在Java中声明和初始化二维数组的不同方法
多维数组称为多维数组。最常用的多维数组是 2-D 和 3-D 数组。我们可以说任何高维数组基本上都是数组的数组。二维数组的一个非常常见的例子是国际象棋棋盘。棋盘是一个包含 64 个 1×1 方盒的网格。您可以类似地可视化二维数组。在二维数组中,每个元素都与行号和列号相关联。访问二维数组的任何元素类似于使用行号和列号访问 Excel 文件的记录。 2D 数组在实现井字游戏、国际象棋甚至存储图像像素时很有用。
在Java中声明二维数组:
任何二维数组都可以声明如下:
句法:
data_type array_name[][]; (OR) data_type[][] array_name;- data_type:因为Java是一种静态类型语言(即它期望它的变量在可以被赋值之前被声明)。因此,指定数据类型决定了它将接受的元素类型。例如,仅存储整数值,数据类型将被声明为 int。
- array_name:它是赋予二维数组的名称。例如科目、学生、水果、部门等。
注意:我们可以在 data_type 之后写 [ ][ ] ,也可以在声明二维数组时在 array_name 之后写 [ ][ ] 。
Java
// java program showing declaration of arrays
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] integer2DArray; // 2D integer array
String[][] string2DArray; // 2D String array
double[][] double2DArray; // 2D double array
boolean[][] boolean2DArray; // 2D boolean array
float[][] float2DArray; // 2D float array
double[][] double2DArray; // 2D double array
}
}Java
// java program to initialize a 2D array
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaration along with initialisation
// 2D integer array with 5 rows and 3 columns
// integer array elements are initialised with 0
int[][] integer2DArray = new int[5][3];
System.out.println(
"Default value of int array element: "
+ integer2DArray[0][0]);
// 2D String array with 4 rows and 4 columns
// String array elements are initialised with null
String[][] string2DArray = new String[4][4];
System.out.println(
"Default value of String array element: "
+ string2DArray[0][0]);
// 2D boolean array with 3 rows and 5 columns
// boolean array elements are initialised with false
boolean[][] boolean2DArray = new boolean[4][4];
System.out.println(
"Default value of boolean array element: "
+ boolean2DArray[0][0]);
// 2D char array with 10 rows and 10 columns
// char array elements are initialised with
// '\u0000'(null character)
char[][] char2DArray = new char[10][10];
System.out.println(
"Default value of char array element: "
+ char2DArray[0][0]);
// First declaration and then initialisation
int[][] arr; // declaration
// System.out.println("arr[0][0]: "+ arr[0][0]);
// The above line will throw an error, as we have
// only declared the 2D array, but not initialised
// it.
arr = new int[5][3]; // initialisation
System.out.println("arr[0][0]: " + arr[0][0]);
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// The line below will throw an error, as the first
// dimension(no. of rows) is not specified
int[][] arr = new int[][3];
// The line below will execute without any error, as
// the first dimension(no. of rows) is specified
int[][] arr = new int[2][];
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String[][] subjects = {
{ "Data Structures & Algorithms",
"Programming & Logic", "Software Engineering",
"Theory of Computation" }, // row 1
{ "Thermodynamics", "Metallurgy",
"Machine Drawing",
"Fluid Mechanics" }, // row2
{ "Signals and Systems", "Digital Electronics",
"Power Electronics" } // row3
};
System.out.println(
"Fundamental Subject in Computer Engineering: "
+ subjects[0][0]);
System.out.println(
"Fundamental Subject in Mechanical Engineering: "
+ subjects[1][3]);
System.out.println(
"Fundamental Subject in Electronics Engineering: "
+ subjects[2][1]);
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] scores = new int[2][2];
// Initializing array element at position[0][0],
// i.e. 0th row and 0th column
scores[0][0] = 15;
// Initializing array element at position[0][1],
// i.e. 0th row and 1st column
scores[0][1] = 23;
// Initializing array element at position[1][0],
// i.e. 1st row and 0th column
scores[1][0] = 30;
// Initializing array element at position[1][1],
// i.e. 1st row and 1st column
scores[1][1] = 21;
// printing the array elements individually
System.out.println("scores[0][0] = "
+ scores[0][0]);
System.out.println("scores[0][1] = "
+ scores[0][1]);
System.out.println("scores[1][0] = "
+ scores[1][0]);
System.out.println("scores[1][1] = "
+ scores[1][1]);
// printing 2D array using Arrays.deepToString() method
System.out.println(
"Printing 2D array using Arrays.deepToString() method: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(scores));
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int rows = 80, columns = 5;
int[][] marks = new int[rows][columns];
// initializing the array elements using for loop
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
marks[i][j] = i + j;
}
}
// printing the first three rows of marks array
System.out.println("First three rows are: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
System.out.printf(marks[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// declaring a 2D array with 2 rows
int jagged[][] = new int[2][];
// not specifying the 2nd dimension,
// and making it as jagged array
// first row has 2 columns
jagged[0] = new int[2];
// second row has 2 columns
jagged[1] = new int[4];
// Initializing the array
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < jagged.length; i++) {
// remember to use jagged[i].length instead of
// jagged[0].length, since every row has
// different number of columns
for (int j = 0; j < jagged[i].length; j++) {
jagged[i][j] = count++;
}
}
// printing the values of 2D Jagged array
System.out.println("The values of 2D jagged array");
for (int i = 0; i < jagged.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < jagged[i].length; j++)
System.out.printf(jagged[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] arr1 = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
int[][] arr2 = { { 4, 5, 6 }, { 1, 3, 2 } };
int[][] sum = new int[2][3];
// adding two 2D arrays element-wise
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr1[0].length; j++) {
sum[i][j] = arr1[i][j] + arr2[i][j];
}
}
System.out.println("Resultant 2D array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < sum.length; i++) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sum[i]));
}
}
}Java中二维数组的初始化:
data_type[][] array_Name = new data_type[no_of_rows][no_of_columns];任何二维数组中的总元素将等于 (no_of_rows) * (no_of_columns)。
- no_of_rows:数组可以存储的行数。例如 no_of_rows = 3,那么数组将有三行。
- no_of_columns:数组可以存储的行数。例如 no_of_columns = 4,那么数组将有四列。
上述数组初始化的语法将根据指定的数据类型为所有数组元素分配默认值。
让我们看看初始化二维数组的各种方法:
方法一
Java
// java program to initialize a 2D array
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaration along with initialisation
// 2D integer array with 5 rows and 3 columns
// integer array elements are initialised with 0
int[][] integer2DArray = new int[5][3];
System.out.println(
"Default value of int array element: "
+ integer2DArray[0][0]);
// 2D String array with 4 rows and 4 columns
// String array elements are initialised with null
String[][] string2DArray = new String[4][4];
System.out.println(
"Default value of String array element: "
+ string2DArray[0][0]);
// 2D boolean array with 3 rows and 5 columns
// boolean array elements are initialised with false
boolean[][] boolean2DArray = new boolean[4][4];
System.out.println(
"Default value of boolean array element: "
+ boolean2DArray[0][0]);
// 2D char array with 10 rows and 10 columns
// char array elements are initialised with
// '\u0000'(null character)
char[][] char2DArray = new char[10][10];
System.out.println(
"Default value of char array element: "
+ char2DArray[0][0]);
// First declaration and then initialisation
int[][] arr; // declaration
// System.out.println("arr[0][0]: "+ arr[0][0]);
// The above line will throw an error, as we have
// only declared the 2D array, but not initialised
// it.
arr = new int[5][3]; // initialisation
System.out.println("arr[0][0]: " + arr[0][0]);
}
}
注意:初始化二维数组时,必须始终指定第一维(行数),但可以省略提供第二维(列数)。
在下面的代码片段中,我们没有指定列数。但是, Java编译器足够聪明,可以通过检查列内元素的数量来操纵大小。
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// The line below will throw an error, as the first
// dimension(no. of rows) is not specified
int[][] arr = new int[][3];
// The line below will execute without any error, as
// the first dimension(no. of rows) is specified
int[][] arr = new int[2][];
}
}
您可以使用行号和列号访问二维数组的任何元素。
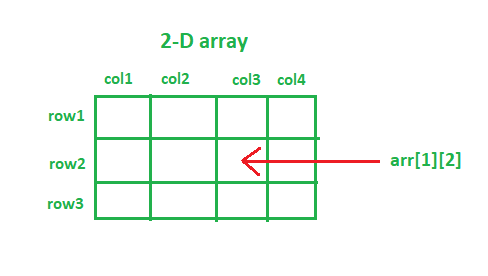
方法二
在下面的代码片段中,我们没有指定行数和列数。但是, Java编译器足够聪明,可以通过检查行和列内的元素数量来操纵大小。
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String[][] subjects = {
{ "Data Structures & Algorithms",
"Programming & Logic", "Software Engineering",
"Theory of Computation" }, // row 1
{ "Thermodynamics", "Metallurgy",
"Machine Drawing",
"Fluid Mechanics" }, // row2
{ "Signals and Systems", "Digital Electronics",
"Power Electronics" } // row3
};
System.out.println(
"Fundamental Subject in Computer Engineering: "
+ subjects[0][0]);
System.out.println(
"Fundamental Subject in Mechanical Engineering: "
+ subjects[1][3]);
System.out.println(
"Fundamental Subject in Electronics Engineering: "
+ subjects[2][1]);
}
}
方法三
此外,我们可以分别初始化数组的每个元素。看看下面的代码片段:
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] scores = new int[2][2];
// Initializing array element at position[0][0],
// i.e. 0th row and 0th column
scores[0][0] = 15;
// Initializing array element at position[0][1],
// i.e. 0th row and 1st column
scores[0][1] = 23;
// Initializing array element at position[1][0],
// i.e. 1st row and 0th column
scores[1][0] = 30;
// Initializing array element at position[1][1],
// i.e. 1st row and 1st column
scores[1][1] = 21;
// printing the array elements individually
System.out.println("scores[0][0] = "
+ scores[0][0]);
System.out.println("scores[0][1] = "
+ scores[0][1]);
System.out.println("scores[1][0] = "
+ scores[1][0]);
System.out.println("scores[1][1] = "
+ scores[1][1]);
// printing 2D array using Arrays.deepToString() method
System.out.println(
"Printing 2D array using Arrays.deepToString() method: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(scores));
}
}
方法四
如果二维数组的大小太大,使用上述方法进行数组初始化将是一项繁琐的任务。在大型二维数组的情况下,有效的方法是使用 for 循环来初始化数组元素。
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int rows = 80, columns = 5;
int[][] marks = new int[rows][columns];
// initializing the array elements using for loop
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
marks[i][j] = i + j;
}
}
// printing the first three rows of marks array
System.out.println("First three rows are: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
System.out.printf(marks[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
我们可以使用 arr。 length 可用于查找行的大小(第一维),而 arr[0].length 可用于查找列的大小(第二维)。
方法 5:(锯齿状数组)
在某些情况下,您可能希望每一行都有不同数量的列。这种类型的数组称为锯齿形数组。
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// declaring a 2D array with 2 rows
int jagged[][] = new int[2][];
// not specifying the 2nd dimension,
// and making it as jagged array
// first row has 2 columns
jagged[0] = new int[2];
// second row has 2 columns
jagged[1] = new int[4];
// Initializing the array
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < jagged.length; i++) {
// remember to use jagged[i].length instead of
// jagged[0].length, since every row has
// different number of columns
for (int j = 0; j < jagged[i].length; j++) {
jagged[i][j] = count++;
}
}
// printing the values of 2D Jagged array
System.out.println("The values of 2D jagged array");
for (int i = 0; i < jagged.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < jagged[i].length; j++)
System.out.printf(jagged[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
执行:
让我们看一个简单的程序来添加两个二维数组:
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] arr1 = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
int[][] arr2 = { { 4, 5, 6 }, { 1, 3, 2 } };
int[][] sum = new int[2][3];
// adding two 2D arrays element-wise
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr1[0].length; j++) {
sum[i][j] = arr1[i][j] + arr2[i][j];
}
}
System.out.println("Resultant 2D array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < sum.length; i++) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sum[i]));
}
}
}