在了解链接列表的类型之前,请确保您了解LinkedList数据结构。
链接列表有三种常见类型。
- 单链表
- 双链表
- 通报链表
单链表
这是最常见的。每个节点都有数据和指向下一个节点的指针。

节点表示为:
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
}可以将三人单链接列表创建为:
/* Initialize nodes */
struct node *head;
struct node *one = NULL;
struct node *two = NULL;
struct node *three = NULL;
/* Allocate memory */
one = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
two = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
three = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/* Assign data values */
one->data = 1;
two->data = 2;
three->data = 3;
/* Connect nodes */
one->next = two;
two->next = three;
three->next = NULL;
/* Save address of first node in head */
head = one;双链表
我们在双向链表中添加一个指向前一个节点的指针。因此,我们可以朝任一方向前进:前进或后退。
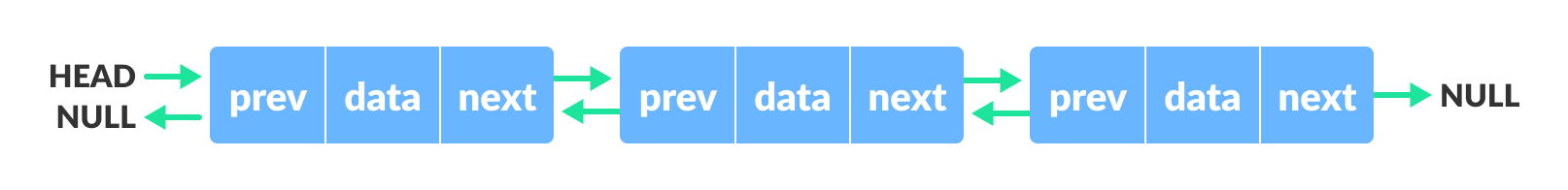
节点表示为
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
}可以创建一个三人双向链接列表
/* Initialize nodes */
struct node *head;
struct node *one = NULL;
struct node *two = NULL;
struct node *three = NULL;
/* Allocate memory */
one = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
two = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
three = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/* Assign data values */
one->data = 1;
two->data = 2;
three->data = 3;
/* Connect nodes */
one->next = two;
one->prev = NULL;
two->next = three;
two->prev = one;
three->next = NULL;
three->prev = two;
/* Save address of first node in head */
head = one;通报链表
循环链表是链表的变体,其中最后一个元素链接到第一个元素。这形成一个循环。
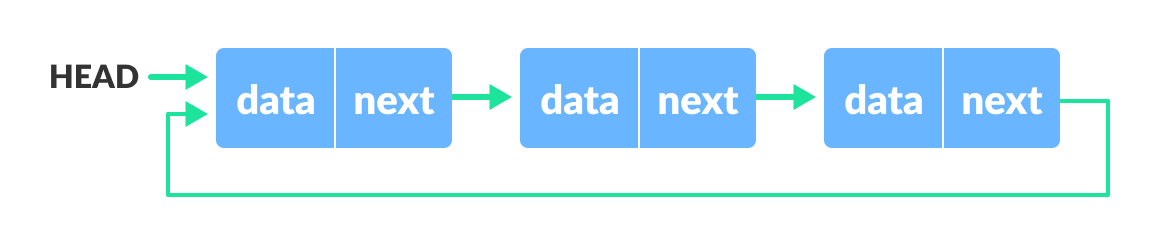
循环链表可以是单链或双链。
- 对于单链表,最后一项的下一个指针指向第一个项
- 在双向链表,第一个项目点,还有最后一个项目的上一个指针。
可以将三人循环单链接列表创建为:
/* Initialize nodes */
struct node *head;
struct node *one = NULL;
struct node *two = NULL;
struct node *three = NULL;
/* Allocate memory */
one = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
two = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
three = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/* Assign data values */
one->data = 1;
two->data = 2;
three->data = 3;
/* Connect nodes */
one->next = two;
two->next = three;
three->next = one;
/* Save address of first node in head */
head = one;