链表是一种线性数据结构,其中元素不存储在连续的内存位置。链表中的元素使用指针链接。简单来说,链表由节点组成,其中每个节点都包含一个数据字段和指向列表中下一个节点的引用(链接)。
链表的类型
- 单向链表:它是最简单的链表类型,其中每个节点都包含一些数据和一个指向相同数据类型的下一个节点的指针。节点包含指向下一个节点的指针意味着该节点存储序列中下一个节点的地址。单链表只允许以一种方式遍历数据。下面是相同的图像:
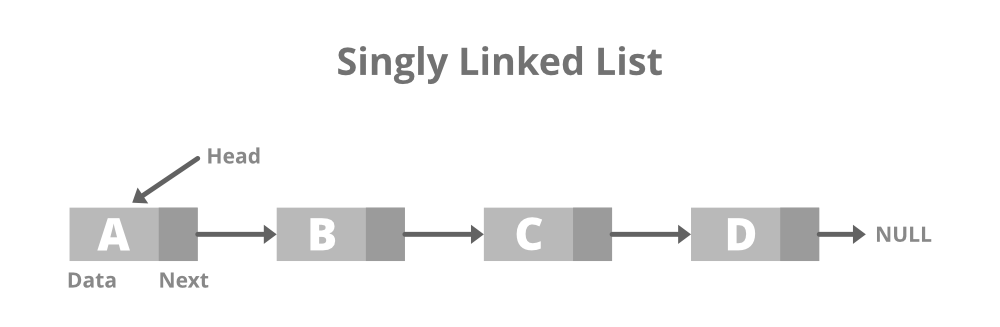
- 单链表的结构:
C++
// Node of a doubly linked list
class Node {
public:
int data;
// Pointer to next node in LL
Node* next;
};Java
// Node of a doubly linked list
static class Node
{
int data;
// Pointer to next node in LL
Node next;
};
//this code is contributed by shivaniPython3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = NoneC#
// Structure of Node
public class Node
{
public int data;
// Pointer to next node in LL
public Node next;
};
//this code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110C++
// C++ program to illustrate creation
// and traversal of Singly Linked List
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of Node
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
// Function to print the content of
// linked list starting from the
// given node
void printList(Node* n)
{
// Iterate till n reaches NULL
while (n != NULL) {
// Print the data
cout << n->data << " ";
n = n->next;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
Node* second = NULL;
Node* third = NULL;
// Allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = new Node();
second = new Node();
third = new Node();
// Assign data in first node
head->data = 1;
// Link first node with second
head->next = second;
// Assign data to second node
second->data = 2;
second->next = third;
// Assign data to third node
third->data = 3;
third->next = NULL;
printList(head);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to illustrate
// creation and traversal of
// Singly Linked List
class GFG{
// Structure of Node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
};
// Function to print the content of
// linked list starting from the
// given node
static void printList(Node n)
{
// Iterate till n reaches null
while (n != null)
{
// Print the data
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = null;
Node second = null;
Node third = null;
// Allocate 3 nodes in
// the heap
head = new Node();
second = new Node();
third = new Node();
// Assign data in first
// node
head.data = 1;
// Link first node with
// second
head.next = second;
// Assign data to second
// node
second.data = 2;
second.next = third;
// Assign data to third
// node
third.data = 3;
third.next = null;
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi SinghC#
// C# program to illustrate
// creation and traversal of
// Singly Linked List
using System;
class GFG{
// Structure of Node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
};
// Function to print the content of
// linked list starting from the
// given node
static void printList(Node n)
{
// Iterate till n reaches null
while (n != null)
{
// Print the data
Console.Write(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = null;
Node second = null;
Node third = null;
// Allocate 3 nodes in
// the heap
head = new Node();
second = new Node();
third = new Node();
// Assign data in first
// node
head.data = 1;
// Link first node with
// second
head.next = second;
// Assign data to second
// node
second.data = 2;
second.next = third;
// Assign data to third
// node
third.data = 3;
third.next = null;
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit KatiyarPython3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.last_node = None
# function to add elements to linked list
def append(self, data):
# if linked list is empty then last_node will be none so in if condition head will be created
if self.last_node is None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.head
# adding node to the tail of linked list
else:
self.last_node.next = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.last_node.next
# function to print the content of linked list
def display(self):
current = self.head
# traversing the linked list
while current is not None:
# at each node printing its data
print(current.data, end=' ')
# giving current next node
current = current.next
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = LinkedList()
# adding elements to the linked list
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
# displaying elements of linked list
L.display()Javascript
C++
// Node of a doubly linked list
struct Node {
int data;
// Pointer to next node in DLL
struct Node* next;
// Pointer to the previous node in DLL
struct Node* prev;
};Java
// Doubly linked list
// node
static class Node
{
int data;
// Pointer to next node in DLL
Node next;
// Pointer to the previous node in DLL
Node prev;
};
// This code is contributed by shivaniPython3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.previous = None
self.data = data
self.next = NoneC++
// C++ program to illustrate creation
// and traversal of Doubly Linked List
#include
using namespace std;
// Doubly linked list node
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node* prev;
};
// Function to push a new element in
// the Doubly Linked List
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node* new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// Make next of new node as
// head and previous as NULL
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
new_node->prev = NULL;
// Change prev of head node to
// the new node
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Function to traverse the Doubly LL
// in the forward & backward direction
void printList(Node* node)
{
Node* last;
cout << "\nTraversal in forward"
<< " direction \n";
while (node != NULL) {
// Print the data
cout << " " << node->data << " ";
last = node;
node = node->next;
}
cout << "\nTraversal in reverse"
<< " direction \n";
while (last != NULL) {
// Print the data
cout << " " << last->data << " ";
last = last->prev;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Start with the empty list
Node* head = NULL;
// Insert 6.
// So linked list becomes 6->NULL
push(&head, 6);
// Insert 7 at the beginning. So
// linked list becomes 7->6->NULL
push(&head, 7);
// Insert 1 at the beginning. So
// linked list becomes 1->7->6->NULL
push(&head, 1);
cout << "Created DLL is: ";
printList(head);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to illustrate
// creation and traversal of
// Doubly Linked List
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Doubly linked list
// node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
};
static Node head_ref;
// Function to push a new
// element in the Doubly
// Linked List
static void push(int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Make next of new node as
// head and previous as null
new_node.next = head_ref;
new_node.prev = null;
// Change prev of head node to
// the new node
if (head_ref != null)
head_ref.prev = new_node;
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
head_ref = new_node;
}
// Function to traverse the
// Doubly LL in the forward
// & backward direction
static void printList(Node node)
{
Node last = null;
System.out.print("\nTraversal in forward" +
" direction \n");
while (node != null)
{
// Print the data
System.out.print(" " + node.data +
" ");
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
System.out.print("\nTraversal in reverse" +
" direction \n");
while (last != null)
{
// Print the data
System.out.print(" " + last.data +
" ");
last = last.prev;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Start with the empty list
head_ref = null;
// Insert 6.
// So linked list becomes
// 6.null
push(6);
// Insert 7 at the beginning.
// So linked list becomes
// 7.6.null
push(7);
// Insert 1 at the beginning.
// So linked list becomes
// 1.7.6.null
push(1);
System.out.print("Created DLL is: ");
printList(head_ref);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi SinghPython3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.previous = None
self.data = data
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.start_node = None
self.last_node = None
# function to add elements to doubly linked list
def append(self, data):
# is doubly linked list is empty then last_node will be none so in if condition head will be created
if self.last_node is None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.head
# adding node to the tail of doubly linked list
else:
new_node = Node(data)
self.last_node.next = new_node
new_node.previous = self.last_node
new_node.next = None
self.last_node = new_node
# function to printing and traversing the content of doubly linked list from left to right and right to left
def display(self, Type):
if Type == 'Left_To_Right':
current = self.head
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
print()
else:
current = self.last_node
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.previous
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = DoublyLinkedList()
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
L.display('Left_To_Right')
L.display('Right_To_Left')C#
// C# program to illustrate
// creation and traversal of
// Doubly Linked List
using System;
class GFG{
// Doubly linked list
// node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node prev;
};
static Node head_ref;
// Function to push a new
// element in the Doubly
// Linked List
static void push(int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Make next of new node as
// head and previous as null
new_node.next = head_ref;
new_node.prev = null;
// Change prev of head node to
// the new node
if (head_ref != null)
head_ref.prev = new_node;
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
head_ref = new_node;
}
// Function to traverse the
// Doubly LL in the forward
// & backward direction
static void printList(Node node)
{
Node last = null;
Console.Write("\nTraversal in forward" +
" direction \n");
while (node != null)
{
// Print the data
Console.Write(" " + node.data +
" ");
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
Console.Write("\nTraversal in reverse" +
" direction \n");
while (last != null)
{
// Print the data
Console.Write(" " + last.data +
" ");
last = last.prev;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Start with the empty list
head_ref = null;
// Insert 6.
// So linked list becomes
// 6.null
push(6);
// Insert 7 at the beginning.
// So linked list becomes
// 7.6.null
push(7);
// Insert 1 at the beginning.
// So linked list becomes
// 1.7.6.null
push(1);
Console.Write("Created DLL is: ");
printList(head_ref);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit KatiyarC++
// Structure for a node
class Node {
public:
int data;
// Pointer to next node in CLL
Node* next;
};Python3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = NoneC++
// C++ program to illustrate creation
// and traversal of Circular LL
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure for a node
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
// Function to insert a node at the
// beginning of Circular LL
void push(Node** head_ref, int data)
{
Node* ptr1 = new Node();
Node* temp = *head_ref;
ptr1->data = data;
ptr1->next = *head_ref;
// If linked list is not NULL then
// set the next of last node
if (*head_ref != NULL) {
while (temp->next != *head_ref) {
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = ptr1;
}
// For the first node
else
ptr1->next = ptr1;
*head_ref = ptr1;
}
// Function to print nodes in the
// Circular Linked List
void printList(Node* head)
{
Node* temp = head;
if (head != NULL) {
do {
// Print the data
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != head);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Initialize list as empty
Node* head = NULL;
// Created linked list will
// be 11->2->56->12
push(&head, 12);
push(&head, 56);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 11);
cout << "Contents of Circular"
<< " Linked List\n ";
printList(head);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to illustrate
// creation and traversal of
// Circular LL
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Structure for a
// node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
};
// Function to insert a node
// at the beginning of Circular
// LL
static Node push(Node head_ref,
int data)
{
Node ptr1 = new Node();
Node temp = head_ref;
ptr1.data = data;
ptr1.next = head_ref;
// If linked list is not
// null then set the next
// of last node
if (head_ref != null)
{
while (temp.next != head_ref)
{
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = ptr1;
}
// For the first node
else
ptr1.next = ptr1;
head_ref = ptr1;
return head_ref;
}
// Function to print nodes in
// the Circular Linked List
static void printList(Node head)
{
Node temp = head;
if (head != null)
{
do
{
// Print the data
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initialize list as empty
Node head = null;
// Created linked list will
// be 11.2.56.12
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 56);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 11);
System.out.print("Contents of Circular" +
" Linked List\n ");
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1Python3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class CircularLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.last_node = None
# function to add elements to circular linked list
def append(self, data):
# is circular linked list is empty then last_node will be none so in if condition head will be created
if self.last_node is None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.head
# adding node to the tail of circular linked list
else:
self.last_node.next = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.last_node.next
self.last_node.next = self.head
# function to print the content of circular linked list
def display(self):
current = self.head
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
if current == self.head:
break
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = CircularLinkedList()
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
L.display()C#
// C# program to illustrate
// creation and traversal of
// Circular LL
using System;
class GFG{
// Structure for a
// node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
};
// Function to insert a node
// at the beginning of Circular
// LL
static Node push(Node head_ref,
int data)
{
Node ptr1 = new Node();
Node temp = head_ref;
ptr1.data = data;
ptr1.next = head_ref;
// If linked list is not
// null then set the next
// of last node
if (head_ref != null)
{
while (temp.next != head_ref)
{
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = ptr1;
}
// For the first node
else
ptr1.next = ptr1;
head_ref = ptr1;
return head_ref;
}
// Function to print nodes in
// the Circular Linked List
static void printList(Node head)
{
Node temp = head;
if (head != null)
{
do
{
// Print the data
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Initialize list as empty
Node head = null;
// Created linked list will
// be 11.2.56.12
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 56);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 11);
Console.Write("Contents of Circular " +
"Linked List\n ");
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1C++
// Node of doubly circular linked list
struct Node {
int data;
// Pointer to next node in DCLL
struct Node* next;
// Pointer to the previous node in DCLL
struct Node* prev;
};Python3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.previous = None
self.data = data
self.next = NoneC++
// C++ program to illustrate creation
// & traversal of Doubly Circular LL
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a Node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
// Function to insert Node at
// the beginning of the List
void insertBegin(struct Node** start,
int value)
{
// If the list is empty
if (*start == NULL) {
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = value;
new_node->next
= new_node->prev = new_node;
*start = new_node;
return;
}
// Pointer points to last Node
struct Node* last = (*start)->prev;
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
// Inserting the data
new_node->data = value;
// Update the previous and
// next of new node
new_node->next = *start;
new_node->prev = last;
// Update next and previous
// pointers of start & last
last->next = (*start)->prev
= new_node;
// Update start pointer
*start = new_node;
}
// Function to traverse the circular
// doubly linked list
void display(struct Node* start)
{
struct Node* temp = start;
printf("\nTraversal in"
" forward direction \n");
while (temp->next != start) {
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("%d ", temp->data);
printf("\nTraversal in "
"reverse direction \n");
Node* last = start->prev;
temp = last;
while (temp->prev != last) {
// Print the data
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->prev;
}
printf("%d ", temp->data);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Start with the empty list
struct Node* start = NULL;
// Insert 5
// So linked list becomes 5->NULL
insertBegin(&start, 5);
// Insert 4 at the beginning
// So linked list becomes 4->5
insertBegin(&start, 4);
// Insert 7 at the end
// So linked list becomes 7->4->5
insertBegin(&start, 7);
printf("Created circular doubly"
" linked list is: ");
display(start);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to illustrate creation
// & traversal of Doubly Circular LL
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Structure of a Node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
};
// Start with the empty list
static Node start = null;
// Function to insert Node at
// the beginning of the List
static void insertBegin(
int value)
{
// If the list is empty
if (start == null)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = value;
new_node.next
= new_node.prev = new_node;
start = new_node;
return;
}
// Pointer points to last Node
Node last = (start).prev;
Node new_node = new Node();
// Inserting the data
new_node.data = value;
// Update the previous and
// next of new node
new_node.next = start;
new_node.prev = last;
// Update next and previous
// pointers of start & last
last.next = (start).prev
= new_node;
// Update start pointer
start = new_node;
}
// Function to traverse the circular
// doubly linked list
static void display()
{
Node temp = start;
System.out.printf("\nTraversal in"
+" forward direction \n");
while (temp.next != start)
{
System.out.printf("%d ", temp.data);
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.printf("%d ", temp.data);
System.out.printf("\nTraversal in "
+ "reverse direction \n");
Node last = start.prev;
temp = last;
while (temp.prev != last)
{
// Print the data
System.out.printf("%d ", temp.data);
temp = temp.prev;
}
System.out.printf("%d ", temp.data);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Insert 5
// So linked list becomes 5.null
insertBegin( 5);
// Insert 4 at the beginning
// So linked list becomes 4.5
insertBegin( 4);
// Insert 7 at the end
// So linked list becomes 7.4.5
insertBegin( 7);
System.out.printf("Created circular doubly"
+ " linked list is: ");
display();
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajputPython3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.previous = None
self.data = data
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.start_node = None
self.last_node = None
# function to add elements to doubly linked list
def append(self, data):
# is doubly linked list is empty then last_node will be none so in if condition head will be created
if self.last_node is None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.head
# adding node to the tail of doubly linked list
else:
new_node = Node(data)
self.last_node.next = new_node
new_node.previous = self.last_node
new_node.next = self.head
self.last_node = new_node
# function to print the content of doubly linked list
def display(self, Type = 'Left_To_Right'):
if Type == 'Left_To_Right':
current = self.head
while current.next is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
if current == self.head:
break
print()
else:
current = self.last_node
while current.previous is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.previous
if current == self.last_node.next:
print(self.last_node.next.data, end=' ')
break
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = DoublyLinkedList()
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
L.display('Left_To_Right')
L.display('Right_To_Left')C#
// C# program to illustrate creation
// & traversal of Doubly Circular LL
using System;
public class GFG{
// Structure of a Node
public
class Node
{
public
int data;
public
Node next;
public
Node prev;
};
// Start with the empty list
static Node start = null;
// Function to insert Node at
// the beginning of the List
static void insertBegin(
int value)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
// If the list is empty
if (start == null)
{
new_node.data = value;
new_node.next
= new_node.prev = new_node;
start = new_node;
return;
}
// Pointer points to last Node
Node last = (start).prev;
// Inserting the data
new_node.data = value;
// Update the previous and
// next of new node
new_node.next = start;
new_node.prev = last;
// Update next and previous
// pointers of start & last
last.next = (start).prev
= new_node;
// Update start pointer
start = new_node;
}
// Function to traverse the circular
// doubly linked list
static void display()
{
Node temp = start;
Console.Write("\nTraversal in"
+" forward direction \n");
while (temp.next != start)
{
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
Console.Write("\nTraversal in "
+ "reverse direction \n");
Node last = start.prev;
temp = last;
while (temp.prev != last)
{
// Print the data
Console.Write( temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.prev;
}
Console.Write( temp.data + " ");
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Insert 5
// So linked list becomes 5.null
insertBegin( 5);
// Insert 4 at the beginning
// So linked list becomes 4.5
insertBegin( 4);
// Insert 7 at the end
// So linked list becomes 7.4.5
insertBegin( 7);
Console.Write("Created circular doubly"
+ " linked list is: ");
display();
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarC++
// Structure of the list
struct link {
int info;
// Pointer to the next node
struct link* next;
};Python3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = NoneC++
// C++ program to illustrate creation
// and traversal of Header Linked List
#include
// #include
// #include
// Structure of the list
struct link {
int info;
struct link* next;
};
// Empty List
struct link* start = NULL;
// Function to create header of the
// header linked list
struct link* create_header_list(int data)
{
// Create a new node
struct link *new_node, *node;
new_node = (struct link*)
malloc(sizeof(struct link));
new_node->info = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
// If it is the first node
if (start == NULL) {
// Initialize the start
start = (struct link*)
malloc(sizeof(struct link));
start->next = new_node;
}
else {
// Insert the node in the end
node = start;
while (node->next != NULL) {
node = node->next;
}
node->next = new_node;
}
return start;
}
// Function to display the
// header linked list
struct link* display()
{
struct link* node;
node = start;
node = node->next;
// Traverse until node is
// not NULL
while (node != NULL) {
// Print the data
printf("%d ", node->info);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\n");
// Return the start pointer
return start;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Create the list
create_header_list(11);
create_header_list(12);
create_header_list(13);
// Print the list
printf("List After inserting"
" 3 elements:\n");
display();
create_header_list(14);
create_header_list(15);
// Print the list
printf("List After inserting"
" 2 more elements:\n");
display();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to illustrate creation
// and traversal of Header Linked List
class GFG{
// Structure of the list
static class link {
int info;
link next;
};
// Empty List
static link start = null;
// Function to create header of the
// header linked list
static link create_header_list(int data)
{
// Create a new node
link new_node, node;
new_node = new link();
new_node.info = data;
new_node.next = null;
// If it is the first node
if (start == null) {
// Initialize the start
start = new link();
start.next = new_node;
}
else {
// Insert the node in the end
node = start;
while (node.next != null) {
node = node.next;
}
node.next = new_node;
}
return start;
}
// Function to display the
// header linked list
static link display()
{
link node;
node = start;
node = node.next;
// Traverse until node is
// not null
while (node != null) {
// Print the data
System.out.printf("%d ", node.info);
node = node.next;
}
System.out.printf("\n");
// Return the start pointer
return start;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create the list
create_header_list(11);
create_header_list(12);
create_header_list(13);
// Print the list
System.out.printf("List After inserting"
+ " 3 elements:\n");
display();
create_header_list(14);
create_header_list(15);
// Print the list
System.out.printf("List After inserting"
+ " 2 more elements:\n");
display();
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = Node(0)
self.last_node = self.head
# function to add elements to header linked list
def append(self, data):
self.last_node.next = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.last_node.next
# function to print the content of header linked list
def display(self):
current = self.head.next
# traversing the header linked list
while current is not None:
# at each node printing its data
print(current.data, end=' ')
# giving current next node
current = current.next
# print(self.head.data)
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = LinkedList()
# adding elements to the header linked list
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
# displaying elements of header linked list
L.display()C#
// C# program to illustrate creation
// and traversal of Header Linked List
using System;
public class GFG{
// Structure of the list
public class link {
public int info;
public link next;
};
// Empty List
static link start = null;
// Function to create header of the
// header linked list
static link create_header_list(int data)
{
// Create a new node
link new_node, node;
new_node = new link();
new_node.info = data;
new_node.next = null;
// If it is the first node
if (start == null) {
// Initialize the start
start = new link();
start.next = new_node;
}
else {
// Insert the node in the end
node = start;
while (node.next != null) {
node = node.next;
}
node.next = new_node;
}
return start;
}
// Function to display the
// header linked list
static link display()
{
link node;
node = start;
node = node.next;
// Traverse until node is
// not null
while (node != null) {
// Print the data
Console.Write("{0} ", node.info);
node = node.next;
}
Console.Write("\n");
// Return the start pointer
return start;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Create the list
create_header_list(11);
create_header_list(12);
create_header_list(13);
// Print the list
Console.Write("List After inserting"
+ " 3 elements:\n");
display();
create_header_list(14);
create_header_list(15);
// Print the list
Console.Write("List After inserting"
+ " 2 more elements:\n");
display();
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar- 单链表的创建和遍历:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate creation
// and traversal of Singly Linked List
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of Node
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
// Function to print the content of
// linked list starting from the
// given node
void printList(Node* n)
{
// Iterate till n reaches NULL
while (n != NULL) {
// Print the data
cout << n->data << " ";
n = n->next;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
Node* second = NULL;
Node* third = NULL;
// Allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = new Node();
second = new Node();
third = new Node();
// Assign data in first node
head->data = 1;
// Link first node with second
head->next = second;
// Assign data to second node
second->data = 2;
second->next = third;
// Assign data to third node
third->data = 3;
third->next = NULL;
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to illustrate
// creation and traversal of
// Singly Linked List
class GFG{
// Structure of Node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
};
// Function to print the content of
// linked list starting from the
// given node
static void printList(Node n)
{
// Iterate till n reaches null
while (n != null)
{
// Print the data
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = null;
Node second = null;
Node third = null;
// Allocate 3 nodes in
// the heap
head = new Node();
second = new Node();
third = new Node();
// Assign data in first
// node
head.data = 1;
// Link first node with
// second
head.next = second;
// Assign data to second
// node
second.data = 2;
second.next = third;
// Assign data to third
// node
third.data = 3;
third.next = null;
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
C#
// C# program to illustrate
// creation and traversal of
// Singly Linked List
using System;
class GFG{
// Structure of Node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
};
// Function to print the content of
// linked list starting from the
// given node
static void printList(Node n)
{
// Iterate till n reaches null
while (n != null)
{
// Print the data
Console.Write(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = null;
Node second = null;
Node third = null;
// Allocate 3 nodes in
// the heap
head = new Node();
second = new Node();
third = new Node();
// Assign data in first
// node
head.data = 1;
// Link first node with
// second
head.next = second;
// Assign data to second
// node
second.data = 2;
second.next = third;
// Assign data to third
// node
third.data = 3;
third.next = null;
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
蟒蛇3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.last_node = None
# function to add elements to linked list
def append(self, data):
# if linked list is empty then last_node will be none so in if condition head will be created
if self.last_node is None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.head
# adding node to the tail of linked list
else:
self.last_node.next = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.last_node.next
# function to print the content of linked list
def display(self):
current = self.head
# traversing the linked list
while current is not None:
# at each node printing its data
print(current.data, end=' ')
# giving current next node
current = current.next
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = LinkedList()
# adding elements to the linked list
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
# displaying elements of linked list
L.display()
Javascript
输出
1 2 3 - 双向链表:双向链表或双向链表是一种更复杂的链表类型,它依次包含指向下一个节点和上一个节点的指针,因此它包含三个部分,数据,指针到下一个节点,以及一个指向前一个节点的指针。这将使我们也可以向后遍历列表。下面是相同的图像:
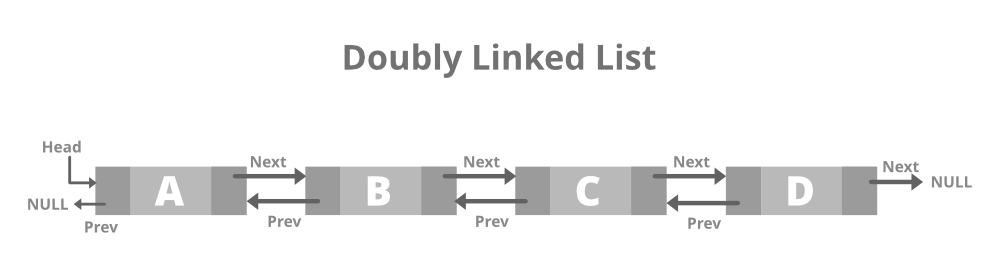
- 双向链表的结构:
C++
// Node of a doubly linked list
struct Node {
int data;
// Pointer to next node in DLL
struct Node* next;
// Pointer to the previous node in DLL
struct Node* prev;
};
Java
// Doubly linked list
// node
static class Node
{
int data;
// Pointer to next node in DLL
Node next;
// Pointer to the previous node in DLL
Node prev;
};
// This code is contributed by shivani
蟒蛇3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.previous = None
self.data = data
self.next = None
- 双向链表的创建和遍历:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate creation
// and traversal of Doubly Linked List
#include
using namespace std;
// Doubly linked list node
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node* prev;
};
// Function to push a new element in
// the Doubly Linked List
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node* new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// Make next of new node as
// head and previous as NULL
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
new_node->prev = NULL;
// Change prev of head node to
// the new node
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Function to traverse the Doubly LL
// in the forward & backward direction
void printList(Node* node)
{
Node* last;
cout << "\nTraversal in forward"
<< " direction \n";
while (node != NULL) {
// Print the data
cout << " " << node->data << " ";
last = node;
node = node->next;
}
cout << "\nTraversal in reverse"
<< " direction \n";
while (last != NULL) {
// Print the data
cout << " " << last->data << " ";
last = last->prev;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Start with the empty list
Node* head = NULL;
// Insert 6.
// So linked list becomes 6->NULL
push(&head, 6);
// Insert 7 at the beginning. So
// linked list becomes 7->6->NULL
push(&head, 7);
// Insert 1 at the beginning. So
// linked list becomes 1->7->6->NULL
push(&head, 1);
cout << "Created DLL is: ";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to illustrate
// creation and traversal of
// Doubly Linked List
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Doubly linked list
// node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
};
static Node head_ref;
// Function to push a new
// element in the Doubly
// Linked List
static void push(int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Make next of new node as
// head and previous as null
new_node.next = head_ref;
new_node.prev = null;
// Change prev of head node to
// the new node
if (head_ref != null)
head_ref.prev = new_node;
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
head_ref = new_node;
}
// Function to traverse the
// Doubly LL in the forward
// & backward direction
static void printList(Node node)
{
Node last = null;
System.out.print("\nTraversal in forward" +
" direction \n");
while (node != null)
{
// Print the data
System.out.print(" " + node.data +
" ");
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
System.out.print("\nTraversal in reverse" +
" direction \n");
while (last != null)
{
// Print the data
System.out.print(" " + last.data +
" ");
last = last.prev;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Start with the empty list
head_ref = null;
// Insert 6.
// So linked list becomes
// 6.null
push(6);
// Insert 7 at the beginning.
// So linked list becomes
// 7.6.null
push(7);
// Insert 1 at the beginning.
// So linked list becomes
// 1.7.6.null
push(1);
System.out.print("Created DLL is: ");
printList(head_ref);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
蟒蛇3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.previous = None
self.data = data
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.start_node = None
self.last_node = None
# function to add elements to doubly linked list
def append(self, data):
# is doubly linked list is empty then last_node will be none so in if condition head will be created
if self.last_node is None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.head
# adding node to the tail of doubly linked list
else:
new_node = Node(data)
self.last_node.next = new_node
new_node.previous = self.last_node
new_node.next = None
self.last_node = new_node
# function to printing and traversing the content of doubly linked list from left to right and right to left
def display(self, Type):
if Type == 'Left_To_Right':
current = self.head
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
print()
else:
current = self.last_node
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.previous
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = DoublyLinkedList()
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
L.display('Left_To_Right')
L.display('Right_To_Left')
C#
// C# program to illustrate
// creation and traversal of
// Doubly Linked List
using System;
class GFG{
// Doubly linked list
// node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node prev;
};
static Node head_ref;
// Function to push a new
// element in the Doubly
// Linked List
static void push(int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Make next of new node as
// head and previous as null
new_node.next = head_ref;
new_node.prev = null;
// Change prev of head node to
// the new node
if (head_ref != null)
head_ref.prev = new_node;
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
head_ref = new_node;
}
// Function to traverse the
// Doubly LL in the forward
// & backward direction
static void printList(Node node)
{
Node last = null;
Console.Write("\nTraversal in forward" +
" direction \n");
while (node != null)
{
// Print the data
Console.Write(" " + node.data +
" ");
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
Console.Write("\nTraversal in reverse" +
" direction \n");
while (last != null)
{
// Print the data
Console.Write(" " + last.data +
" ");
last = last.prev;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Start with the empty list
head_ref = null;
// Insert 6.
// So linked list becomes
// 6.null
push(6);
// Insert 7 at the beginning.
// So linked list becomes
// 7.6.null
push(7);
// Insert 1 at the beginning.
// So linked list becomes
// 1.7.6.null
push(1);
Console.Write("Created DLL is: ");
printList(head_ref);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
输出
Created DLL is:
Traversal in forward direction
1 7 6
Traversal in reverse direction
6 7 1- 循环链表:循环链表的最后一个节点包含指向列表第一个节点的指针。在遍历循环喜欢的列表时,我们可以从任何节点开始,并以任何方向向前和向后遍历列表,直到到达我们开始的同一节点。因此,循环链表没有开始也没有结束。下面是相同的图像:
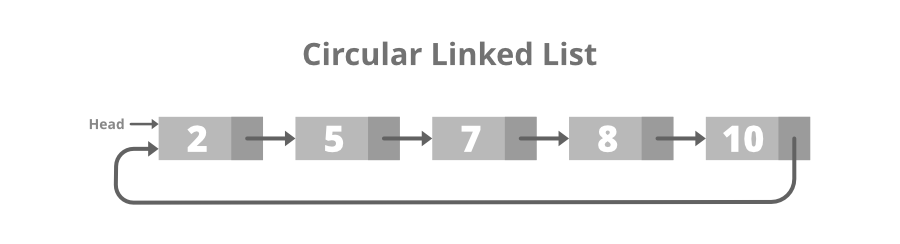
- 循环链表的结构:
C++
// Structure for a node
class Node {
public:
int data;
// Pointer to next node in CLL
Node* next;
};
蟒蛇3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
- 循环链表的创建和遍历:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate creation
// and traversal of Circular LL
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure for a node
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
// Function to insert a node at the
// beginning of Circular LL
void push(Node** head_ref, int data)
{
Node* ptr1 = new Node();
Node* temp = *head_ref;
ptr1->data = data;
ptr1->next = *head_ref;
// If linked list is not NULL then
// set the next of last node
if (*head_ref != NULL) {
while (temp->next != *head_ref) {
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = ptr1;
}
// For the first node
else
ptr1->next = ptr1;
*head_ref = ptr1;
}
// Function to print nodes in the
// Circular Linked List
void printList(Node* head)
{
Node* temp = head;
if (head != NULL) {
do {
// Print the data
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != head);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Initialize list as empty
Node* head = NULL;
// Created linked list will
// be 11->2->56->12
push(&head, 12);
push(&head, 56);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 11);
cout << "Contents of Circular"
<< " Linked List\n ";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to illustrate
// creation and traversal of
// Circular LL
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Structure for a
// node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
};
// Function to insert a node
// at the beginning of Circular
// LL
static Node push(Node head_ref,
int data)
{
Node ptr1 = new Node();
Node temp = head_ref;
ptr1.data = data;
ptr1.next = head_ref;
// If linked list is not
// null then set the next
// of last node
if (head_ref != null)
{
while (temp.next != head_ref)
{
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = ptr1;
}
// For the first node
else
ptr1.next = ptr1;
head_ref = ptr1;
return head_ref;
}
// Function to print nodes in
// the Circular Linked List
static void printList(Node head)
{
Node temp = head;
if (head != null)
{
do
{
// Print the data
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initialize list as empty
Node head = null;
// Created linked list will
// be 11.2.56.12
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 56);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 11);
System.out.print("Contents of Circular" +
" Linked List\n ");
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
蟒蛇3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class CircularLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.last_node = None
# function to add elements to circular linked list
def append(self, data):
# is circular linked list is empty then last_node will be none so in if condition head will be created
if self.last_node is None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.head
# adding node to the tail of circular linked list
else:
self.last_node.next = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.last_node.next
self.last_node.next = self.head
# function to print the content of circular linked list
def display(self):
current = self.head
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
if current == self.head:
break
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = CircularLinkedList()
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
L.display()
C#
// C# program to illustrate
// creation and traversal of
// Circular LL
using System;
class GFG{
// Structure for a
// node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
};
// Function to insert a node
// at the beginning of Circular
// LL
static Node push(Node head_ref,
int data)
{
Node ptr1 = new Node();
Node temp = head_ref;
ptr1.data = data;
ptr1.next = head_ref;
// If linked list is not
// null then set the next
// of last node
if (head_ref != null)
{
while (temp.next != head_ref)
{
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = ptr1;
}
// For the first node
else
ptr1.next = ptr1;
head_ref = ptr1;
return head_ref;
}
// Function to print nodes in
// the Circular Linked List
static void printList(Node head)
{
Node temp = head;
if (head != null)
{
do
{
// Print the data
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Initialize list as empty
Node head = null;
// Created linked list will
// be 11.2.56.12
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 56);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 11);
Console.Write("Contents of Circular " +
"Linked List\n ");
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
输出
Contents of Circular Linked List
11 2 56 12- 双循环链表:双循环链表或循环双向链表是一种更复杂的链表类型,它包含指向序列中下一个节点和前一个节点的指针。双向链表和循环双链表的区别与单链表和循环链表的区别是一样的。循环双向链表在第一个节点的前一个字段中不包含空值。下面是相同的图像:
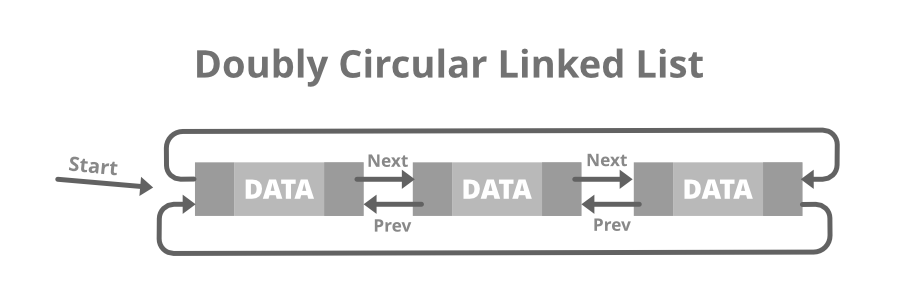
- 双循环链表的结构:
C++
// Node of doubly circular linked list
struct Node {
int data;
// Pointer to next node in DCLL
struct Node* next;
// Pointer to the previous node in DCLL
struct Node* prev;
};
蟒蛇3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.previous = None
self.data = data
self.next = None
- 双循环链表的创建和遍历:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate creation
// & traversal of Doubly Circular LL
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a Node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
// Function to insert Node at
// the beginning of the List
void insertBegin(struct Node** start,
int value)
{
// If the list is empty
if (*start == NULL) {
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = value;
new_node->next
= new_node->prev = new_node;
*start = new_node;
return;
}
// Pointer points to last Node
struct Node* last = (*start)->prev;
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
// Inserting the data
new_node->data = value;
// Update the previous and
// next of new node
new_node->next = *start;
new_node->prev = last;
// Update next and previous
// pointers of start & last
last->next = (*start)->prev
= new_node;
// Update start pointer
*start = new_node;
}
// Function to traverse the circular
// doubly linked list
void display(struct Node* start)
{
struct Node* temp = start;
printf("\nTraversal in"
" forward direction \n");
while (temp->next != start) {
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("%d ", temp->data);
printf("\nTraversal in "
"reverse direction \n");
Node* last = start->prev;
temp = last;
while (temp->prev != last) {
// Print the data
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->prev;
}
printf("%d ", temp->data);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Start with the empty list
struct Node* start = NULL;
// Insert 5
// So linked list becomes 5->NULL
insertBegin(&start, 5);
// Insert 4 at the beginning
// So linked list becomes 4->5
insertBegin(&start, 4);
// Insert 7 at the end
// So linked list becomes 7->4->5
insertBegin(&start, 7);
printf("Created circular doubly"
" linked list is: ");
display(start);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to illustrate creation
// & traversal of Doubly Circular LL
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Structure of a Node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
};
// Start with the empty list
static Node start = null;
// Function to insert Node at
// the beginning of the List
static void insertBegin(
int value)
{
// If the list is empty
if (start == null)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = value;
new_node.next
= new_node.prev = new_node;
start = new_node;
return;
}
// Pointer points to last Node
Node last = (start).prev;
Node new_node = new Node();
// Inserting the data
new_node.data = value;
// Update the previous and
// next of new node
new_node.next = start;
new_node.prev = last;
// Update next and previous
// pointers of start & last
last.next = (start).prev
= new_node;
// Update start pointer
start = new_node;
}
// Function to traverse the circular
// doubly linked list
static void display()
{
Node temp = start;
System.out.printf("\nTraversal in"
+" forward direction \n");
while (temp.next != start)
{
System.out.printf("%d ", temp.data);
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.printf("%d ", temp.data);
System.out.printf("\nTraversal in "
+ "reverse direction \n");
Node last = start.prev;
temp = last;
while (temp.prev != last)
{
// Print the data
System.out.printf("%d ", temp.data);
temp = temp.prev;
}
System.out.printf("%d ", temp.data);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Insert 5
// So linked list becomes 5.null
insertBegin( 5);
// Insert 4 at the beginning
// So linked list becomes 4.5
insertBegin( 4);
// Insert 7 at the end
// So linked list becomes 7.4.5
insertBegin( 7);
System.out.printf("Created circular doubly"
+ " linked list is: ");
display();
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
蟒蛇3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.previous = None
self.data = data
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.start_node = None
self.last_node = None
# function to add elements to doubly linked list
def append(self, data):
# is doubly linked list is empty then last_node will be none so in if condition head will be created
if self.last_node is None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.head
# adding node to the tail of doubly linked list
else:
new_node = Node(data)
self.last_node.next = new_node
new_node.previous = self.last_node
new_node.next = self.head
self.last_node = new_node
# function to print the content of doubly linked list
def display(self, Type = 'Left_To_Right'):
if Type == 'Left_To_Right':
current = self.head
while current.next is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
if current == self.head:
break
print()
else:
current = self.last_node
while current.previous is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.previous
if current == self.last_node.next:
print(self.last_node.next.data, end=' ')
break
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = DoublyLinkedList()
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
L.display('Left_To_Right')
L.display('Right_To_Left')
C#
// C# program to illustrate creation
// & traversal of Doubly Circular LL
using System;
public class GFG{
// Structure of a Node
public
class Node
{
public
int data;
public
Node next;
public
Node prev;
};
// Start with the empty list
static Node start = null;
// Function to insert Node at
// the beginning of the List
static void insertBegin(
int value)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
// If the list is empty
if (start == null)
{
new_node.data = value;
new_node.next
= new_node.prev = new_node;
start = new_node;
return;
}
// Pointer points to last Node
Node last = (start).prev;
// Inserting the data
new_node.data = value;
// Update the previous and
// next of new node
new_node.next = start;
new_node.prev = last;
// Update next and previous
// pointers of start & last
last.next = (start).prev
= new_node;
// Update start pointer
start = new_node;
}
// Function to traverse the circular
// doubly linked list
static void display()
{
Node temp = start;
Console.Write("\nTraversal in"
+" forward direction \n");
while (temp.next != start)
{
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
Console.Write("\nTraversal in "
+ "reverse direction \n");
Node last = start.prev;
temp = last;
while (temp.prev != last)
{
// Print the data
Console.Write( temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.prev;
}
Console.Write( temp.data + " ");
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Insert 5
// So linked list becomes 5.null
insertBegin( 5);
// Insert 4 at the beginning
// So linked list becomes 4.5
insertBegin( 4);
// Insert 7 at the end
// So linked list becomes 7.4.5
insertBegin( 7);
Console.Write("Created circular doubly"
+ " linked list is: ");
display();
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
输出
Created circular doubly linked list is:
Traversal in forward direction
7 4 5
Traversal in reverse direction
5 4 7- 头链表:头链表是一种特殊类型的链表,它在链表的开头包含一个头节点。因此,在头链表中, START不会指向链表的第一个节点,但START将包含头节点的地址。下面是 Grounded Header Linked List 的图像:
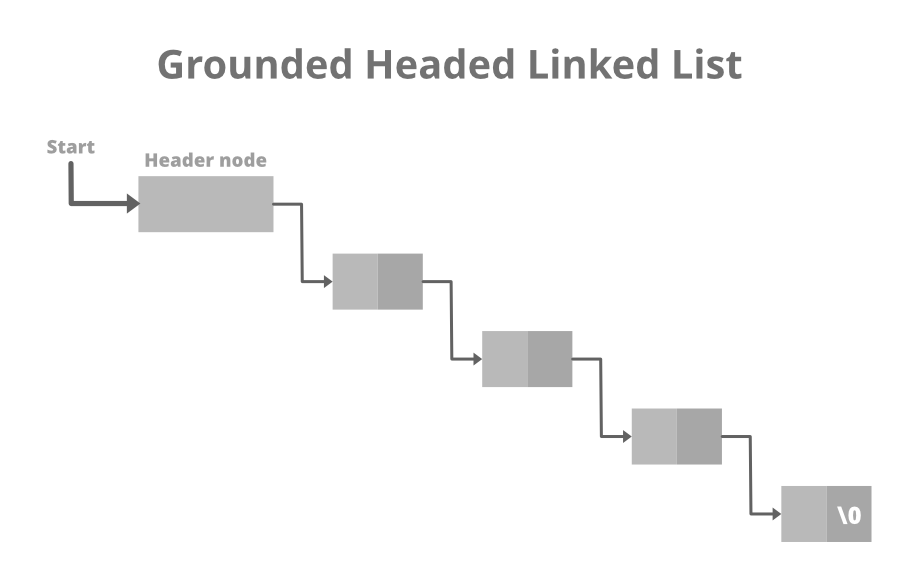
- Grounded Header 链表的结构:
C++
// Structure of the list
struct link {
int info;
// Pointer to the next node
struct link* next;
};
蟒蛇3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
- 头链表的创建和遍历:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate creation
// and traversal of Header Linked List
#include
// #include
// #include
// Structure of the list
struct link {
int info;
struct link* next;
};
// Empty List
struct link* start = NULL;
// Function to create header of the
// header linked list
struct link* create_header_list(int data)
{
// Create a new node
struct link *new_node, *node;
new_node = (struct link*)
malloc(sizeof(struct link));
new_node->info = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
// If it is the first node
if (start == NULL) {
// Initialize the start
start = (struct link*)
malloc(sizeof(struct link));
start->next = new_node;
}
else {
// Insert the node in the end
node = start;
while (node->next != NULL) {
node = node->next;
}
node->next = new_node;
}
return start;
}
// Function to display the
// header linked list
struct link* display()
{
struct link* node;
node = start;
node = node->next;
// Traverse until node is
// not NULL
while (node != NULL) {
// Print the data
printf("%d ", node->info);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\n");
// Return the start pointer
return start;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Create the list
create_header_list(11);
create_header_list(12);
create_header_list(13);
// Print the list
printf("List After inserting"
" 3 elements:\n");
display();
create_header_list(14);
create_header_list(15);
// Print the list
printf("List After inserting"
" 2 more elements:\n");
display();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to illustrate creation
// and traversal of Header Linked List
class GFG{
// Structure of the list
static class link {
int info;
link next;
};
// Empty List
static link start = null;
// Function to create header of the
// header linked list
static link create_header_list(int data)
{
// Create a new node
link new_node, node;
new_node = new link();
new_node.info = data;
new_node.next = null;
// If it is the first node
if (start == null) {
// Initialize the start
start = new link();
start.next = new_node;
}
else {
// Insert the node in the end
node = start;
while (node.next != null) {
node = node.next;
}
node.next = new_node;
}
return start;
}
// Function to display the
// header linked list
static link display()
{
link node;
node = start;
node = node.next;
// Traverse until node is
// not null
while (node != null) {
// Print the data
System.out.printf("%d ", node.info);
node = node.next;
}
System.out.printf("\n");
// Return the start pointer
return start;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create the list
create_header_list(11);
create_header_list(12);
create_header_list(13);
// Print the list
System.out.printf("List After inserting"
+ " 3 elements:\n");
display();
create_header_list(14);
create_header_list(15);
// Print the list
System.out.printf("List After inserting"
+ " 2 more elements:\n");
display();
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
蟒蛇3
# structure of Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = Node(0)
self.last_node = self.head
# function to add elements to header linked list
def append(self, data):
self.last_node.next = Node(data)
self.last_node = self.last_node.next
# function to print the content of header linked list
def display(self):
current = self.head.next
# traversing the header linked list
while current is not None:
# at each node printing its data
print(current.data, end=' ')
# giving current next node
current = current.next
# print(self.head.data)
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
L = LinkedList()
# adding elements to the header linked list
L.append(1)
L.append(2)
L.append(3)
L.append(4)
# displaying elements of header linked list
L.display()
C#
// C# program to illustrate creation
// and traversal of Header Linked List
using System;
public class GFG{
// Structure of the list
public class link {
public int info;
public link next;
};
// Empty List
static link start = null;
// Function to create header of the
// header linked list
static link create_header_list(int data)
{
// Create a new node
link new_node, node;
new_node = new link();
new_node.info = data;
new_node.next = null;
// If it is the first node
if (start == null) {
// Initialize the start
start = new link();
start.next = new_node;
}
else {
// Insert the node in the end
node = start;
while (node.next != null) {
node = node.next;
}
node.next = new_node;
}
return start;
}
// Function to display the
// header linked list
static link display()
{
link node;
node = start;
node = node.next;
// Traverse until node is
// not null
while (node != null) {
// Print the data
Console.Write("{0} ", node.info);
node = node.next;
}
Console.Write("\n");
// Return the start pointer
return start;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Create the list
create_header_list(11);
create_header_list(12);
create_header_list(13);
// Print the list
Console.Write("List After inserting"
+ " 3 elements:\n");
display();
create_header_list(14);
create_header_list(15);
// Print the list
Console.Write("List After inserting"
+ " 2 more elements:\n");
display();
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
输出
List After inserting 3 elements:
11 12 13
List After inserting 2 more elements:
11 12 13 14 15如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。