背景
Bitonic Sort是经典的并行排序算法。
- 双音排序进行O(n Log 2 n)比较。
- 通过Bitonic排序完成的比较次数比像Merge Sort [做O(nLogn)比较]这样的流行排序算法要多,但是Bitonice排序更适合并行实现,因为我们总是按预定义的顺序比较元素,并且比较顺序不会取决于数据。因此,它适合在硬件和并行处理器阵列中实施。
- 如果要排序的元素数为2 ^ n,则必须完成Bitonic排序。如果元素的数量不精确地在上述数量内,则双音序列的程序将失败。
要了解Bitonic排序,我们首先必须了解什么是Bitonic序列以及如何使给定序列为Bitonic。
双音序列
如果序列先增加然后减少,则称为Bitonic。换句话说,如果存在索引i,其中0 <= i <= n-1,则数组arr [0..ni]是Bitonic的
x0 <= x1 …..<= xi and xi >= xi+1….. >= xn-1 - 按升序排序的序列被视为Bitonic,而降序部分为空。类似地,降序序列被认为是Bitonic,升序部分为空。
- 双音序列的旋转也是双音的。
如何从随机输入中形成一个双音序列?
我们从连续的2元素序列中形成4元素双音序列开始。考虑序列x0,x1,x2,x3中的4个元素。我们以升序对x0和x1进行排序,并以降序对x2和x3进行排序。然后,我们将这两对连接起来,形成一个4元素的双音序列。
接下来,我们采用两个4个元素的双音序列,以升序排序,另一个以降序排序(使用我们将在下面讨论的Bitonic排序),依此类推,直到获得双音序列为止。
例子:
将以下序列转换为双音序列:3、7、4、8、6、2、1、5
步骤1 :将每个2个连续元素视为双音序列,并对每个2对元素进行双音排序。下一步,取两个4元素双音序列,依此类推。
![]()
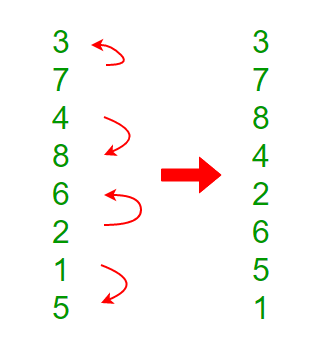
注意: x0和x1以升序排序,x2和x3以降序排序,依此类推
第2步:两个4元素双音序列:比较器长度为2的A (3,7,8,4)和B (2,6,5,1)
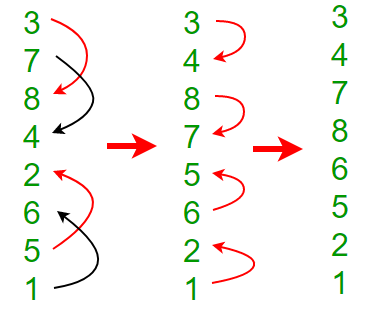
完成此步骤后,我们将获得长度为8的Bitonic序列。
3, 4, 7, 8, 6, 5, 2, 1双音排序
它主要涉及两个步骤。
- 形成一个双音序列(上面已详细讨论)。完成此步骤后,我们进入下图的第四阶段,即数组变为{3,4,7,8,8,6,5,2,1}
- 从重音序列中创建一个排序序列:第一步后,上半部分按升序排序,后半部分按降序排序。
我们将上半部分的第一个元素与下半部分的第一个元素进行比较,然后将上半部分的第二个元素与第二个第二个元素的第二个元素进行比较,依此类推。如果前一半的元素较小,我们将交换元素。
经过上面的比较和交换步骤,我们得到了阵列中的两个双音序列。请参见下图的第五阶段。在第五阶段,我们有{3,4,2,1,6,5,7,8}。如果我们仔细看一下元素,我们会注意到有两个长度为n / 2的双音序列,因此第一个双音序列{3,4,2,1}中的所有元素都小于第二个双音序列的所有元素{6,5,7,8}。
我们在两个双音序列中重复相同的过程,得到四个长度为n / 4的双音序列,这样最左边的双音序列的所有元素都较小,而最右边的所有音元素都更小。参见下图的第六阶段,数组为{2,1,3,4,6,5,5,7,8}。
如果再重复一次此过程,我们将得到8个大小为n / 8的双音序列,即1。由于所有这些双音序列都已排序,并且每个双音序列都有一个元素,因此我们得到了排序后的数组。
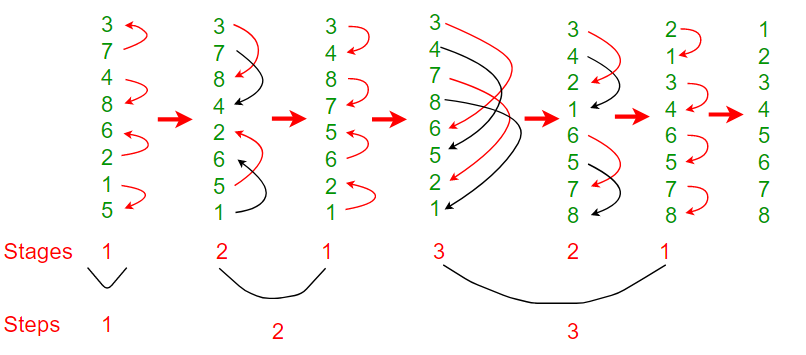
以下是Bitonic Sort的实现。
C++
/* C++ Program for Bitonic Sort. Note that this program
works only when size of input is a power of 2. */
#include
using namespace std;
/*The parameter dir indicates the sorting direction, ASCENDING
or DESCENDING; if (a[i] > a[j]) agrees with the direction,
then a[i] and a[j] are interchanged.*/
void compAndSwap(int a[], int i, int j, int dir)
{
if (dir==(a[i]>a[j]))
swap(a[i],a[j]);
}
/*It recursively sorts a bitonic sequence in ascending order,
if dir = 1, and in descending order otherwise (means dir=0).
The sequence to be sorted starts at index position low,
the parameter cnt is the number of elements to be sorted.*/
void bitonicMerge(int a[], int low, int cnt, int dir)
{
if (cnt>1)
{
int k = cnt/2;
for (int i=low; i1)
{
int k = cnt/2;
// sort in ascending order since dir here is 1
bitonicSort(a, low, k, 1);
// sort in descending order since dir here is 0
bitonicSort(a, low+k, k, 0);
// Will merge wole sequence in ascending order
// since dir=1.
bitonicMerge(a,low, cnt, dir);
}
}
/* Caller of bitonicSort for sorting the entire array of
length N in ASCENDING order */
void sort(int a[], int N, int up)
{
bitonicSort(a,0, N, up);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int a[]= {3, 7, 4, 8, 6, 2, 1, 5};
int N = sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);
int up = 1; // means sort in ascending order
sort(a, N, up);
printf("Sorted array: \n");
for (int i=0; i Java
/* Java program for Bitonic Sort. Note that this program
works only when size of input is a power of 2. */
public class BitonicSort
{
/* The parameter dir indicates the sorting direction,
ASCENDING or DESCENDING; if (a[i] > a[j]) agrees
with the direction, then a[i] and a[j] are
interchanged. */
void compAndSwap(int a[], int i, int j, int dir)
{
if ( (a[i] > a[j] && dir == 1) ||
(a[i] < a[j] && dir == 0))
{
// Swapping elements
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
/* It recursively sorts a bitonic sequence in ascending
order, if dir = 1, and in descending order otherwise
(means dir=0). The sequence to be sorted starts at
index position low, the parameter cnt is the number
of elements to be sorted.*/
void bitonicMerge(int a[], int low, int cnt, int dir)
{
if (cnt>1)
{
int k = cnt/2;
for (int i=low; i1)
{
int k = cnt/2;
// sort in ascending order since dir here is 1
bitonicSort(a, low, k, 1);
// sort in descending order since dir here is 0
bitonicSort(a,low+k, k, 0);
// Will merge wole sequence in ascending order
// since dir=1.
bitonicMerge(a, low, cnt, dir);
}
}
/*Caller of bitonicSort for sorting the entire array
of length N in ASCENDING order */
void sort(int a[], int N, int up)
{
bitonicSort(a, 0, N, up);
}
/* A utility function to print array of size n */
static void printArray(int arr[])
{
int n = arr.length;
for (int i=0; i Python
# Python program for Bitonic Sort. Note that this program
# works only when size of input is a power of 2.
# The parameter dir indicates the sorting direction, ASCENDING
# or DESCENDING; if (a[i] > a[j]) agrees with the direction,
# then a[i] and a[j] are interchanged.*/
def compAndSwap(a, i, j, dire):
if (dire==1 and a[i] > a[j]) or (dire==0 and a[i] < a[j]):
a[i],a[j] = a[j],a[i]
# It recursively sorts a bitonic sequence in ascending order,
# if dir = 1, and in descending order otherwise (means dir=0).
# The sequence to be sorted starts at index position low,
# the parameter cnt is the number of elements to be sorted.
def bitonicMerge(a, low, cnt, dire):
if cnt > 1:
k = cnt/2
for i in range(low , low+k):
compAndSwap(a, i, i+k, dire)
bitonicMerge(a, low, k, dire)
bitonicMerge(a, low+k, k, dire)
# This funcion first produces a bitonic sequence by recursively
# sorting its two halves in opposite sorting orders, and then
# calls bitonicMerge to make them in the same order
def bitonicSort(a, low, cnt,dire):
if cnt > 1:
k = cnt/2
bitonicSort(a, low, k, 1)
bitonicSort(a, low+k, k, 0)
bitonicMerge(a, low, cnt, dire)
# Caller of bitonicSort for sorting the entire array of length N
# in ASCENDING order
def sort(a,N, up):
bitonicSort(a,0, N, up)
# Driver code to test above
a = [3, 7, 4, 8, 6, 2, 1, 5]
n = len(a)
up = 1
sort(a, n, up)
print ("\n\nSorted array is")
for i in range(n):
print("%d" %a[i]),C#
/* C# Program for Bitonic Sort. Note that this program
works only when size of input is a power of 2. */
using System;
/*The parameter dir indicates the sorting direction, ASCENDING
or DESCENDING; if (a[i] > a[j]) agrees with the direction,
then a[i] and a[j] are interchanged.*/
class GFG
{
/* To swap values */
static void Swap(ref T lhs, ref T rhs)
{
T temp;
temp = lhs;
lhs = rhs;
rhs = temp;
}
public static void compAndSwap(int[] a, int i, int j, int dir)
{
int k;
if((a[i]>a[j]))
k=1;
else
k=0;
if (dir==k)
Swap(ref a[i],ref a[j]);
}
/*It recursively sorts a bitonic sequence in ascending order,
if dir = 1, and in descending order otherwise (means dir=0).
The sequence to be sorted starts at index position low,
the parameter cnt is the number of elements to be sorted.*/
public static void bitonicMerge(int[] a, int low, int cnt, int dir)
{
if (cnt>1)
{
int k = cnt/2;
for (int i=low; i1)
{
int k = cnt/2;
// sort in ascending order since dir here is 1
bitonicSort(a, low, k, 1);
// sort in descending order since dir here is 0
bitonicSort(a, low+k, k, 0);
// Will merge wole sequence in ascending order
// since dir=1.
bitonicMerge(a,low, cnt, dir);
}
}
/* Caller of bitonicSort for sorting the entire array of
length N in ASCENDING order */
public static void sort(int[] a, int N, int up)
{
bitonicSort(a,0, N, up);
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int[] a= {3, 7, 4, 8, 6, 2, 1, 5};
int N = a.Length;
int up = 1; // means sort in ascending order
sort(a, N, up);
Console.Write("Sorted array: \n");
for (int i=0; i 输出:
Sorted array:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8双音排序的分析
为了从长度为n / 2的两个排序序列中形成长度为n的排序序列,需要进行log(n)比较(例如:当序列大小时log(8)=3。因此,比较的次数T(n)为整个排序如下:
T(n)= log(n)+ T(n / 2)
这个递归方程的解是
T(n)= log(n)+ log(n)-1 + log(n)-2 +…+ 1 = log(n)·(log(n)+1)/ 2
因为,分类网络的每个阶段都由n / 2个比较器组成。因此共有?(n log 2 n)个比较器。
参考:
1. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GEQ8y26blEY
2. http://www.iti.fh-flensburg.de/lang/algorithmen/sortieren/bitonic/bitonicen.htm
3. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bitonic_sorter