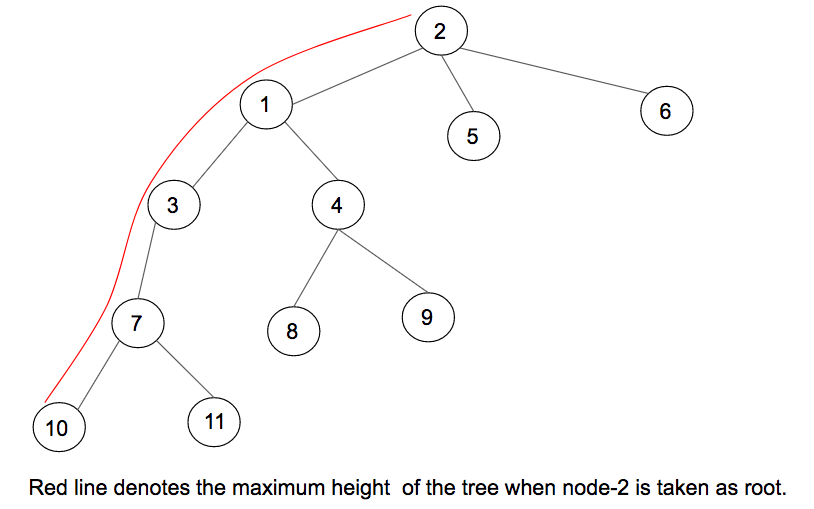
在上图中,当将2视为根时,找到的最长路径是红色。天真的方法是使用DFS遍历每个节点遍历树,并在将节点视为树的根节点时计算最大高度。遍历树的DFS的时间复杂度为O(N)。所有N个节点的DFS的总时间复杂度将为O(N)* N,即O(N 2 ) 。
通过使用“树上动态编程”可以解决上述问题。要解决此问题,请为每个节点预先计算两件事。一个最大的高度是通过树枝向下延伸到树叶时的最大高度。而另一个则是通过其父级向上移动到任何叶子时的最大高度。
最佳子结构:
当节点i被视为根节点时,
in [i]是当我们通过其子树和树叶向下行驶时的最大树高。
同样, out [i]是通过父树向上行驶时树的最大高度。
The maximum height of tree when node i is
considered as root will be max(in[i], out[i]).
in [i]的计算:
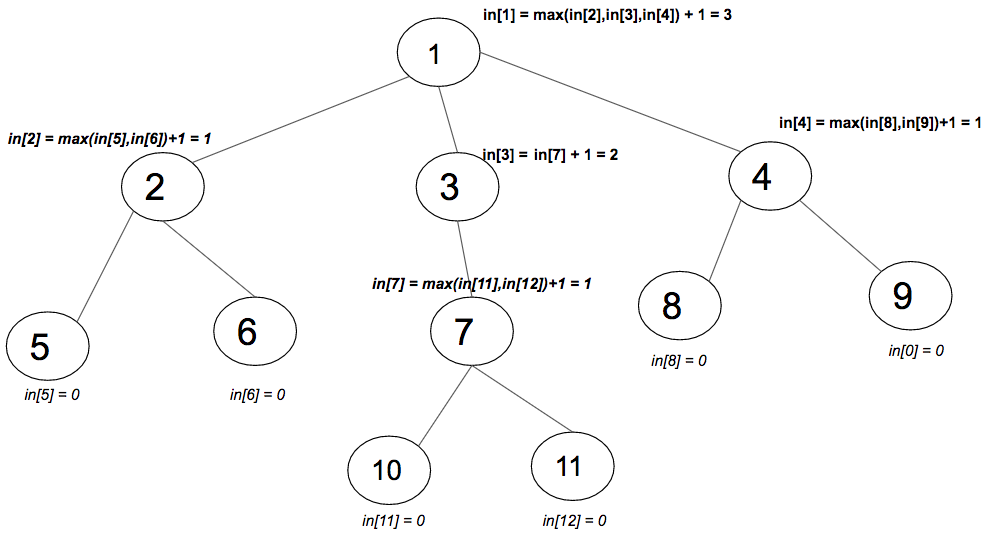
在上图中,已经为每个节点i计算了in [i]的值。取每个子树的最大值,并将其加1到该子树的父树。在父树和子树之间的边缘加1。使用DFS遍历树,并为每个节点将in [i]计算为max(in [i],1 + in [child]) 。
out [i]的计算:
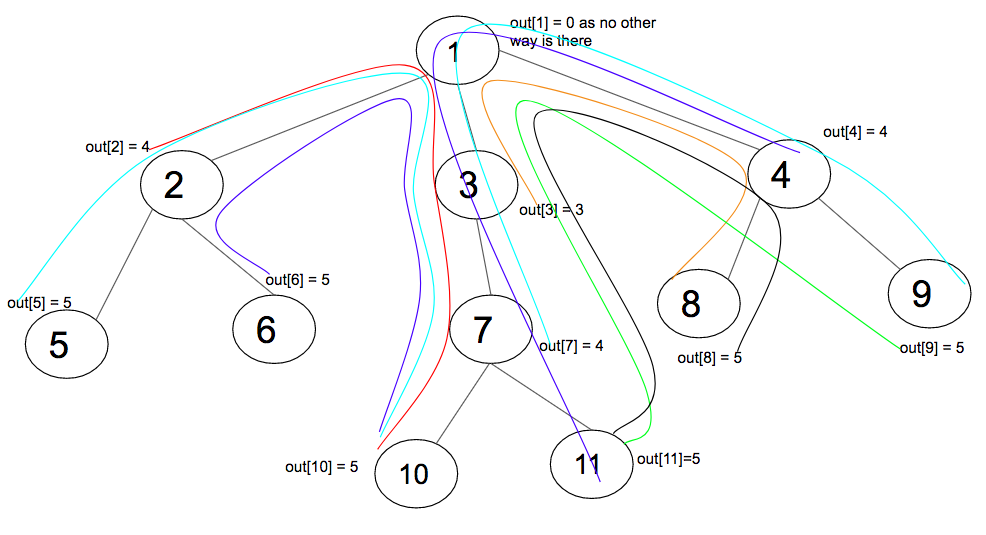
上图显示了所有out [i]值和路径。为了计算out [i],向上移动到节点i的父节点。从节点i的父节点开始,有两种移动方法,一种将在父节点的所有分支中。另一个方向是移动到节点i的父节点(称为parent1)的父节点(称为parent2以避免混淆)。通过parent2向上的最大高度本身是out [parent1] 。通常,out [node i]为1 + max(out [i],所有分支的1 + max)。在节点和父节点之间的边缘加1。
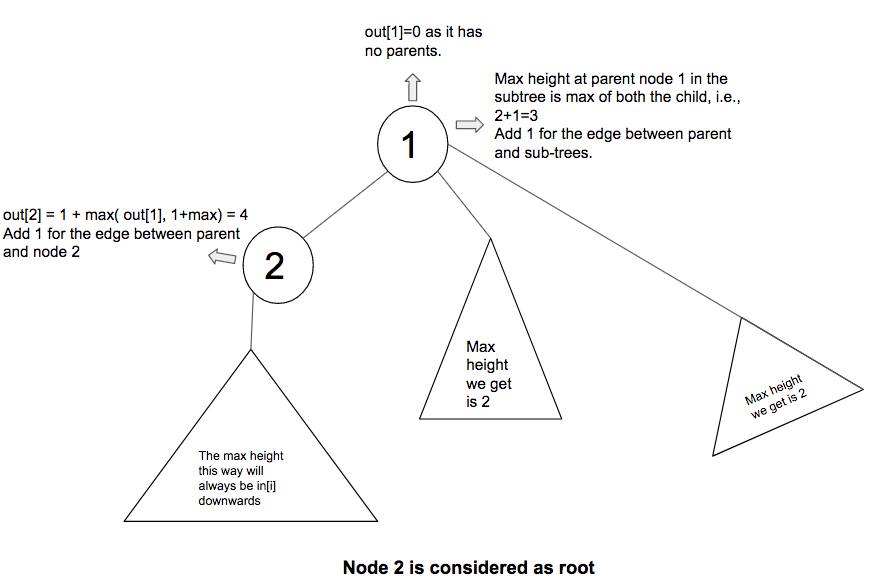
上图说明了将2视为树的根时out [i]的计算。由于已经计算出通过该路径的最大高度并将其存储在i [2]中,因此不计入节点2的分支。向上移动,在这种情况下,2的父级(即1)没有父级。因此,在计算最大值时会考虑除具有该节点的分支以外的分支。
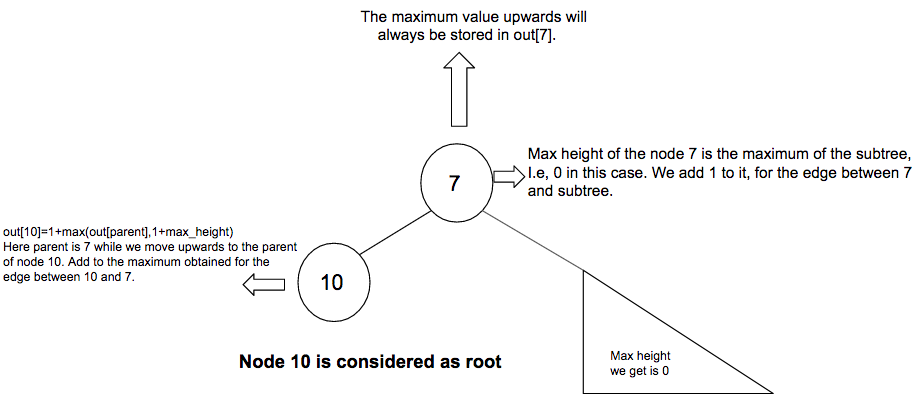
上图说明了out [10]的计算。节点10的父节点(即7)具有一个父节点和一个分支(在这种情况下,恰好是一个子节点)。因此,在存在父级和分支的情况下,将两者的最大高度都计算在内。
如果父级有多个分支,则取其中最长的一个进行计数(不包括该节点所在的分支)
计算连接到父级的所有分支的最大高度:
in [i]存储向下移动时的最大高度。无需存储所有长度的分支。所有分支中只有第一和第二最大长度会给出答案。由于所使用的算法基于DFS,因此将考虑连接到父级的所有分支,包括具有节点的分支。如果由此获得的第一条最大路径与in [i]相同,则maximum1是节点i所在分支的长度。在这种情况下,我们的最长路径将为max2。
in [i]和out [i]的递归关系:
in[i] = max(in[i], 1 + in[child])
out[i] = 1 + max(out[parent of i], 1 + longest path of all branches of parent of i)
下面是上述想法的实现:
C++
// C++ code to find the maximum path length
// considering any node as root
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX_NODES = 100;
int in[MAX_NODES];
int out[MAX_NODES];
// function to pre-calculate the array in[]
// which stores the maximum height when travelled
// via branches
void dfs1(vector v[], int u, int parent)
{
// initially every node has 0 height
in[u] = 0;
// traverse in the subtree of u
for (int child : v[u]) {
// if child is same as parent
if (child == parent)
continue;
// dfs called
dfs1(v, child, u);
// recursively calculate the max height
in[u] = max(in[u], 1 + in[child]);
}
}
// function to pre-calculate the array ouut[]
// which stores the maximum height when traveled
// via parent
void dfs2(vector v[], int u, int parent)
{
// stores the longest and second
// longest branches
int mx1 = -1, mx2 = -1;
// traverse in the subtress of u
for (int child : v[u]) {
if (child == parent)
continue;
// compare and store the longest
// and second longest
if (in[child] >= mx1) {
mx2 = mx1;
mx1 = in[child];
}
else if (in[child] > mx2)
mx2 = in[child];
}
// traverse in the subtree of u
for (int child : v[u]) {
if (child == parent)
continue;
int longest = mx1;
// if longest branch has the node, then
// consider the second longest branch
if (mx1 == in[child])
longest = mx2;
// recursively calculate out[i]
out[child] = 1 + max(out[u], 1 + longest);
// dfs function call
dfs2(v, child, u);
}
}
// function to print all the maximum heights
// from every node
void printHeights(vector v[], int n)
{
// traversal to calculate in[] array
dfs1(v, 1, 0);
// traversal to calculate out[] array
dfs2(v, 1, 0);
// print all maximum heights
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << "The maximum height when node "
<< i << " is considered as root"
<< " is " << max(in[i], out[i])
<< "\n";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 11;
vector v[n + 1];
// initialize the tree given in the diagram
v[1].push_back(2), v[2].push_back(1);
v[1].push_back(3), v[3].push_back(1);
v[1].push_back(4), v[4].push_back(1);
v[2].push_back(5), v[5].push_back(2);
v[2].push_back(6), v[6].push_back(2);
v[3].push_back(7), v[7].push_back(3);
v[7].push_back(10), v[10].push_back(7);
v[7].push_back(11), v[11].push_back(7);
v[4].push_back(8), v[8].push_back(4);
v[4].push_back(9), v[9].push_back(4);
// function to print the maximum height from every node
printHeights(v, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java code to find the maximum path length
// considering any node as root
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static final int MAX_NODES = 100;
static int in[] = new int[MAX_NODES];
static int out[] = new int[MAX_NODES];
// Function to pre-calculate the array in[]
// which stores the maximum height when travelled
// via branches
static void dfs1(ArrayList> v,
int u, int parent)
{
// Initially every node has 0 height
in[u] = 0;
// Traverse in the subtree of u
for(int j = 0; j < v.get(u).size(); j++)
{
int child = v.get(u).get(j);
// If child is same as parent
if (child == parent)
continue;
// dfs called
dfs1(v, child, u);
// Recursively calculate the max height
in[u] = Math.max(in[u], 1 + in[child]);
}
}
// Function to pre-calculate the array ouut[]
// which stores the maximum height when traveled
// via parent
static void dfs2(ArrayList> v,
int u, int parent)
{
// Stores the longest and second
// longest branches
int mx1 = -1, mx2 = -1;
// Traverse in the subtress of u
for(int j = 0; j < v.get(u).size(); j++)
{
int child = v.get(u).get(j);
if (child == parent)
continue;
// Compare and store the longest
// and second longest
if (in[child] >= mx1)
{
mx2 = mx1;
mx1 = in[child];
}
else if (in[child] > mx2)
mx2 = in[child];
}
// Traverse in the subtree of u
for(int j = 0; j < v.get(u).size(); j++)
{
int child = v.get(u).get(j);
if (child == parent)
continue;
int longest = mx1;
// If longest branch has the node, then
// consider the second longest branch
if (mx1 == in[child])
longest = mx2;
// Recursively calculate out[i]
out[child] = 1 + Math.max(out[u], 1 + longest);
// dfs function call
dfs2(v, child, u);
}
}
static void addEdge(ArrayList> adj,
int u, int v)
{
adj.get(u).add(v);
adj.get(v).add(u);
}
// Function to print all the maximum heights
// from every node
static void printHeights(ArrayList> v,
int n)
{
// Traversal to calculate in[] array
dfs1(v, 1, 0);
// Traversal to calculate out[] array
dfs2(v, 1, 0);
// Print all maximum heights
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
System.out.println(
"The maximum height when node " + i +
" is considered as root is " +
Math.max(in[i], out[i]));
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a graph with 11 vertices
int V = 12;
ArrayList> adj = new ArrayList>(V + 1);
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj.add(new ArrayList());
// Initialize the tree given in the diagram
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 1, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 4);
addEdge(adj, 2, 5);
addEdge(adj, 2, 6);
addEdge(adj, 3, 7);
addEdge(adj, 7, 10);
addEdge(adj, 7, 11);
addEdge(adj, 4, 8);
addEdge(adj, 4, 9);
// Function to print the maximum height
// from every node
printHeights(adj, V);
}
}
// This code is contributed by decoding Python3
# Python3 code to find the maximum path length
# considering any node as root
inn = [0] * 100
out = [0] * 100
# function to pre-calculate the array inn[]
# which stores the maximum height when travelled
# via branches
def dfs1(v, u, parent):
global inn, out
# initially every node has 0 height
inn[u] = 0
# traverse in the subtree of u
for child in v[u]:
# if child is same as parent
if (child == parent):
continue
# dfs called
dfs1(v, child, u)
# recursively calculate the max height
inn[u] = max(inn[u], 1 + inn[child])
# function to pre-calculate the array ouut[]
# which stores the maximum height when traveled
# via parent
def dfs2(v, u, parent):
global inn, out
# stores the longest and second
# longest branches
mx1, mx2 = -1, -1
# traverse in the subtress of u
for child in v[u]:
if (child == parent):
continue
# compare and store the longest
# and second longest
if (inn[child] >= mx1):
mx2 = mx1
mx1 = inn[child]
elif (inn[child] > mx2):
mx2 = inn[child]
# traverse in the subtree of u
for child in v[u]:
if (child == parent):
continue
longest = mx1
# if longest branch has the node, then
# consider the second longest branch
if (mx1 == inn[child]):
longest = mx2
# recursively calculate out[i]
out[child] = 1 + max(out[u], 1 + longest)
# dfs function call
dfs2(v, child, u)
# function to prall the maximum heights
# from every node
def printHeights(v, n):
global inn, out
# traversal to calculate inn[] array
dfs1(v, 1, 0)
# traversal to calculate out[] array
dfs2(v, 1, 0)
# prall maximum heights
for i in range(1, n + 1):
print("The maximum height when node", i, "is considered as root is", max(inn[i], out[i]))
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 11
v = [[] for i in range(n + 1)]
# initialize the tree given in the diagram
v[1].append(2)
v[2].append(1)
v[1].append(3)
v[3].append(1)
v[1].append(4)
v[4].append(1)
v[2].append(5)
v[5].append(2)
v[2].append(6)
v[6].append(2)
v[3].append(7)
v[7].append(3)
v[7].append(10)
v[10].append(7)
v[7].append(11)
v[11].append(7)
v[4].append(8)
v[8].append(4)
v[4].append(9)
v[9].append(4)
# function to prthe maximum height from every node
printHeights(v, n)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29.The maximum height when node 1 is considered as root is 3
The maximum height when node 2 is considered as root is 4
The maximum height when node 3 is considered as root is 3
The maximum height when node 4 is considered as root is 4
The maximum height when node 5 is considered as root is 5
The maximum height when node 6 is considered as root is 5
The maximum height when node 7 is considered as root is 4
The maximum height when node 8 is considered as root is 5
The maximum height when node 9 is considered as root is 5
The maximum height when node 10 is considered as root is 5
The maximum height when node 11 is considered as root is 5时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)