给定一个二维数组, arr[][]表示二维空间上N个顶点的坐标列表,该列表已经按 x 坐标和 y 坐标排序,任务是找到从最左边开始的游览的最小距离顶点,严格地向右走,然后在到达最右边的顶点时,游览严格地从右到左回到起始顶点。
例子:
Input: N = 7, arr[][] = {{0, 6}, {1 0}, {2 3}, {5 4}, {6 1}, {7 5}, {8 2}}
Output: 25.582
Explanation:
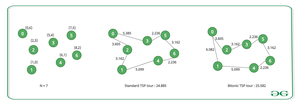
The TSP tour: 0-3-5-6-4-1-2-0 is not a Bitonic TSP tour because although the tour initially goes from left to right (0-3-5-6) and then goes back from right to left (6-4-1), it then makes another left to right (1-2) and then right to left (2-0) steps.
The tour: 0-2-3-5-6-4-1-0 is a valid Bitonic TSP tour because it can be decomposed into two paths: 0-2-3-5-6 that goes from left to right and 6-4-1-0 that goes back from right to left.
Input: N = 3, arr[][] = {{1, 1}, {2, 3}, {3, 1}}
Output: 6.47
方法:上述问题可以使用动态规划解决。为了便于理解,问题可以改成两个人。两者都应该同时从最左边的点开始。沿着两条不同的路径走,最后到达最右边的点,除了起点和终点。
- 每一点碰巧被一个人通过。这里, dp[i][j]表示第一个人走到i和第二个人走到j 的距离。
- 解中dp[i][j]表示1到max(i,j)都走了,两人当前的位置分别是i和j ,需要走多远。
- 另外,可以推论dp[i][j]等于dp[j][i] ,所以从现在开始规定i总是大于j,即i>j状态。
- 这样,不管那个人,下一步只能去到i+1、i+2、……这些点。
- 因此,状态dp[i][j]只能转移到dp[i+1][j]或dp[i][i+1]。
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 创建一个大小为N*N的二维数组dp[][] 。
- 迭代表的最后一行dp ,并将dp[N-1][i]更新为distance(N-1, N)和distance(i, N) 之和,其中distance(x, y)表示arr 的xth和yth点之间的欧几里德距离。
- 创建一个递归函数findTour(i, j)来填充所有其他单元格
- 将dp[i][j]更新为findTour(i+1, j)+distance(i, i+1)和findTour(i+1, i)+distance(j, i+1) 的最小值。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Size of the array a[]
const int mxN = 1005;
// Structure to store the x and
// y coordinates of a point
struct Coordinates {
double x, y;
} a[mxN];
// Declare a 2-D dp array
float dp[mxN][mxN];
// Function to calculate the
// distance between two points
// in a Euclidian plane
float distance(int i, int j)
{
// Return the distance
return sqrt(
(a[i].x - a[j].x) * (a[i].x - a[j].x)
+ (a[i].y - a[j].y) * (a[i].y - a[j].y));
}
// Utility recursive function to find
// the bitonic tour distance
float findTourDistance(int i, int j)
{
// Memoization
if (dp[i][j] > 0)
return dp[i][j];
// Update dp[i][j]
dp[i][j] = min(
findTourDistance(i + 1, j) + distance(i, i + 1),
findTourDistance(i + 1, i) + distance(j, i + 1));
return dp[i][j];
}
// Function to find the
// bitonic tour distance
void bitonicTSP(int N)
{
// Initialize the dp array
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
// Base Case
for (int j = 1; j < N - 1; j++)
dp[N - 1][j] = distance(N - 1, N)
+ distance(j, N);
// Print the answer
printf("%.2f\n", findTourDistance(1, 1));
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Input
int N = 3;
a[1].x = 1, a[1].y = 1;
a[2].x = 2, a[2].y = 3;
a[3].x = 3, a[3].y = 1;
// Function Call
bitonicTSP(N);
} 6.47时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
辅助空间: O(N 2 )