先决条件:
- 一元树的直径
- 图中两个节点之间的路径
给定一棵N元树,其中N个节点的编号从0到N-1,并列出了无向边的列表,任务是在给定树的中心找到一个或多个节点。
Eccentricity: The eccentricity of any vertex V in a given tree is the maximum distance between the given vertex V and any other vertex of the tree.
Centre: The centre of a tree is the vertex having the minimum eccentricity. Hence, it means that in order to find the centre we have to minimise this eccentricity.
例子:
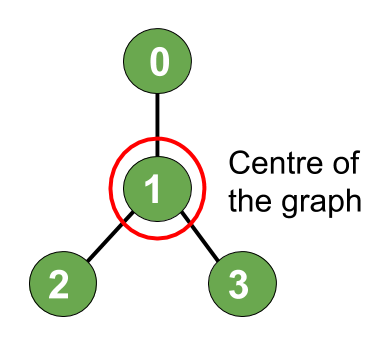
Input: N = 4, Edges[] = { (1, 0), (1, 2), (1, 3)}
Output: 1
Explanation:
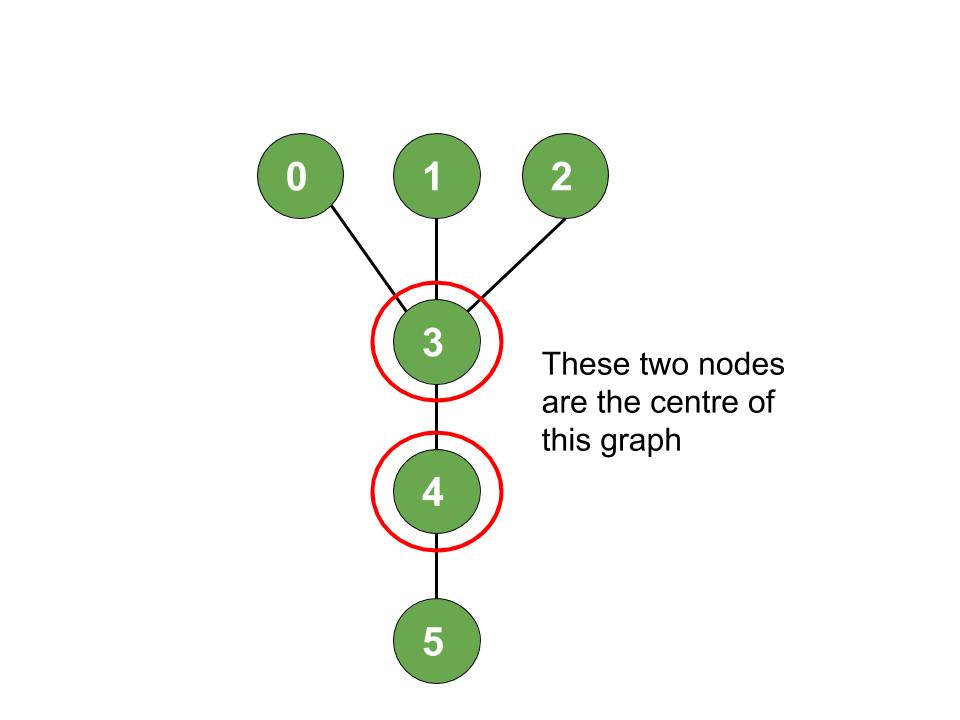
Input: N = 6, Edges[] = { (0, 3), (1, 3), (2, 3), (4, 3), (5, 4)}
Output: 3, 4
Explanation:
方法:可以看出,最大偏心距的路径是树的直径。因此,树直径的中心也将是树的中心。
证明:
- For example, Let’s consider a case where the longest path consists of odd number of vertices. Let the longest path be X —— O ——– Y where X and Y are the two endpoints of the path and O is the middle vertex.
- For a contradiction, if the centre of the tree is not O but some other vertex O’, then at least one of the following two statements must be true.
- Path XO’ is strictly longer than path XO
- Path YO’ is strictly longer than path YO
- This means O’ will not satisfy the condition of minimum eccentricity. Hence by contradiction, we have proved that the centre of the tree is actually the centre of the diameter path.
- 现在,如果直径包含奇数个节点,则仅存在1个中心(也称为Central Tree )。
- 如果直径由偶数个节点组成,则有2个中心节点(也称为双中心树)。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// To create tree
map > tree;
// Function to store the path
// from given vertex to the target
// vertex in a vector path
bool getDiameterPath(int vertex,
int targetVertex,
int parent,
vector& path)
{
// If the target node is found,
// push it into path vector
if (vertex == targetVertex) {
path.push_back(vertex);
return true;
}
for (auto i : tree[vertex]) {
// To prevent visiting a
// node already visited
if (i == parent)
continue;
// Recursive call to the neighbours
// of current node inorder
// to get the path
if (getDiameterPath(i, targetVertex,
vertex, path)) {
path.push_back(vertex);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Function to obtain and return the
// farthest node from a given vertex
void farthestNode(int vertex, int parent,
int height, int& maxHeight,
int& maxHeightNode)
{
// If the current height is maximum
// so far, then save the current node
if (height > maxHeight) {
maxHeight = height;
maxHeightNode = vertex;
}
// Iterate over all the neighbours
// of current node
for (auto i : tree[vertex]) {
// This is to prevent visiting
// a already visited node
if (i == parent)
continue;
// Next call will be at 1 height
// higher than our current height
farthestNode(i, vertex,
height + 1,
maxHeight,
maxHeightNode);
}
}
// Function to add edges
void addedge(int a, int b)
{
tree[a].push_back(b);
tree[b].push_back(a);
}
void FindCentre(int n)
{
// Now we will find the 1st farthest
// node from 0(any arbitary node)
// Perform DFS from 0 and update
// the maxHeightNode to obtain
// the farthest node from 0
// Reset to -1
int maxHeight = -1;
// Reset to -1
int maxHeightNode = -1;
farthestNode(0, -1, 0, maxHeight,
maxHeightNode);
// Stores one end of the diamter
int leaf1 = maxHeightNode;
// Similarly the other end of
// the diameter
// Reset the maxHeight
maxHeight = -1;
farthestNode(maxHeightNode,
-1, 0, maxHeight,
maxHeightNode);
// Stores the second end
// of the diameter
int leaf2 = maxHeightNode;
// Store the diameter into
// the vector path
vector path;
// Diamter is equal to the
// path between the two farthest
// nodes leaf1 and leaf2
getDiameterPath(leaf1, leaf2,
-1, path);
int pathSize = path.size();
if (pathSize % 2) {
cout << path[pathSize / 2]
<< endl;
}
else {
cout << path[pathSize / 2]
<< ", "
<< path[(pathSize - 1) / 2]
<< endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 4;
addedge(1, 0);
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(1, 3);
FindCentre(N);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// To create tree
static Map> tree;
static ArrayList path;
static int maxHeight, maxHeightNode;
// Function to store the path
// from given vertex to the target
// vertex in a vector path
static boolean getDiameterPath(int vertex,
int targetVertex,
int parent,
ArrayList path)
{
// If the target node is found,
// push it into path vector
if (vertex == targetVertex)
{
path.add(vertex);
return true;
}
for(Integer i : tree.get(vertex))
{
// To prevent visiting a
// node already visited
if (i == parent)
continue;
// Recursive call to the neighbours
// of current node inorder
// to get the path
if (getDiameterPath(i, targetVertex,
vertex, path))
{
path.add(vertex);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Function to obtain and return the
// farthest node from a given vertex
static void farthestNode(int vertex, int parent,
int height)
{
// If the current height is maximum
// so far, then save the current node
if (height > maxHeight)
{
maxHeight = height;
maxHeightNode = vertex;
}
// Iterate over all the neighbours
// of current node
if (tree.get(vertex) != null)
for(Integer i : tree.get(vertex))
{
// This is to prevent visiting
// a already visited node
if (i == parent)
continue;
// Next call will be at 1 height
// higher than our current height
farthestNode(i, vertex,
height + 1);
}
}
// Function to add edges
static void addedge(int a, int b)
{
if (tree.get(a) == null)
tree.put(a, new ArrayList<>());
tree.get(a).add(b);
if (tree.get(b) == null)
tree.put(b, new ArrayList<>());
tree.get(b).add(a);
}
static void FindCentre(int n)
{
// Now we will find the 1st farthest
// node from 0(any arbitary node)
// Perform DFS from 0 and update
// the maxHeightNode to obtain
// the farthest node from 0
// Reset to -1
maxHeight = -1;
// Reset to -1
maxHeightNode = -1;
farthestNode(0, -1, 0);
// Stores one end of the diamter
int leaf1 = maxHeightNode;
// Similarly the other end of
// the diameter
// Reset the maxHeight
maxHeight = -1;
farthestNode(maxHeightNode,
-1, 0);
// Stores the second end
// of the diameter
int leaf2 = maxHeightNode;
// Store the diameter into
// the vector path
path = new ArrayList<>();
// Diameter is equal to the
// path between the two farthest
// nodes leaf1 and leaf2
getDiameterPath(leaf1, leaf2,
-1, path);
int pathSize = path.size();
if (pathSize % 2 == 1)
{
System.out.println(path.get(pathSize / 2));
}
else {
System.out.println(path.get(pathSize / 2) +
", " + path.get((pathSize - 1) / 2));
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4;
tree = new HashMap<>();
addedge(1, 0);
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(1, 3);
FindCentre(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat 输出:
1
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)