最长增长子序列(LIS)问题是找到给定序列的最长子序列的长度,以使子序列的所有元素都按升序排序。例如,{10、22、9、33、21、50、41、60、80}的LIS长度为6,LIS为{10、22、33、50、60、80}。 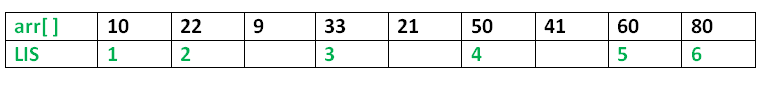
更多示例:
Input : arr[] = {3, 10, 2, 1, 20}
Output : Length of LIS = 3
The longest increasing subsequence is 3, 10, 20
Input : arr[] = {3, 2}
Output : Length of LIS = 1
The longest increasing subsequences are {3} and {2}
Input : arr[] = {50, 3, 10, 7, 40, 80}
Output : Length of LIS = 4
The longest increasing subsequence is {3, 7, 40, 80}
最佳子结构:
令arr [0..n-1]为输入数组,令L(i)为以索引i结尾的LIS的长度,以使arr [i]为LIS的最后一个元素。
然后,L(i)可以递归写为:
L(i)= 1 + max(L(j))其中0
为了找到给定数组的LIS,我们需要返回max(L(i)),其中0 因此,我们看到LIS问题满足最佳子结构属性,因为可以使用子问题的解决方案来解决主要问题。
以下是LIS问题的简单递归实现。它遵循上面讨论的递归结构。
# A naive Python implementation of LIS problem
""" To make use of recursive calls, this function must return
two things:
1) Length of LIS ending with element arr[n-1]. We use
max_ending_here for this purpose
2) Overall maximum as the LIS may end with an element
before arr[n-1] max_ref is used this purpose.
The value of LIS of full array of size n is stored
in * max_ref which is our final result """
# global variable to store the maximum
global maximum
def _lis(arr, n ):
# to allow the access of global variable
global maximum
# Base Case
if n == 1 :
return 1
# maxEndingHere is the length of LIS ending with arr[n-1]
maxEndingHere = 1
"""Recursively get all LIS ending with arr[0], arr[1]..arr[n-2]
IF arr[n-1] is maller than arr[n-1], and max ending with
arr[n-1] needs to be updated, then update it"""
for i in xrange(1, n):
res = _lis(arr, i)
if arr[i-1] < arr[n-1] and res + 1 > maxEndingHere:
maxEndingHere = res + 1
# Compare maxEndingHere with overall maximum. And
# update the overall maximum if needed
maximum = max(maximum, maxEndingHere)
return maxEndingHere
def lis(arr):
# to allow the access of global variable
global maximum
# length of arr
n = len(arr)
# maximum variable holds the result
maximum = 1
# The function _lis() stores its result in maximum
_lis(arr, n)
return maximum
# Driver program to test the above function
arr = [10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60]
n = len(arr)
print "Length of lis is ", lis(arr)
# This code is contributed by NIKHIL KUMAR SINGH
输出:
Length of lis is 5
重叠子问题:
考虑到上述实现,下面是大小为4的数组的递归树。lis(n)给出了arr []的LIS长度。
lis(4)
/ |
lis(3) lis(2) lis(1)
/ /
lis(2) lis(1) lis(1)
/
lis(1)
我们可以看到,有许多子问题一次又一次地得到解决。因此,此问题具有“重叠子结构”属性,可以通过使用“记忆化”或“制表”来避免相同子问题的重新计算。以下是LIS问题的列表化实施。
# Dynamic programming Python implementation of LIS problem
# lis returns length of the longest increasing subsequence
# in arr of size n
def lis(arr):
n = len(arr)
# Declare the list (array) for LIS and initialize LIS
# values for all indexes
lis = [1]*n
# Compute optimized LIS values in bottom up manner
for i in range (1, n):
for j in range(0, i):
if arr[i] > arr[j] and lis[i]< lis[j] + 1 :
lis[i] = lis[j]+1
# Initialize maximum to 0 to get the maximum of all
# LIS
maximum = 0
# Pick maximum of all LIS values
for i in range(n):
maximum = max(maximum, lis[i])
return maximum
# end of lis function
# Driver program to test above function
arr = [10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60]
print "Length of lis is", lis(arr)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh
输出:
Length of lis is 5
请参考有关动态编程的完整文章。设置3(最长递增子序列)以获取更多详细信息!