Quicksort是一种基于分而治之方法的算法,其中将数组分为子数组,然后递归调用这些子数组来对元素进行排序。
QuickSort如何工作?
- 从数组中选择枢轴元素。您可以从数组中选择任何元素作为枢轴元素。
在这里,我们将数组的最右边(即最后一个元素)作为枢轴元素。

选择一个枢轴元素 - 小于枢轴元素的元素放在左侧,大于枢轴元素的元素放在右侧。

将所有较小的元素放在枢轴元素的左侧,较大的元素放在枢轴元素的右侧 通过以下步骤实现上述布置。
- 指针固定在枢轴元件上。将枢轴元素与从第一个索引开始的元素进行比较。如果达到大于枢轴元素的元素,则为该元素设置第二个指针。
- 现在,将枢轴元素与其他元素(第三个指针)进行比较。如果到达的元素小于枢轴元素,则将较小的元素替换为较早找到的较大的元素。
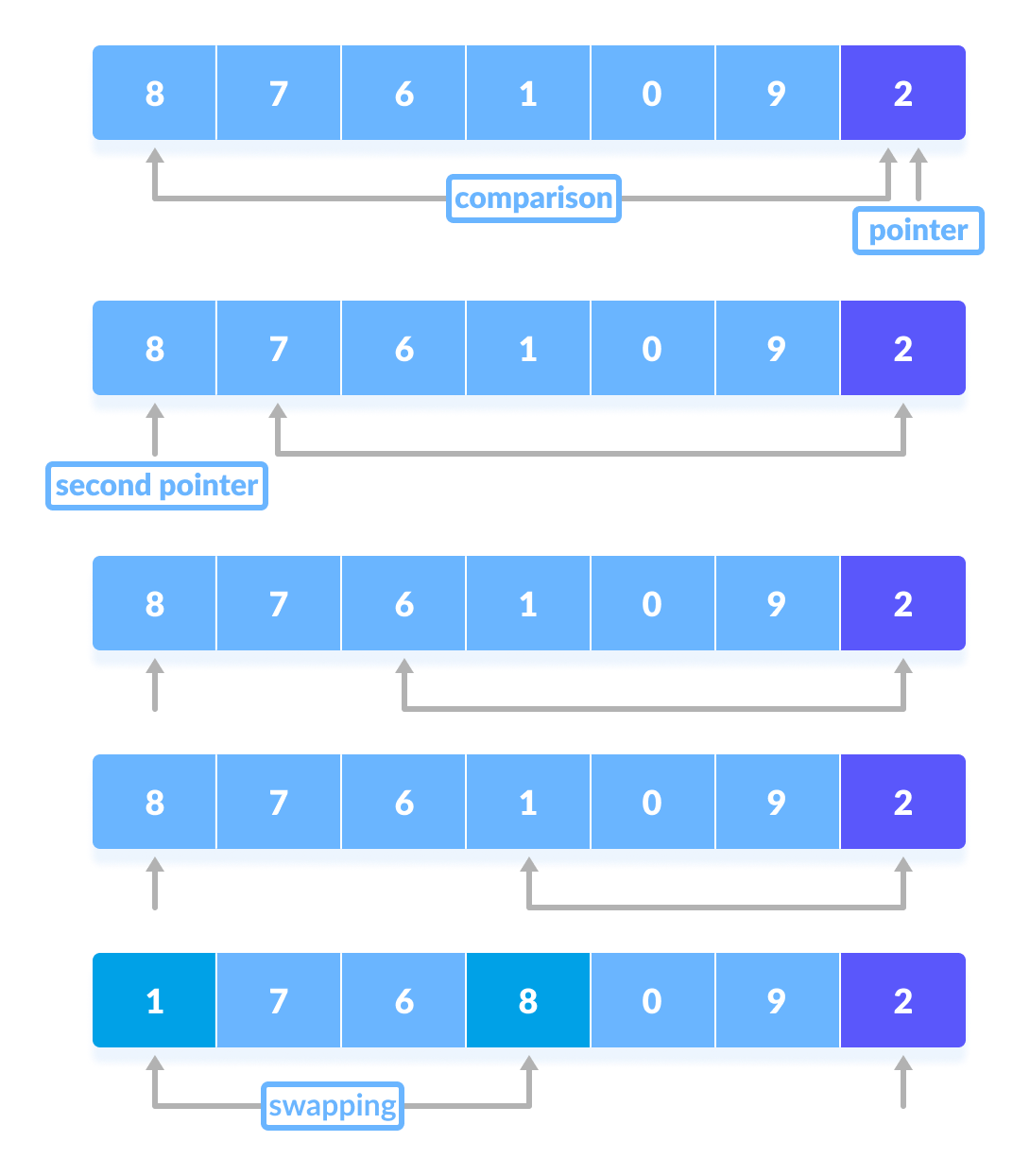
枢轴元素与其他元素的比较 - 该过程一直进行到到达倒数第二个元素为止。
最后,枢轴元素与第二个指针交换。
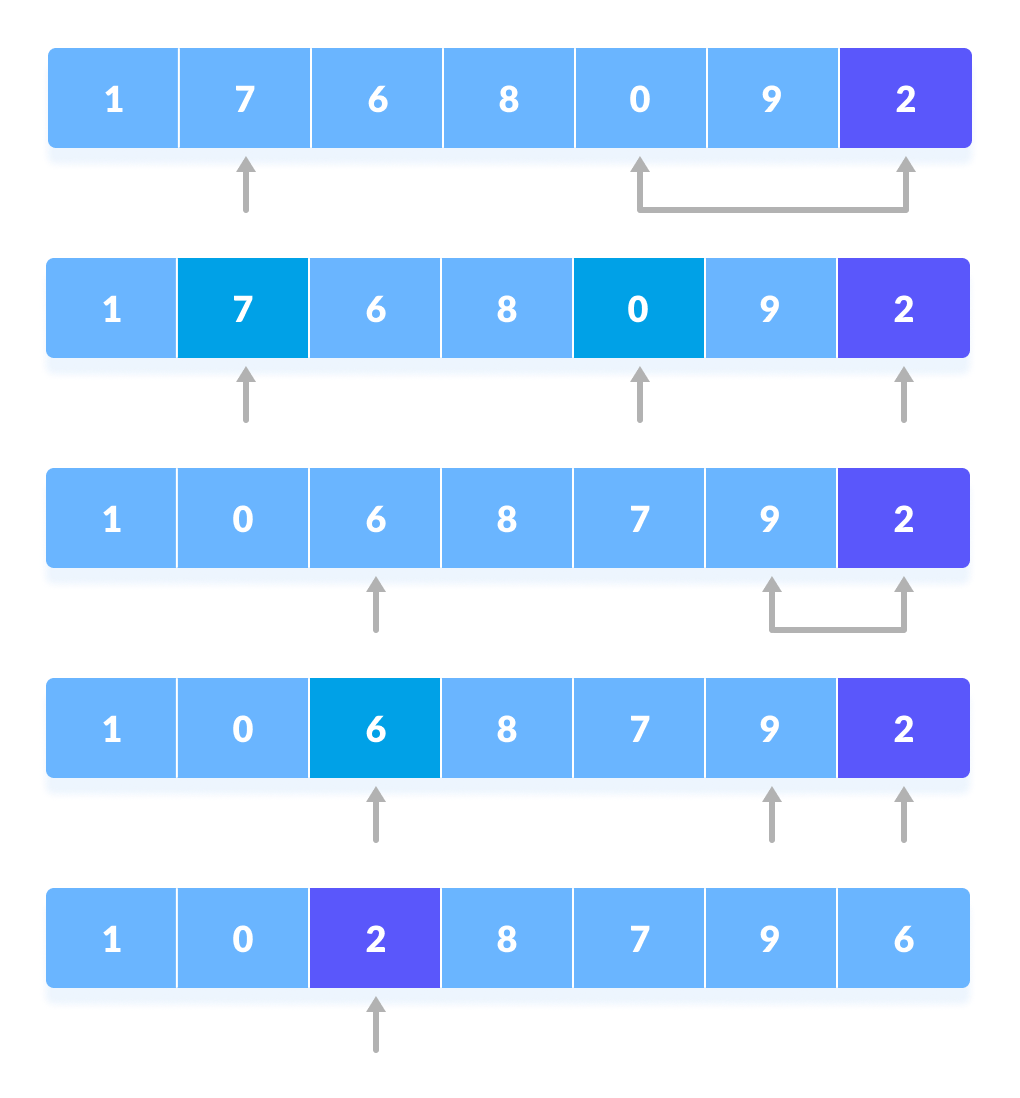
用第二个指针交换枢轴元素 - 现在,该枢轴元素的左右子部分将在以下步骤中进行进一步处理。
- 再次分别为左子部分和右子部分选择了枢轴元素。在这些子部件中,枢轴元件放置在它们的正确位置。然后,重复步骤2。
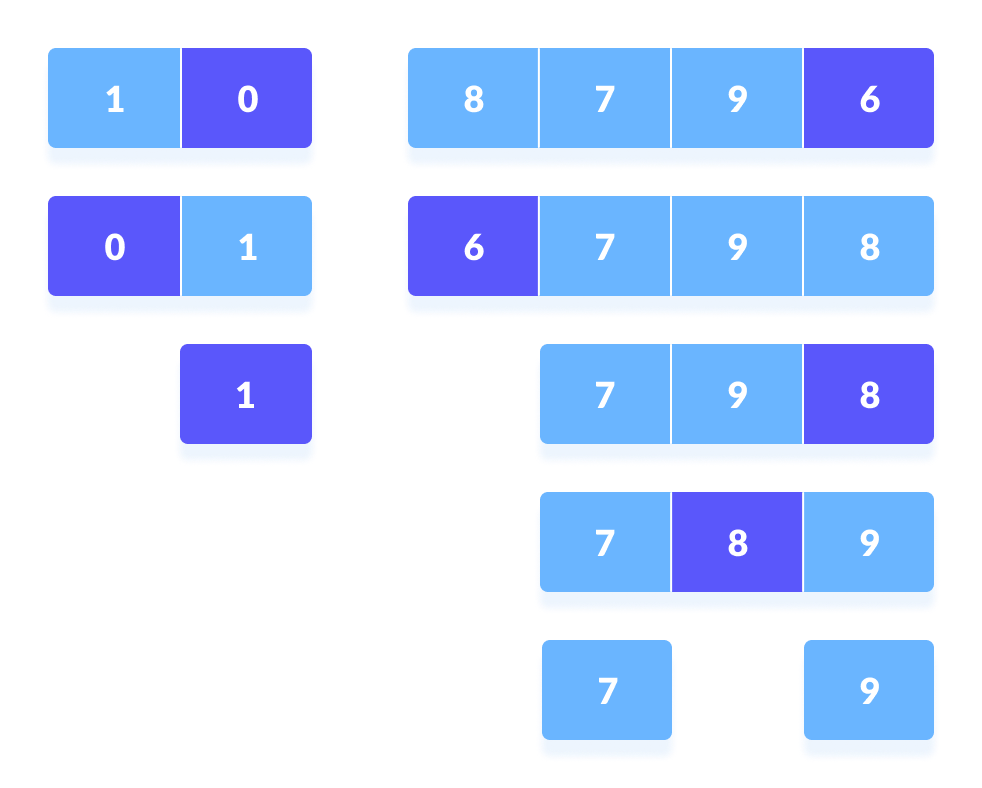
在每一半中选择的枢轴元素,然后使用递归将其放置在正确的位置 - 将子部分再次划分为较小的子部分,直到每个子部分由单个元素形成。
- 至此,该数组已经排序。
Quicksort使用递归对子部分进行排序。
在分而治之的基础上,快速排序算法可以解释为:
- 划分
将该数组分为多个子部分,这些子部分将枢轴作为分割点。小于枢轴的元素放置在枢轴的左侧,大于枢轴的元素放置在右侧。 - 征服
通过选择左,右子部分的枢轴元素,再次对它们进行分区。这可以通过将子部分递归传递到算法中来实现。 - 结合
此步骤在快速排序中不起作用。该数组已在征服步骤的末尾排序。
您可以在以下插图的帮助下了解快速排序的工作方式。
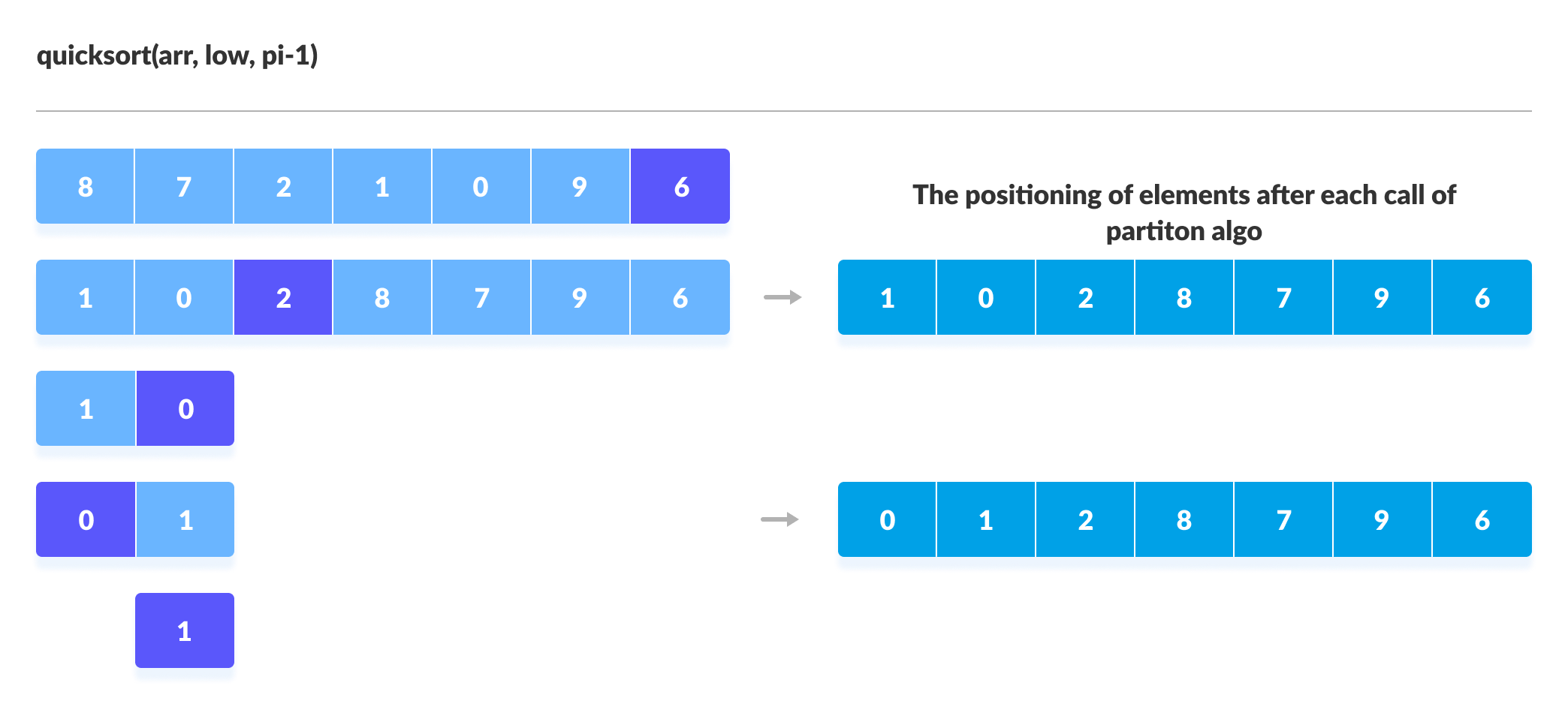
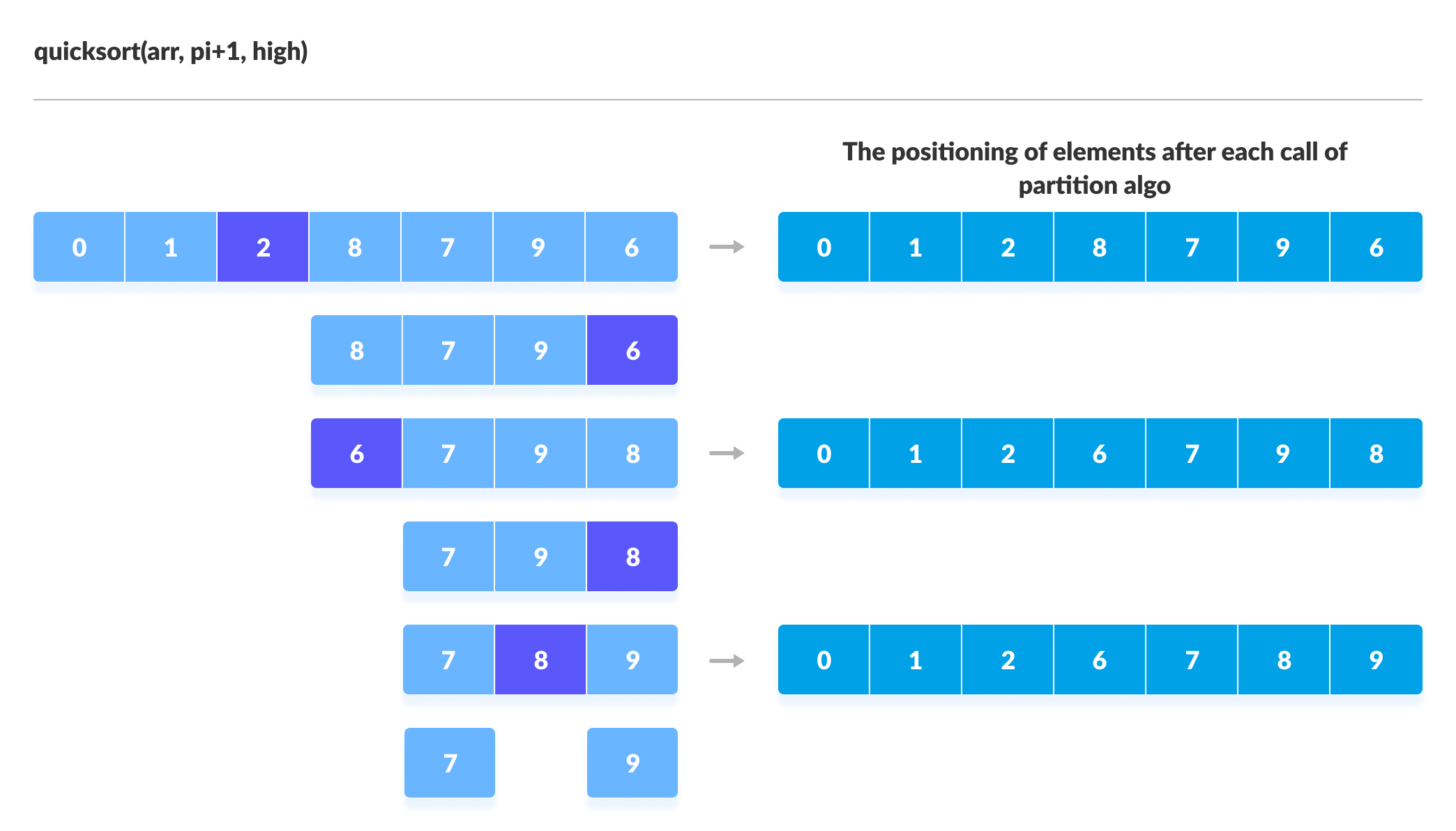
快速排序算法
quickSort(array, leftmostIndex, rightmostIndex)
if (leftmostIndex < rightmostIndex)
pivotIndex Python,Java和C / C++示例
Python
爪哇
C
C +
# Quick sort in Python
# Function to partition the array on the basis of pivot element
def partition(array, low, high):
# Select the pivot element
pivot = array[high]
i = low - 1
# Put the elements smaller than pivot on the left and greater
#than pivot on the right of pivot
for j in range(low, high):
if array[j] <= pivot:
i = i + 1
(array[i], array[j]) = (array[j], array[i])
(array[i + 1], array[high]) = (array[high], array[i + 1])
return i + 1
def quickSort(array, low, high):
if low < high:
# Select pivot position and put all the elements smaller
# than pivot on left and greater than pivot on right
pi = partition(array, low, high)
# Sort the elements on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1)
# Sort the elements on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high)
data = [8, 7, 2, 1, 0, 9, 6]
size = len(data)
quickSort(data, 0, size - 1)
print('Sorted Array in Ascending Order:')
print(data)// Quick sort in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class QuickSort {
// Function to partition the array on the basis of pivot element
int partition(int array[], int low, int high) {
// Select the pivot element
int pivot = array[high];
int i = (low - 1);
// Put the elements smaller than pivot on the left and
// greater than pivot on the right of pivot
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
int temp = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = array[high];
array[high] = temp;
return (i + 1);
}
void quickSort(int array[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// Select pivot position and put all the elements smaller
// than pivot on left and greater than pivot on right
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
// Sort the elements on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
// Sort the elements on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { 8, 7, 2, 1, 0, 9, 6 };
int size = data.length;
QuickSort qs = new QuickSort();
qs.quickSort(data, 0, size - 1);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}// Quick sort in C
#include
// Function to swap position of elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
// Function to partition the array on the basis of pivot element
int partition(int array[], int low, int high) {
// Select the pivot element
int pivot = array[high];
int i = (low - 1);
// Put the elements smaller than pivot on the left
// and greater than pivot on the right of pivot
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
swap(&array[i], &array[j]);
}
}
swap(&array[i + 1], &array[high]);
return (i + 1);
}
void quickSort(int array[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// Select pivot position and put all the elements smaller
// than pivot on left and greater than pivot on right
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
// Sort the elements on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
// Sort the elements on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// Function to print eklements of an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {8, 7, 2, 1, 0, 9, 6};
int n = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
quickSort(data, 0, n - 1);
printf("Sorted array in ascending order: \n");
printArray(data, n);
} // Quick sort in C++
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to swap position of elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
// Function to print eklements of an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << array[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// Function to partition the array on the basis of pivot element
int partition(int array[], int low, int high) {
// Select the pivot element
int pivot = array[high];
int i = (low - 1);
// Put the elements smaller than pivot on the left
// and greater than pivot on the right of pivot
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
swap(&array[i], &array[j]);
}
}
printArray(array, 7);
cout << "........\n";
swap(&array[i + 1], &array[high]);
return (i + 1);
}
void quickSort(int array[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// Select pivot position and put all the elements smaller
// than pivot on left and greater than pivot on right
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
// Sort the elements on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
// Sort the elements on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {8, 7, 6, 1, 0, 9, 2};
int n = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
quickSort(data, 0, n - 1);
cout << "Sorted array in ascending order: \n";
printArray(data, n);
} 快速排序的复杂性
时间复杂度
-
最坏情况的复杂度[Big-O] :
O(n 2 )
当拾取的枢轴元素是最大或最小元素时,就会发生这种情况。
这种情况导致枢轴元素位于已排序数组的最末端的情况。一个子数组始终为空,另一个子数组包含n - 1元素。因此,仅在此子阵列上调用quicksort。
但是,快速排序算法对于分散的数据透视表具有更好的性能。 - 最佳情况复杂度[Big-omega] :
O(n*log n)
当枢轴元素始终是中间元素或靠近中间元素时,会发生这种情况。 - 平均案例复杂度[Big-theta] :
O(n*log n)
当不出现上述情况时,就会发生这种情况。
空间复杂度
quicksort的空间复杂度为O(log n) 。
Quicksort应用
快速排序在以下情况下实施
- 编程语言适合递归
- 时间复杂度很重要
- 空间复杂性很重要