羧基命名法
羧酸是我们每天使用的一种常见物质。柠檬酸是一种羧酸,负责柠檬的酸味。醋只不过是一种被称为乙酸的羧酸,是家庭用品中最常见的防腐剂之一。我们需要了解如何命名这些常见的酸以及与之相关的定律。
在蚂蚁和黄蜂的叮咬中发现的甲酸会导致我们的身体燃烧。但是您知道甲酸和甲酸是同一事物的两个不同名称吗?甲酸被称为甲酸,因为蚂蚁的拉丁词是“Formica”。它首先是通过蒸馏蚂蚁尸体而分离出来的。醋,俗称醋酸或乙酸,是一种常见的厨房防腐剂。醋这个名字背后的故事是什么?在本文中,我们将了解羧基。
羧基
它是一类重要的有机化学品。羧基是具有通过单键与碳原子连接的羰基和羟基的官能团。另一方面,羧酸是具有羧基的有机物质。请记住,羰基是与氧双键的碳,而 OH 基团是 OH 基团。
RC(O)OH是该类的通式。在该式中,R是烷基或芳基。羧酸的天然来源比比皆是。然而,该组的大多数成员都是合成创建的。

羧酸
Carboxylic acids are compounds that have a carbon atom bonded to the functional group COOH (carboxyl group). The attachment of a hydroxyl group to a carbonyl group, however, can result in the production of a carboxyl group, hence the name “carboxyl group.”
根据存在的基团,羧酸可分为脂肪族或芳香族。如果有烷基(RCOOH)和如果有芳基(ArCOOH)。脂肪酸是脂肪族羧酸的 C12-C18 成员。天然脂肪或甘油酯是您在自然界中发现的。此外,酯、酰氯、酸酐、酰胺和其他必需的有机分子都是从这个基团开始的。
羧酸存在于多种天然产品中。例如,昆虫叮咬中含有甲酸,黄油中含有丁酸,血液和组织的碳酸氢盐系统中含有碳酸,椰子油中含有月桂酸,棕榈油中含有棕榈酸,花生油中含有花生酸和硬脂酸。在巧克力、蜡、肥皂和油中。在本文中,我们将研究羧基的特性和结构如何影响羧酸分子的性质。
羧酸的例子
- 羧酸是最著名的碳基羧基实例之一。用于制造蛋白质的氨基酸和乙酸含有羧酸。
- 该分子最常见的是羧酸根阴离子 R-COO-,因为氢离子很容易分离。阴离子因后缀“-ate”而得名。乙酸(一种羧酸)转化时形成乙酸根离子。
羧酸的命名法
最早从自然界中分离出来的有机化合物之一属于这一类。因此,此类中的几种化合物具有更常用的名称。
通用名称
- 许多羧酸基团的通用名称来源于其天然来源的拉丁或希腊名称。后缀-ic酸通常用于通用名称。例如,HCOOH 是甲酸。
- “formica”一词在拉丁语中意为“蚂蚁”。红蚂蚁是甲酸的主要来源。拉丁语“acetum”指的是醋,它是乙酸 (CH 3 COOH) 的来源。丁酸,在拉丁语中被称为丁酸,也存在于腐臭的黄油中。
IUPAC 名称
通过用 -oic 酸替换各个烷烃的“e”,IUPAC 系统使脂肪族羧酸的命名变得简单。在羧酸中,羧基碳是要编号的第一个碳原子。因此,母链中的第一个碳将始终是羧基碳。
如果一个分子具有多个羧基,则对烷基链进行编号至关重要。通过将乘法前缀添加到母体烷基链的名称中,例如二羧酸、三羧酸等,您可以确定化学品中所含羧酸的数量。为了指定给定化合物中 –COOH 基团的位置,阿拉伯数字必须写在乘法前缀之前。
甲酸、乙酸、丙酸、丁酸和该物质家族的其他简单成员的名称如下: 另一方面,芳香族羧酸并不总是具有统一的命名法。他们甚至有一个独特的 IUPAC 批准的命名法,如苯甲酸。化合物也可以根据它们相对于主要化合物的位置和字母顺序来命名。

2-氯-3甲基丁酸
当化学品具有多个官能团时,使用羧基代替命名法中的其他官能团。羧基比其他官能团更有价值。
下例中的分子不是醇,而是羧酸。

4-羟基-2-甲基丁酸
我们已经知道,在命名化学物质时,羧基碳原子始终是碳 1。因此,在指定羧基时,我们不需要使用定位符。
羧酸命名
这些名称由化学家给出,以描述化合物的形成来源。化合物的源名称以 –ic 为后缀。以下是其中一些化学物质: Formula Common Name IUPAC Name HCOOH Formic acid Methanoic acid CH3COOH Acetic acid Ethanoic acid CH3CH2COOH Propionic acid Propanoic acid CH3(CH2)2COOH Butyric acid Butanoic acid CH3(CH2)3COOH Valeric acid Pentanoic acid CH3(CH2)4COOH Caproic acid Hexanoic acid CH3(CH2)5COOH Enanthic acid Heptanoic acid
羧酸的结构
功能性有机化合物是羧基。在该羧基结构中,碳原子通过双键与氧原子结合。它也有一个与之键合的羟基。羧酸是羧化化合物。许多有机酸,如乙酸和氨基酸,都属于这一类。
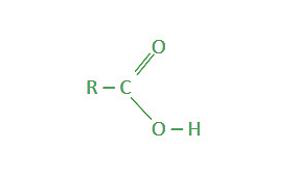
羧酸的结构
在分子的侧面,通常存在羧基。羟基部分中所含的H原子被羧基离子化并作为游离的H +离子或质子释放。该成分的其余部分,即 O,带有负电荷。电荷在两个氧分子之间的空间中前后流动,保持电离状态稳定。

羧基
共振结构
羧酸在一个平面上具有羧基碳中的所有键。羧基碳键的角度约为 120 度。由于其共振结构,羧基碳的亲电性低于羰基碳。

示例问题
问题1:羧酸的专有名称是什么?
回答:
The parent chain in IUPAC nomenclature is the carbon chain with the longest carboxylic group. The carboxyl group occupies the lowest position (always 1) among the other functional groups, and is numbered appropriately. These functional groups, whose names are listed alphabetically, act as substituents. -anoic replaces the -ane of the parent carbon chain. Adding -oic to the name of the parent chain follows the prefixes used for substituents. Carboxylic acids, on the other hand, get their names from the place where they’re isolated.
问题2:乙酸和醋一样吗?
回答:
Ethanoic acid is referred to as “vinegar.” Acetic acid is another term for it. The common names of carboxylic acids come from the place where they were isolated. Vinegar is known as acetic acid because of its Latin name, acetum.
问题 3:写出以下结构的通用名称和 IUPAC 名称:
- CH 3 CH 2 COOH
- CH 3 (CH 2 ) 4 COOH
- CH 3 (CH 2 ) 5 COOH
回答:
- CH3CH2COOH
Common Name – Propionic acid
IUPAC Name – Propanoic acid
- CH3(CH2)4COOH
Common Name – Caproic acid
IUPAC Name – Hexanoic acid
- CH3(CH2)5COOH
Common Name – Enanthic acid
IUPAC Name – Heptanoic acid
问题4:简要解释羧酸的结构。
回答:
A functional organic compound is a carboxyl group. A carbon atom is joined to an oxygen atom by a double bond in this carboxyl group structure. It also has a single hydroxyl group with which it is bonded. Carboxylic acids are carboxylated compounds. Many organic acids, such as acetic acid and amino acid, fall under this category.
On the sides of the molecules, the carboxyl group is usually present. The H atom contained in the hydroxyl group portion ionizes and is released as a free H+ ion or proton by the carboxyl group. The rest of the component, which is O, has a negative charge on it. The charge flows forward and backward in the space between the two oxygen molecules, keeping the ionization state stable.
问题5:构成羧基的成分是什么?
回答:
The carboxyl group is made up of carbon atoms that have a hydrogen atom attached to them. Oxygen and the hydroxyl group are bonded together. Some more elements are linked to the Carboxyl group. Many qualities are provided by the compound that is created. Organic elements with carboxyl groups, such as carboxylic acids, are common.
RCOOH is a symbol for the carboxyl group. R can represent any carbon-containing chemical or element. The carbon is connected to oxygen by a double bond and to the hydroxyl group, OH, by a single bond in this type of carboxylic group structure. Amino acids, fatty acids, keto acids, and other compounds are examples of carboxylic acids.
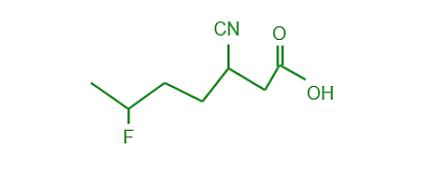
问题 6:写下下列化合物的 IUPAC 名称——
答案:
Heptane is the parent chain, which contains seven carbon atoms. So we’ve got heptanoic acid on our hands. On the priority list of functional groups, halogens and nitrile groups are at the bottom. As a result, they are treated as substitutes and are assigned a prefix. In alphabetical sequence, the prefix “fluoro” is applied to fluorine, whereas the prefix “cyano” is applied to nitrile.
Hence, IUPAC name of compound is,

3-cyano-6-fluoroheptanoic acid