给定一个输入字符串和一个单词词典,请找出输入字符串可以分割成以空格分隔的词典单词序列。有关更多详细信息,请参见以下示例。
这是一个著名的Google面试问题,如今也有许多其他公司在询问。
Consider the following dictionary
{ i, like, sam, sung, samsung, mobile, ice,
cream, icecream, man, go, mango}
Input: ilike
Output: Yes
The string can be segmented as "i like".
Input: ilikesamsung
Output: Yes
The string can be segmented as "i like samsung"
or "i like sam sung".递归实现:
这个想法很简单,我们考虑每个前缀并在字典中搜索它。如果字典中存在前缀,则重复查找其余的字符串(或后缀)。
Python3
def wordBreak(wordList, word):
if word == '':
return True
else:
wordLen = len(word)
return any([(word[:i] in wordList) and wordBreak(wordList, word[i:]) for i in range(1, wordLen+1)])C++
// A recursive program to test whether a given
// string can be segmented into space separated
// words in dictionary
#include
using namespace std;
/* A utility function to check whether a word is
present in dictionary or not. An array of strings
is used for dictionary. Using array of strings for
dictionary is definitely not a good idea. We have
used for simplicity of the program*/
int dictionaryContains(string word)
{
string dictionary[] = {"mobile","samsung","sam","sung",
"man","mango","icecream","and",
"go","i","like","ice","cream"};
int size = sizeof(dictionary)/sizeof(dictionary[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (dictionary[i].compare(word) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// returns true if string can be segmented into space
// separated words, otherwise returns false
bool wordBreak(string str)
{
int size = str.size();
// Base case
if (size == 0) return true;
// Try all prefixes of lengths from 1 to size
for (int i=1; i<=size; i++)
{
// The parameter for dictionaryContains is
// str.substr(0, i) which is prefix (of input
// string) of length 'i'. We first check whether
// current prefix is in dictionary. Then we
// recursively check for remaining string
// str.substr(i, size-i) which is suffix of
// length size-i
if (dictionaryContains( str.substr(0, i) ) &&
wordBreak( str.substr(i, size-i) ))
return true;
}
// If we have tried all prefixes and
// none of them worked
return false;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
wordBreak("ilikesamsung")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("iiiiiiii")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmango")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmangok")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
return 0;
} Java
import java.util.*;
// Recursive implementation of
// word break problem in java
public class WordBreakProblem
{
// set to hold dictionary values
private static Set dictionary = new HashSet<>();
public static void main(String []args)
{
// array of strings to be added in dictionary set.
String temp_dictionary[] = {"mobile","samsung","sam","sung",
"man","mango","icecream","and",
"go","i","like","ice","cream"};
// loop to add all strings in dictionary set
for (String temp :temp_dictionary)
{
dictionary.add(temp);
}
// sample input cases
System.out.println(wordBreak("ilikesamsung"));
System.out.println(wordBreak("iiiiiiii"));
System.out.println(wordBreak(""));
System.out.println(wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii"));
System.out.println(wordBreak("samsungandmango"));
System.out.println(wordBreak("samsungandmangok"));
}
// returns true if the word can be segmented into parts such
// that each part is contained in dictionary
public static boolean wordBreak(String word)
{
int size = word.length();
// base case
if (size == 0)
return true;
//else check for all words
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
{
// Now we will first divide the word into two parts ,
// the prefix will have a length of i and check if it is
// present in dictionary ,if yes then we will check for
// suffix of length size-i recursively. if both prefix and
// suffix are present the word is found in dictionary.
if (dictionary.contains(word.substring(0,i)) &&
wordBreak(word.substring(i,size)))
return true;
}
// if all cases failed then return false
return false;
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sparsh Singhal CPP
// A Dynamic Programming based program to test whether a given string can
// be segmented into space separated words in dictionary
#include
#include
using namespace std;
/* A utility function to check whether a word is present in dictionary or not.
An array of strings is used for dictionary. Using array of strings for
dictionary is definitely not a good idea. We have used for simplicity of
the program*/
int dictionaryContains(string word)
{
string dictionary[] = {"mobile","samsung","sam","sung","man","mango",
"icecream","and","go","i","like","ice","cream"};
int size = sizeof(dictionary)/sizeof(dictionary[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (dictionary[i].compare(word) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns true if string can be segmented into space separated
// words, otherwise returns false
bool wordBreak(string str)
{
int size = str.size();
if (size == 0) return true;
// Create the DP table to store results of subroblems. The value wb[i]
// will be true if str[0..i-1] can be segmented into dictionary words,
// otherwise false.
bool wb[size+1];
memset(wb, 0, sizeof(wb)); // Initialize all values as false.
for (int i=1; i<=size; i++)
{
// if wb[i] is false, then check if current prefix can make it true.
// Current prefix is "str.substr(0, i)"
if (wb[i] == false && dictionaryContains( str.substr(0, i) ))
wb[i] = true;
// wb[i] is true, then check for all substrings starting from
// (i+1)th character and store their results.
if (wb[i] == true)
{
// If we reached the last prefix
if (i == size)
return true;
for (int j = i+1; j <= size; j++)
{
// Update wb[j] if it is false and can be updated
// Note the parameter passed to dictionaryContains() is
// substring starting from index 'i' and length 'j-i'
if (wb[j] == false && dictionaryContains( str.substr(i, j-i) ))
wb[j] = true;
// If we reached the last character
if (j == size && wb[j] == true)
return true;
}
}
}
/* Uncomment these lines to print DP table "wb[]"
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
cout << " " << wb[i]; */
// If we have tried all prefixes and none of them worked
return false;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
wordBreak("ilikesamsung")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("iiiiiiii")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmango")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmangok")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
return 0;
} CPP
// A Dynamic Programming based program to test
// whether a given string can be segmented into
// space separated words in dictionary
#include
using namespace std;
/* A utility function to check whether a word
is present in dictionary or not. An array of
strings is used for dictionary. Using array
of strings for dictionary is definitely not
a good idea. We have used for simplicity of
the program*/
int dictionaryContains(string word)
{
string dictionary[]
= { "mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man",
"mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i",
"like", "ice", "cream" };
int size = sizeof(dictionary) / sizeof(dictionary[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (dictionary[i].compare(word) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns true if string can be segmented into space
// separated words, otherwise returns false
bool wordBreak(string s)
{
int n = s.size();
if (n == 0)
return true;
// Create the DP table to store results of subroblems.
// The value dp[i] will be true if str[0..i] can be
// segmented into dictionary words, otherwise false.
vector dp(n + 1, 0); // Initialize all values
// as false.
// matched_index array represents the indexes for which
// dp[i] is true. Initially only -1 element is present
// in this array.
vector matched_index;
matched_index.push_back(-1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int msize = matched_index.size();
// Flag value which tells that a substring matches
// with given words or not.
int f = 0;
// Check all the substring from the indexes matched
// earlier. If any of that substring matches than
// make flag value = 1;
for (int j = msize - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
// sb is substring starting from
// matched_index[j]
// + 1 and of length i - matched_index[j]
string sb = s.substr(matched_index[j] + 1,
i - matched_index[j]);
if (dictionaryContains(sb)) {
f = 1;
break;
}
}
// If substring matches than do dp[i] = 1 and
// push that index in matched_index array.
if (f == 1) {
dp[i] = 1;
matched_index.push_back(i);
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
wordBreak("ilikesamsung") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("iiiiiiii") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("") ? cout << "Yes\n" : cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmango") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmangok") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// 2-pointer Approach of Word Break Problem
class GFG {
// The solution function
public static int wordBreak(String A,
ArrayList B)
{
// store two pointers to start with
int i = 0, j = 1;
// store the length of the String to be segmented
int n = A.length();
// this is a counter to count the characters after
// each successful segment by successful we mean
// that is present in the List B
int totalSegmented = 0;
// iterate through the string A with pointer j
while (j <= n) {
// check whether the current segment is present
// in List B
if (B.contains(A.substring(i, j))) {
// count the characters segmented so far
totalSegmented += j - i;
// store the start of next segment(the
// pointer i) and keep incrementing the
// pointer j
i = j;
j++;
}
// the case when current segment is not present
// in List B, we need continue incrementing
// pointer-j
else {
j++;
}
}
// If the string was successfully segmented, the
// total segmented characters must be equal to total
// string length
if (totalSegmented == A.length())
return 1;
// If the segmented characters were not equal to
// String's length, we need to output zero
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Store the given list of words
ArrayList dictionary
= new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(
"mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man",
"mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i",
"like", "ice", "cream"));
String segmentThis = "ilike";
// Calling the function to check a word break is
// possible
if (wordBreak(segmentThis, dictionary) == 1)
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
} // contributed by shivendr7 输出
如果对后缀的递归调用返回true,则返回true,否则尝试下一个前缀。如果我们尝试了所有前缀,但没有一个导致解决方案,则返回false。
我们强烈建议您查看在以下实现中广泛使用的substr函数。
C++
// A recursive program to test whether a given
// string can be segmented into space separated
// words in dictionary
#include
using namespace std;
/* A utility function to check whether a word is
present in dictionary or not. An array of strings
is used for dictionary. Using array of strings for
dictionary is definitely not a good idea. We have
used for simplicity of the program*/
int dictionaryContains(string word)
{
string dictionary[] = {"mobile","samsung","sam","sung",
"man","mango","icecream","and",
"go","i","like","ice","cream"};
int size = sizeof(dictionary)/sizeof(dictionary[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (dictionary[i].compare(word) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// returns true if string can be segmented into space
// separated words, otherwise returns false
bool wordBreak(string str)
{
int size = str.size();
// Base case
if (size == 0) return true;
// Try all prefixes of lengths from 1 to size
for (int i=1; i<=size; i++)
{
// The parameter for dictionaryContains is
// str.substr(0, i) which is prefix (of input
// string) of length 'i'. We first check whether
// current prefix is in dictionary. Then we
// recursively check for remaining string
// str.substr(i, size-i) which is suffix of
// length size-i
if (dictionaryContains( str.substr(0, i) ) &&
wordBreak( str.substr(i, size-i) ))
return true;
}
// If we have tried all prefixes and
// none of them worked
return false;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
wordBreak("ilikesamsung")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("iiiiiiii")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmango")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmangok")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.*;
// Recursive implementation of
// word break problem in java
public class WordBreakProblem
{
// set to hold dictionary values
private static Set dictionary = new HashSet<>();
public static void main(String []args)
{
// array of strings to be added in dictionary set.
String temp_dictionary[] = {"mobile","samsung","sam","sung",
"man","mango","icecream","and",
"go","i","like","ice","cream"};
// loop to add all strings in dictionary set
for (String temp :temp_dictionary)
{
dictionary.add(temp);
}
// sample input cases
System.out.println(wordBreak("ilikesamsung"));
System.out.println(wordBreak("iiiiiiii"));
System.out.println(wordBreak(""));
System.out.println(wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii"));
System.out.println(wordBreak("samsungandmango"));
System.out.println(wordBreak("samsungandmangok"));
}
// returns true if the word can be segmented into parts such
// that each part is contained in dictionary
public static boolean wordBreak(String word)
{
int size = word.length();
// base case
if (size == 0)
return true;
//else check for all words
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
{
// Now we will first divide the word into two parts ,
// the prefix will have a length of i and check if it is
// present in dictionary ,if yes then we will check for
// suffix of length size-i recursively. if both prefix and
// suffix are present the word is found in dictionary.
if (dictionary.contains(word.substring(0,i)) &&
wordBreak(word.substring(i,size)))
return true;
}
// if all cases failed then return false
return false;
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sparsh Singhal
输出
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
动态编程
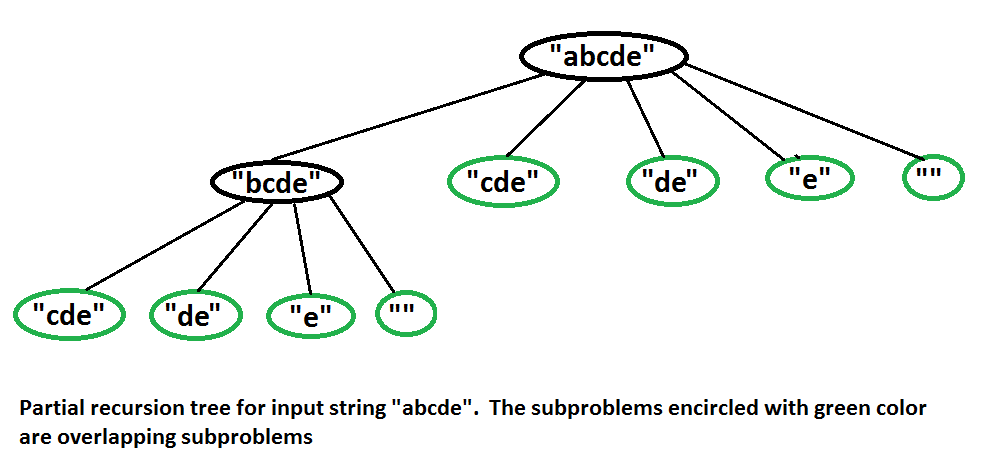
为什么要动态编程?上述问题表现出重叠的子问题。例如,在最坏的情况下,请参见以下字符串“ abcde”的部分递归树。
CPP
// A Dynamic Programming based program to test whether a given string can
// be segmented into space separated words in dictionary
#include
#include
using namespace std;
/* A utility function to check whether a word is present in dictionary or not.
An array of strings is used for dictionary. Using array of strings for
dictionary is definitely not a good idea. We have used for simplicity of
the program*/
int dictionaryContains(string word)
{
string dictionary[] = {"mobile","samsung","sam","sung","man","mango",
"icecream","and","go","i","like","ice","cream"};
int size = sizeof(dictionary)/sizeof(dictionary[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (dictionary[i].compare(word) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns true if string can be segmented into space separated
// words, otherwise returns false
bool wordBreak(string str)
{
int size = str.size();
if (size == 0) return true;
// Create the DP table to store results of subroblems. The value wb[i]
// will be true if str[0..i-1] can be segmented into dictionary words,
// otherwise false.
bool wb[size+1];
memset(wb, 0, sizeof(wb)); // Initialize all values as false.
for (int i=1; i<=size; i++)
{
// if wb[i] is false, then check if current prefix can make it true.
// Current prefix is "str.substr(0, i)"
if (wb[i] == false && dictionaryContains( str.substr(0, i) ))
wb[i] = true;
// wb[i] is true, then check for all substrings starting from
// (i+1)th character and store their results.
if (wb[i] == true)
{
// If we reached the last prefix
if (i == size)
return true;
for (int j = i+1; j <= size; j++)
{
// Update wb[j] if it is false and can be updated
// Note the parameter passed to dictionaryContains() is
// substring starting from index 'i' and length 'j-i'
if (wb[j] == false && dictionaryContains( str.substr(i, j-i) ))
wb[j] = true;
// If we reached the last character
if (j == size && wb[j] == true)
return true;
}
}
}
/* Uncomment these lines to print DP table "wb[]"
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
cout << " " << wb[i]; */
// If we have tried all prefixes and none of them worked
return false;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
wordBreak("ilikesamsung")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("iiiiiiii")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmango")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmangok")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
输出
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
优化的动态规划:
用这种方法,除了dp表外,我们还维护所有早先匹配的索引。然后,我们将检查从那些索引到当前索引的子字符串。如果任何一个匹配,那么我们可以将字符串除以该索引。
在此程序中,我们使用了一些额外的空间。但是,其时间复杂度为O(n * s),其中s是字典中最大字符串的长度,n是给定字符串的长度。
CPP
// A Dynamic Programming based program to test
// whether a given string can be segmented into
// space separated words in dictionary
#include
using namespace std;
/* A utility function to check whether a word
is present in dictionary or not. An array of
strings is used for dictionary. Using array
of strings for dictionary is definitely not
a good idea. We have used for simplicity of
the program*/
int dictionaryContains(string word)
{
string dictionary[]
= { "mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man",
"mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i",
"like", "ice", "cream" };
int size = sizeof(dictionary) / sizeof(dictionary[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (dictionary[i].compare(word) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns true if string can be segmented into space
// separated words, otherwise returns false
bool wordBreak(string s)
{
int n = s.size();
if (n == 0)
return true;
// Create the DP table to store results of subroblems.
// The value dp[i] will be true if str[0..i] can be
// segmented into dictionary words, otherwise false.
vector dp(n + 1, 0); // Initialize all values
// as false.
// matched_index array represents the indexes for which
// dp[i] is true. Initially only -1 element is present
// in this array.
vector matched_index;
matched_index.push_back(-1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int msize = matched_index.size();
// Flag value which tells that a substring matches
// with given words or not.
int f = 0;
// Check all the substring from the indexes matched
// earlier. If any of that substring matches than
// make flag value = 1;
for (int j = msize - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
// sb is substring starting from
// matched_index[j]
// + 1 and of length i - matched_index[j]
string sb = s.substr(matched_index[j] + 1,
i - matched_index[j]);
if (dictionaryContains(sb)) {
f = 1;
break;
}
}
// If substring matches than do dp[i] = 1 and
// push that index in matched_index array.
if (f == 1) {
dp[i] = 1;
matched_index.push_back(i);
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
wordBreak("ilikesamsung") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("iiiiiiii") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("") ? cout << "Yes\n" : cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmango") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmangok") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
输出
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
两指针方法:
这个想法很简单。我们采用两个索引(i,j)– i指向当前段的起点,j指向终点。迭代j直到找到字典中存在的子字符串。现在将i标记在位置j处,并重复第二步并更新当前片段。另外,请继续计算分段字符,以确认成功进行WORD BREAK。
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// 2-pointer Approach of Word Break Problem
class GFG {
// The solution function
public static int wordBreak(String A,
ArrayList B)
{
// store two pointers to start with
int i = 0, j = 1;
// store the length of the String to be segmented
int n = A.length();
// this is a counter to count the characters after
// each successful segment by successful we mean
// that is present in the List B
int totalSegmented = 0;
// iterate through the string A with pointer j
while (j <= n) {
// check whether the current segment is present
// in List B
if (B.contains(A.substring(i, j))) {
// count the characters segmented so far
totalSegmented += j - i;
// store the start of next segment(the
// pointer i) and keep incrementing the
// pointer j
i = j;
j++;
}
// the case when current segment is not present
// in List B, we need continue incrementing
// pointer-j
else {
j++;
}
}
// If the string was successfully segmented, the
// total segmented characters must be equal to total
// string length
if (totalSegmented == A.length())
return 1;
// If the segmented characters were not equal to
// String's length, we need to output zero
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Store the given list of words
ArrayList dictionary
= new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(
"mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man",
"mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i",
"like", "ice", "cream"));
String segmentThis = "ilike";
// Calling the function to check a word break is
// possible
if (wordBreak(segmentThis, dictionary) == 1)
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
} // contributed by shivendr7
输出
Yes
对于上面的代码:时间复杂度: O(n 2 )和空间复杂度: O(1)
断字问题| (Trie解决方案)
锻炼:
上述解决方案仅找出给定字符串是否可以分段。扩展上述动态编程解决方案以打印输入字符串的所有可能分区。
例子:
Input: ilikeicecreamandmango
Output:
i like ice cream and man go
i like ice cream and mango
i like icecream and man go
i like icecream and mango
Input: ilikesamsungmobile
Output:
i like sam sung mobile
i like samsung mobile