分区问题是确定给定集合是否可以划分为两个子集,以使两个子集中的元素之和相同。
例子:
arr[] = {1, 5, 11, 5}
Output: true
The array can be partitioned as {1, 5, 5} and {11}
arr[] = {1, 5, 3}
Output: false
The array cannot be partitioned into equal sum sets.我们强烈建议您单击此处并进行实践,然后再继续解决方案。
以下是解决此问题的两个主要步骤:
1)计算数组的和。如果sum为奇数,则不能有两个子集具有相等的sum,因此返回false。
2)如果数组元素的总和为偶数,则计算sum / 2并找到sum等于sum / 2的数组子集。
第一步很简单。第二步至关重要,可以使用递归或动态编程来解决。
递归解决方案
以下是上述第二步的递归属性。
Let isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum/2) be the function that returns true if
there is a subset of arr[0..n-1] with sum equal to sum/2
The isSubsetSum problem can be divided into two subproblems
a) isSubsetSum() without considering last element
(reducing n to n-1)
b) isSubsetSum considering the last element
(reducing sum/2 by arr[n-1] and n to n-1)
If any of the above the above subproblems return true, then return true.
isSubsetSum (arr, n, sum/2) = isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum/2) ||
isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum/2 - arr[n-1])下面是上述代码的实现:
C++
// A recursive C++ program for partition problem
#include
using namespace std;
// A utility function that returns true if there is
// a subset of arr[] with sun equal to given sum
bool isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum)
{
// Base Cases
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
// If last element is greater than sum, then
// ignore it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements in array
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
// with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// Find if there is subset with sum equal to
// half of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
cout << "Can be divided into two subsets "
"of equal sum";
else
cout << "Can not be divided into two subsets"
" of equal sum";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
// A recursive C program for partition problem
#include
#include
// A utility function that returns true if there is
// a subset of arr[] with sun equal to given sum
bool isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum)
{
// Base Cases
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
// If last element is greater than sum, then
// ignore it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements in array
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
// with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// Find if there is subset with sum equal to
// half of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
printf("Can be divided into two subsets "
"of equal sum");
else
printf("Can not be divided into two subsets"
" of equal sum");
return 0;
} Java
// A recursive Java solution for partition problem
import java.io.*;
class Partition {
// A utility function that returns true if there is a
// subset of arr[] with sun equal to given sum
static boolean isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum)
{
// Base Cases
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
// If last element is greater than sum, then ignore
// it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
static boolean findPartition(int arr[], int n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements in array
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
// with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// Find if there is subset with sum equal to half
// of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = arr.length;
// Function call
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
System.out.println("Can be divided into two "
+ "subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println(
"Can not be divided into "
+ "two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Devesh Agrawal */Python3
# A recursive Python3 program for
# partition problem
# A utility function that returns
# true if there is a subset of
# arr[] with sun equal to given sum
def isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum):
# Base Cases
if sum == 0:
return True
if n == 0 and sum != 0:
return False
# If last element is greater than sum, then
# ignore it
if arr[n-1] > sum:
return isSubsetSum(arr, n-1, sum)
''' else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element'''
return isSubsetSum(arr, n-1, sum) or isSubsetSum(arr, n-1, sum-arr[n-1])
# Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
# subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
def findPartion(arr, n):
# Calculate sum of the elements in array
sum = 0
for i in range(0, n):
sum += arr[i]
# If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
# with equal sum
if sum % 2 != 0:
return false
# Find if there is subset with sum equal to
# half of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum // 2)
# Driver code
arr = [3, 1, 5, 9, 12]
n = len(arr)
# Function call
if findPartion(arr, n) == True:
print("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
else:
print("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
# This code is contributed by shreyanshi_arun.C#
// A recursive C# solution for partition problem
using System;
class GFG {
// A utility function that returns true if there is a
// subset of arr[] with sun equal to given sum
static bool isSubsetSum(int[] arr, int n, int sum)
{
// Base Cases
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
// If last element is greater than sum, then ignore
// it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
static bool findPartition(int[] arr, int n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements in array
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
// with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// Find if there is subset with sum equal to half
// of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = arr.Length;
// Function call
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
Console.Write("Can be divided into two "
+ "subsets of equal sum");
else
Console.Write("Can not be divided into "
+ "two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007PHP
$sum)
return isSubsetSum ($arr, $n - 1, $sum);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained
by any of the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
return isSubsetSum ($arr, $n - 1, $sum) ||
isSubsetSum ($arr, $n - 1,
$sum - $arr[$n - 1]);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
function findPartiion ($arr, $n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements
// in array
$sum = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
$sum += $arr[$i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be
// two subsets with equal sum
if ($sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// Find if there is subset with sum
// equal to half of total sum
return isSubsetSum ($arr, $n, $sum / 2);
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(3, 1, 5, 9, 12);
$n = count($arr);
// Function call
if (findPartiion($arr, $n) == true)
echo "Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum";
else
echo "Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum";
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
?>C++
// A Dynamic Programming based
// C++ program to partition problem
#include
using namespace std;
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool part[sum / 2 + 1][n + 1];
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column,
// except part[0][0], as 0
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i][0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j] = part[i][j]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
/* // uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
cout< C
// A Dynamic Programming based C program to partition
// problem
#include
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two subsets
// of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool part[sum / 2 + 1][n + 1];
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column, except part[0][0], as 0
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i][0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j] = part[i][j]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
/* // uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
printf ("%4d", part[i][j]);
printf("\n");
} */
return part[sum / 2][n];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
printf(
"Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else
printf("Can not be divided into two subsets of "
"equal sum");
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
// A dynamic programming based Java program for partition
// problem
import java.io.*;
class Partition {
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
static boolean findPartition(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
boolean part[][] = new boolean[sum / 2 + 1][n + 1];
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column, except part[0][0], as
// 0
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i][0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j]
= part[i][j]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
/* // uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
printf ("%4d", part[i][j]);
printf("\n");
} */
return part[sum / 2][n];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.length;
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
System.out.println(
"Can be divided into two " "subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println(
"Can not be divided into" " two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Devesh Agrawal */Python3
# Dynamic Programming based python
# program to partition problem
# Returns true if arr[] can be
# partitioned in two subsets of
# equal sum, otherwise false
def findPartition(arr, n):
sum = 0
i, j = 0, 0
# calculate sum of all elements
for i in range(n):
sum += arr[i]
if sum % 2 != 0:
return false
part = [[True for i in range(n + 1)]
for j in range(sum // 2 + 1)]
# initialize top row as true
for i in range(0, n + 1):
part[0][i] = True
# initialize leftmost column,
# except part[0][0], as 0
for i in range(1, sum // 2 + 1):
part[i][0] = False
# fill the partition table in
# bottom up manner
for i in range(1, sum // 2 + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1]
if i >= arr[j - 1]:
part[i][j] = (part[i][j] or
part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1])
return part[sum // 2][n]
# Driver Code
arr = [3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1]
n = len(arr)
# Function call
if findPartition(arr, n) == True:
print("Can be divided into two",
"subsets of equal sum")
else:
print("Can not be divided into ",
"two subsets of equal sum")
# This code is contributed
# by mohit kumar 29C#
// A dynamic programming based C# program
// for partition problem
using System;
class GFG {
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise
// false
static bool findPartition(int[] arr, int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool[, ] part = new bool[sum / 2 + 1, n + 1];
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0, i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column, except
// part[0][0], as 0
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i, 0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom
// up manner
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i, j] = part[i, j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i, j]
= part[i, j - 1]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1], j - 1];
}
}
/* // uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
printf ("%4d", part[i][j]);
printf("\n");
} */
return part[sum / 2, n];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.Length;
// Function call
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
Console.Write("Can be divided"
+ " into two subsets of"
+ " equal sum");
else
Console.Write("Can not be "
+ "divided into two subsets"
+ " of equal sum");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007.C++
// A Dynamic Programming based
// C++ program to partition problem
#include
using namespace std;
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool part[sum / 2 + 1];
// Initialze the part array
// as 0
for (i = 0; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
part[i] = 0;
}
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// the element to be included
// in the sum cannot be
// greater than the sum
for (j = sum / 2; j >= arr[i];
j--) { // check if sum - arr[i]
// could be formed
// from a subset
// using elements
// before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == 1 || j == arr[i])
part[j] = 1;
}
}
return part[sum / 2];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
cout << "Can be divided into two subsets of equal "
"sum";
else
cout << "Can not be divided into"
<< " two subsets of equal sum";
return 0;
} Java
// A Dynamic Programming based
// Java program to partition problem
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
public static boolean findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
boolean[] part = new boolean[sum / 2 + 1];
// Initialze the part array
// as 0
for(i = 0; i <= sum / 2; i++)
{
part[i] = false;
}
// Fill the partition table in
// bottom up manner
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// The element to be included
// in the sum cannot be
// greater than the sum
for(j = sum / 2; j >= arr[i]; j--)
{
// Check if sum - arr[i] could be
// formed from a subset using elements
// before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == true || j == arr[i])
part[j] = true;
}
}
return part[sum / 2];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 };
int n = 6;
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
System.out.println("Can be divided into two " +
"subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println("Can not be divided into " +
"two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
// This code is contributed by RohitOberoiPython3
# A Dynamic Programming based
# Python3 program to partition problem
# Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
# in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
def findPartiion(arr, n) :
Sum = 0
# Calculate sum of all elements
for i in range(n) :
Sum += arr[i]
if (Sum % 2 != 0) :
return 0
part = [0] * ((Sum // 2) + 1)
# Initialze the part array as 0
for i in range((Sum // 2) + 1) :
part[i] = 0
# Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for i in range(n) :
# the element to be included
# in the sum cannot be
# greater than the sum
for j in range(Sum // 2, arr[i] - 1, -1) :
# check if sum - arr[i]
# could be formed
# from a subset
# using elements
# before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == 1 or j == arr[i]) :
part[j] = 1
return part[Sum // 2]
# Drive code
arr = [ 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 ]
n = len(arr)
# Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == 1) :
print("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
else :
print("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
# This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07C#
// A Dynamic Programming based
// C# program to partition problem
using System;
class GFG
{
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
static bool findPartiion(int[] arr, int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool[] part = new bool[sum / 2 + 1];
// Initialze the part array
// as 0
for(i = 0; i <= sum / 2; i++)
{
part[i] = false;
}
// Fill the partition table in
// bottom up manner
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// The element to be included
// in the sum cannot be
// greater than the sum
for(j = sum / 2; j >= arr[i]; j--)
{
// Check if sum - arr[i] could be
// formed from a subset using elements
// before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == true || j == arr[i])
part[j] = true;
}
}
return part[sum / 2];
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 };
int n = 6;
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
Console.WriteLine("Can be divided into two " +
"subsets of equal sum");
else
Console.WriteLine("Can not be divided into " +
"two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019Javascript
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum时间复杂度: O(2 ^ n)在最坏的情况下,此解决方案为每个元素尝试两种可能性(无论是包含还是排除)。
动态编程解决方案
当元素之和不太大时,可以使用动态编程解决该问题。我们可以创建一个大小为(sum / 2 + 1)*(n + 1)的2D数组part [] []。并且我们可以以自下而上的方式构造解决方案,以使每个填充的条目都具有以下属性
part[i][j] = true if a subset of {arr[0], arr[1], ..arr[j-1]} has sum
equal to i, otherwise falseC++
// A Dynamic Programming based
// C++ program to partition problem
#include
using namespace std;
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool part[sum / 2 + 1][n + 1];
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column,
// except part[0][0], as 0
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i][0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j] = part[i][j]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
/* // uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
cout< C
// A Dynamic Programming based C program to partition
// problem
#include
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two subsets
// of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool part[sum / 2 + 1][n + 1];
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column, except part[0][0], as 0
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i][0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j] = part[i][j]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
/* // uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
printf ("%4d", part[i][j]);
printf("\n");
} */
return part[sum / 2][n];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
printf(
"Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else
printf("Can not be divided into two subsets of "
"equal sum");
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// A dynamic programming based Java program for partition
// problem
import java.io.*;
class Partition {
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
static boolean findPartition(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
boolean part[][] = new boolean[sum / 2 + 1][n + 1];
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column, except part[0][0], as
// 0
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i][0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j]
= part[i][j]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
/* // uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
printf ("%4d", part[i][j]);
printf("\n");
} */
return part[sum / 2][n];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.length;
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
System.out.println(
"Can be divided into two " "subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println(
"Can not be divided into" " two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Devesh Agrawal */
Python3
# Dynamic Programming based python
# program to partition problem
# Returns true if arr[] can be
# partitioned in two subsets of
# equal sum, otherwise false
def findPartition(arr, n):
sum = 0
i, j = 0, 0
# calculate sum of all elements
for i in range(n):
sum += arr[i]
if sum % 2 != 0:
return false
part = [[True for i in range(n + 1)]
for j in range(sum // 2 + 1)]
# initialize top row as true
for i in range(0, n + 1):
part[0][i] = True
# initialize leftmost column,
# except part[0][0], as 0
for i in range(1, sum // 2 + 1):
part[i][0] = False
# fill the partition table in
# bottom up manner
for i in range(1, sum // 2 + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1]
if i >= arr[j - 1]:
part[i][j] = (part[i][j] or
part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1])
return part[sum // 2][n]
# Driver Code
arr = [3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1]
n = len(arr)
# Function call
if findPartition(arr, n) == True:
print("Can be divided into two",
"subsets of equal sum")
else:
print("Can not be divided into ",
"two subsets of equal sum")
# This code is contributed
# by mohit kumar 29
C#
// A dynamic programming based C# program
// for partition problem
using System;
class GFG {
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise
// false
static bool findPartition(int[] arr, int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool[, ] part = new bool[sum / 2 + 1, n + 1];
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0, i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column, except
// part[0][0], as 0
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i, 0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom
// up manner
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i, j] = part[i, j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i, j]
= part[i, j - 1]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1], j - 1];
}
}
/* // uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
printf ("%4d", part[i][j]);
printf("\n");
} */
return part[sum / 2, n];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.Length;
// Function call
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
Console.Write("Can be divided"
+ " into two subsets of"
+ " equal sum");
else
Console.Write("Can not be "
+ "divided into two subsets"
+ " of equal sum");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007.
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum下图显示了分区表中的值。
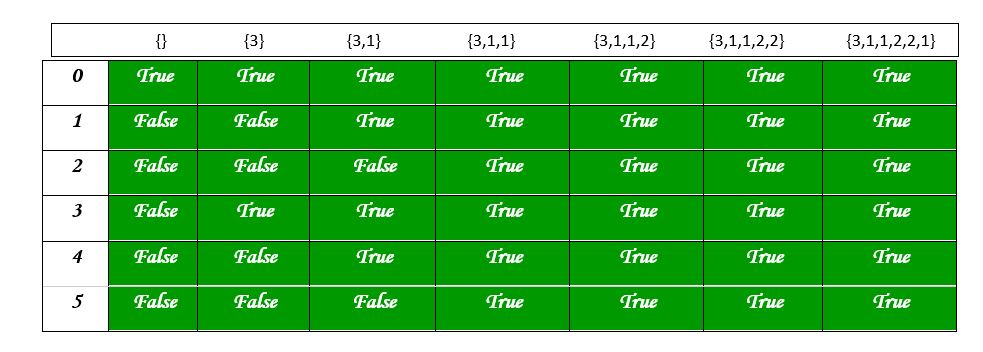
时间复杂度: O(sum * n)
辅助空间: O(sum * n)
请注意,这种解决方案不适用于总和较大的阵列。
动态编程解决方案(优化了空间复杂性)
代替创建大小为(sum / 2 + 1)*(n + 1)的二维数组,我们可以仅使用大小为(sum / 2 + 1)的数组解决此问题。
part[j] = true if there is a subset with sum equal to j, otherwise false.
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// A Dynamic Programming based
// C++ program to partition problem
#include
using namespace std;
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool part[sum / 2 + 1];
// Initialze the part array
// as 0
for (i = 0; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
part[i] = 0;
}
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// the element to be included
// in the sum cannot be
// greater than the sum
for (j = sum / 2; j >= arr[i];
j--) { // check if sum - arr[i]
// could be formed
// from a subset
// using elements
// before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == 1 || j == arr[i])
part[j] = 1;
}
}
return part[sum / 2];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
cout << "Can be divided into two subsets of equal "
"sum";
else
cout << "Can not be divided into"
<< " two subsets of equal sum";
return 0;
}
Java
// A Dynamic Programming based
// Java program to partition problem
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
public static boolean findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
boolean[] part = new boolean[sum / 2 + 1];
// Initialze the part array
// as 0
for(i = 0; i <= sum / 2; i++)
{
part[i] = false;
}
// Fill the partition table in
// bottom up manner
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// The element to be included
// in the sum cannot be
// greater than the sum
for(j = sum / 2; j >= arr[i]; j--)
{
// Check if sum - arr[i] could be
// formed from a subset using elements
// before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == true || j == arr[i])
part[j] = true;
}
}
return part[sum / 2];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 };
int n = 6;
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
System.out.println("Can be divided into two " +
"subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println("Can not be divided into " +
"two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
// This code is contributed by RohitOberoi
Python3
# A Dynamic Programming based
# Python3 program to partition problem
# Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
# in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
def findPartiion(arr, n) :
Sum = 0
# Calculate sum of all elements
for i in range(n) :
Sum += arr[i]
if (Sum % 2 != 0) :
return 0
part = [0] * ((Sum // 2) + 1)
# Initialze the part array as 0
for i in range((Sum // 2) + 1) :
part[i] = 0
# Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for i in range(n) :
# the element to be included
# in the sum cannot be
# greater than the sum
for j in range(Sum // 2, arr[i] - 1, -1) :
# check if sum - arr[i]
# could be formed
# from a subset
# using elements
# before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == 1 or j == arr[i]) :
part[j] = 1
return part[Sum // 2]
# Drive code
arr = [ 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 ]
n = len(arr)
# Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == 1) :
print("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
else :
print("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
# This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07
C#
// A Dynamic Programming based
// C# program to partition problem
using System;
class GFG
{
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
static bool findPartiion(int[] arr, int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool[] part = new bool[sum / 2 + 1];
// Initialze the part array
// as 0
for(i = 0; i <= sum / 2; i++)
{
part[i] = false;
}
// Fill the partition table in
// bottom up manner
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// The element to be included
// in the sum cannot be
// greater than the sum
for(j = sum / 2; j >= arr[i]; j--)
{
// Check if sum - arr[i] could be
// formed from a subset using elements
// before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == true || j == arr[i])
part[j] = true;
}
}
return part[sum / 2];
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 };
int n = 6;
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
Console.WriteLine("Can be divided into two " +
"subsets of equal sum");
else
Console.WriteLine("Can not be divided into " +
"two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019
Java脚本
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum时间复杂度: O(sum * n)
辅助空间:O(sum)
请注意,这种解决方案不适用于总和较大的阵列。
参考:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Partition_problem