动态规划(DP)是一种通过将问题分解为遵循最优子结构的重叠子问题来解决问题的技术。使用 DP 有各种问题,如子集和、背包、硬币找零等。 DP 也可以应用于树来解决一些特定问题。
先决条件: DFS
给定具有 N 个节点和 N-1 条边的树,计算从根到任何叶子的节点值的最大总和,而无需重新访问任何节点。
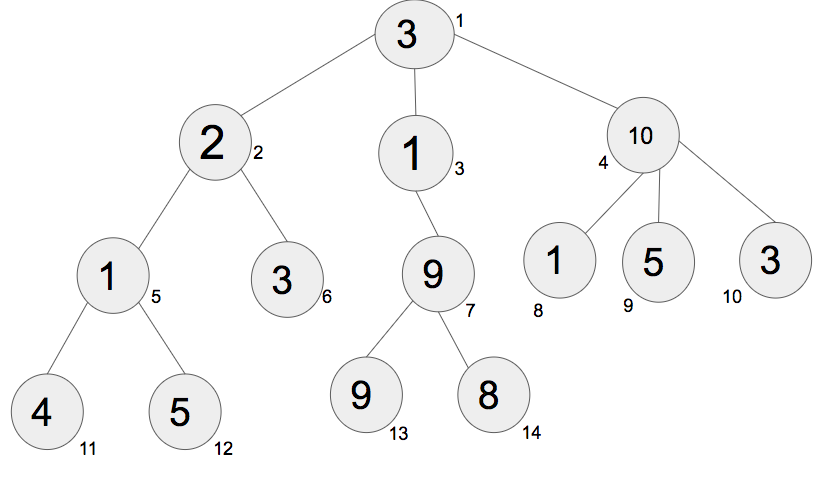
上面给出的是具有N=14 个节点和N-1=13 个边的树的图。对于节点 1、2、3、4….14,节点处的值分别为 3、2、1、10、1、3、9、1、5、3、4、5、9 和 8。
下图显示了从根到叶子的所有路径:
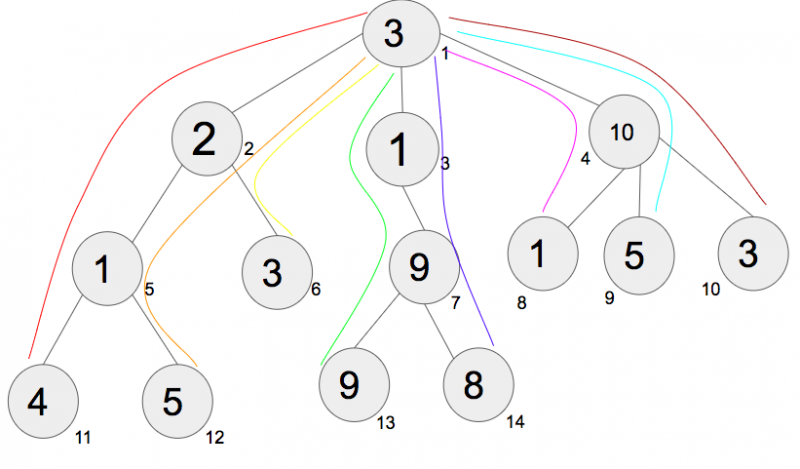
所有路径都用不同的颜色标记:
路径 1(red, 3-2-1-4) :所有节点值的总和 = 10
路径 2(orange, 3-2-1-5) :所有节点值的总和 = 11
路径 3(yellow, 3-2-3) :所有节点值的总和 = 8
路径 4(green, 3-1-9-9) :所有节点值的总和 = 22
路径 5(紫罗兰色,3-1-9-8):所有节点值的总和 = 21
路径 6(粉红色,3-10-1):所有节点值的总和 = 14
路径 7(blue, 3-10-5) :所有节点值的总和 = 18
路径 8(brown, 3-10-3) :所有节点值的总和 = 16
答案是 22,因为路径 4 在其从根到叶的路径中具有最大节点值总和。
在这种情况下,贪婪的方法失败了。从根开始,贪婪地从第一层取3,从下一层取10,从第三层取5。如果遵循贪婪方法,结果是路径 7,因此不要在这里应用贪婪方法。
这个问题可以使用树上的动态规划来解决。从叶子开始记忆并将最大的叶子添加到每个子树的根。在最后一步,将有根和其下的子树,将节点和子树的最大值相加将得到从根到任何叶子的节点值的最大总和。
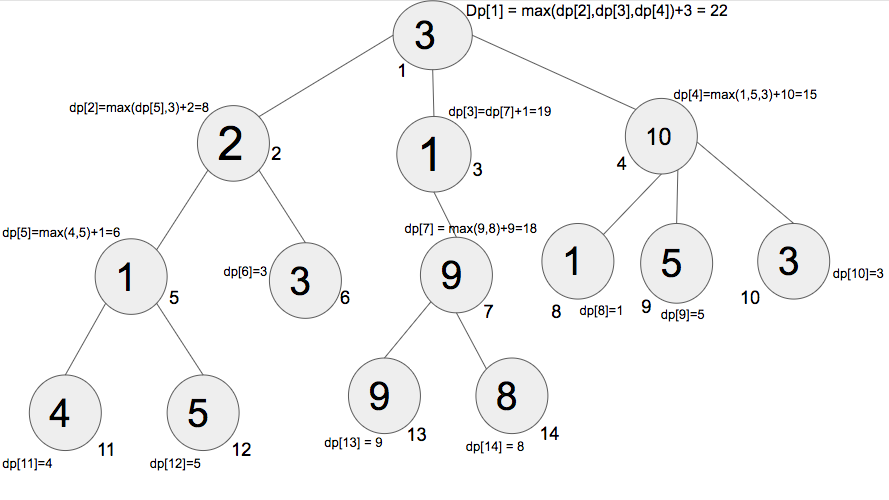
上图显示了如何从叶子开始并将子树的最大叶子添加到其根。向上移动并重复存储每个子树叶子的最大值并将其添加到其根的相同过程。在这个例子中,取节点 11 和 12 的最大值进行计数,然后添加到节点 5(在这个子树中,5 是根,11, 12 是它的叶子)。类似地,取节点13和14的最大值进行计数,然后添加到节点7。对每个子树重复这些步骤,直到我们到达该节点。
令 DP i是 i 与其任何向下移动的叶子之间的路径中节点值的最大总和。使用 DFS 遍历遍历树。存储子树所有叶子的最大值,并将其添加到子树的根。最后,DP 1将拥有从根到任何叶子的节点值的最大总和,而无需重新访问任何节点。
下面是上述想法的实现:
C++
// C++ code to find the maximum path sum
#include
using namespace std;
int dp[100];
// function for dfs traversal and to store the
// maximum value in dp[] for every node till the leaves
void dfs(int a[], vector v[], int u, int parent)
{
// initially dp[u] is always a[u]
dp[u] = a[u - 1];
// stores the maximum value from nodes
int maximum = 0;
// traverse the tree
for (int child : v[u]) {
// if child is parent, then we continue
// without recursing further
if (child == parent)
continue;
// call dfs for further traversal
dfs(a, v, child, u);
// store the maximum of previous visited node
// and present visited node
maximum = max(maximum, dp[child]);
}
// add the maximum value returned to the parent node
dp[u] += maximum;
}
// function that returns the maximum value
int maximumValue(int a[], vector v[])
{
dfs(a, v, 1, 0);
return dp[1];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// number of nodes
int n = 14;
// adjacency list
vector v[n + 1];
// create undirected edges
// initialize the tree given in the diagram
v[1].push_back(2), v[2].push_back(1);
v[1].push_back(3), v[3].push_back(1);
v[1].push_back(4), v[4].push_back(1);
v[2].push_back(5), v[5].push_back(2);
v[2].push_back(6), v[6].push_back(2);
v[3].push_back(7), v[7].push_back(3);
v[4].push_back(8), v[8].push_back(4);
v[4].push_back(9), v[9].push_back(4);
v[4].push_back(10), v[10].push_back(4);
v[5].push_back(11), v[11].push_back(5);
v[5].push_back(12), v[12].push_back(5);
v[7].push_back(13), v[13].push_back(7);
v[7].push_back(14), v[14].push_back(7);
// values of node 1, 2, 3....14
int a[] = { 3, 2, 1, 10, 1, 3, 9, 1, 5, 3, 4, 5, 9, 8 };
// function call
cout << maximumValue(a, v);
return 0;
} Java
// Java code to find the maximum path sum
import java.util.Vector;
class GFG
{
static int[] dp = new int[100];
// function for dfs traversal and to
// store the maximum value in dp[]
// for every node till the leaves
static void dfs(int[] a, Vector[] v,
int u, int parent)
{
// initially dp[u] is always a[u]
dp[u] = a[u - 1];
// stores the maximum value from nodes
int maximum = 0;
// traverse the tree
for (int child : v[u])
{
// if child is parent, then we continue
// without recursing further
if (child == parent)
continue;
// call dfs for further traversal
dfs(a, v, child, u);
// store the maximum of previous visited
// node and present visited node
maximum = Math.max(maximum, dp[child]);
}
// add the maximum value returned
// to the parent node
dp[u] += maximum;
}
// function that returns the maximum value
static int maximumValue(int[] a,
Vector[] v)
{
dfs(a, v, 1, 0);
return dp[1];
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Driver Code
int n = 14;
// adjacency list
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector[] v = new Vector[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < v.length; i++)
v[i] = new Vector<>();
// create undirected edges
// initialize the tree given in the diagram
v[1].add(2); v[2].add(1);
v[1].add(3); v[3].add(1);
v[1].add(4); v[4].add(1);
v[2].add(5); v[5].add(2);
v[2].add(6); v[6].add(2);
v[3].add(7); v[7].add(3);
v[4].add(8); v[8].add(4);
v[4].add(9); v[9].add(4);
v[4].add(10); v[10].add(4);
v[5].add(11); v[11].add(5);
v[5].add(12); v[12].add(5);
v[7].add(13); v[13].add(7);
v[7].add(14); v[14].add(7);
// values of node 1, 2, 3....14
int a[] = { 3, 2, 1, 10, 1, 3, 9,
1, 5, 3, 4, 5, 9, 8 };
// function call
System.out.println(maximumValue(a, v));
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Python3
# Python3 code to find the maximum path sum
dp = [0]*100
# Function for dfs traversal and
# to store the maximum value in
# dp[] for every node till the leaves
def dfs(a, v, u, parent):
# Initially dp[u] is always a[u]
dp[u] = a[u - 1]
# Stores the maximum value from nodes
maximum = 0
# Traverse the tree
for child in v[u]:
# If child is parent, then we continue
# without recursing further
if child == parent:
continue
# Call dfs for further traversal
dfs(a, v, child, u)
# Store the maximum of previous visited
# node and present visited node
maximum = max(maximum, dp[child])
# Add the maximum value
# returned to the parent node
dp[u] += maximum
# Function that returns the maximum value
def maximumValue(a, v):
dfs(a, v, 1, 0)
return dp[1]
# Driver Code
def main():
# Number of nodes
n = 14
# Adjacency list as a dictionary
v = {}
for i in range(n + 1):
v[i] = []
# Create undirected edges
# initialize the tree given in the diagram
v[1].append(2), v[2].append(1)
v[1].append(3), v[3].append(1)
v[1].append(4), v[4].append(1)
v[2].append(5), v[5].append(2)
v[2].append(6), v[6].append(2)
v[3].append(7), v[7].append(3)
v[4].append(8), v[8].append(4)
v[4].append(9), v[9].append(4)
v[4].append(10), v[10].append(4)
v[5].append(11), v[11].append(5)
v[5].append(12), v[12].append(5)
v[7].append(13), v[13].append(7)
v[7].append(14), v[14].append(7)
# Values of node 1, 2, 3....14
a = [ 3, 2, 1, 10, 1, 3, 9,
1, 5, 3, 4, 5, 9, 8 ]
# Function call
print(maximumValue(a, v))
main()
# This code is contributed by stutipathak31janC#
// C# code to find the maximum path sum
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int[] dp = new int[100];
// function for dfs traversal and to
// store the maximum value in []dp
// for every node till the leaves
static void dfs(int[] a, List[] v,
int u, int parent)
{
// initially dp[u] is always a[u]
dp[u] = a[u - 1];
// stores the maximum value from nodes
int maximum = 0;
// traverse the tree
foreach(int child in v[u])
{
// if child is parent, then we continue
// without recursing further
if (child == parent)
continue;
// call dfs for further traversal
dfs(a, v, child, u);
// store the maximum of previous visited
// node and present visited node
maximum = Math.Max(maximum, dp[child]);
}
// add the maximum value returned
// to the parent node
dp[u] += maximum;
}
// function that returns the maximum value
static int maximumValue(int[] a,
List[] v)
{
dfs(a, v, 1, 0);
return dp[1];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Driver Code
int n = 14;
// adjacency list
List[] v = new List[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < v.Length; i++)
v[i] = new List();
// create undirected edges
// initialize the tree given in the diagram
v[1].Add(2); v[2].Add(1);
v[1].Add(3); v[3].Add(1);
v[1].Add(4); v[4].Add(1);
v[2].Add(5); v[5].Add(2);
v[2].Add(6); v[6].Add(2);
v[3].Add(7); v[7].Add(3);
v[4].Add(8); v[8].Add(4);
v[4].Add(9); v[9].Add(4);
v[4].Add(10); v[10].Add(4);
v[5].Add(11); v[11].Add(5);
v[5].Add(12); v[12].Add(5);
v[7].Add(13); v[13].Add(7);
v[7].Add(14); v[14].Add(7);
// values of node 1, 2, 3....14
int []a = { 3, 2, 1, 10, 1, 3, 9,
1, 5, 3, 4, 5, 9, 8 };
// function call
Console.WriteLine(maximumValue(a, v));
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 Javascript
22时间复杂度: O(N),其中 N 是节点数。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。