在Java中实现稀疏向量
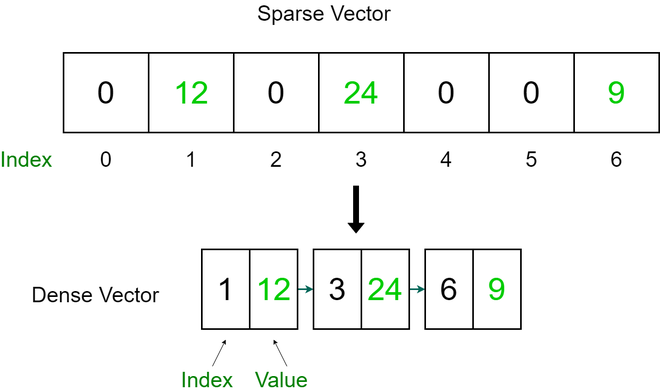
向量或数组列表是一维元素数组。稀疏向量的元素大部分为零值。使用一维数组来存储稀疏向量是低效的。在形成稀疏向量的和时添加值为零的元素也是低效的。我们将一维向量转换为 (index, value) 对的向量。
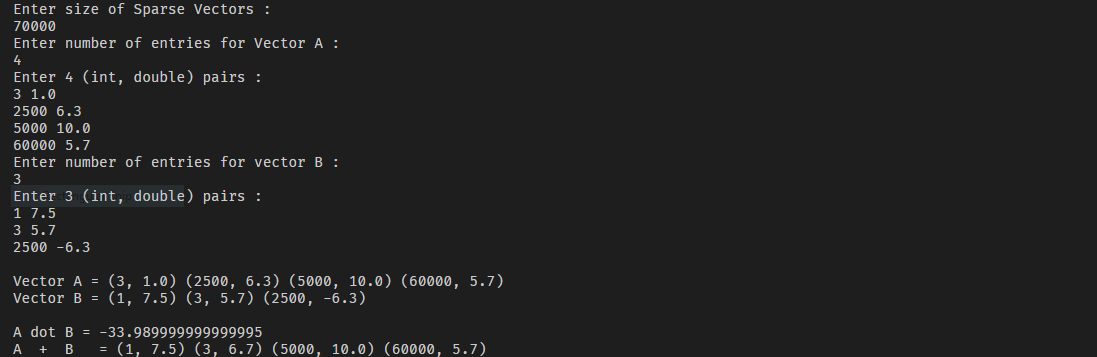
例子
Input:
Enter size of Sparse Vectors :
100
Enter number of entries for Vector A :
5
Enter 5 (int, double) pairs
2 20.0
5 12.2
19 23.1
4 66.0
11 100.0
Enter number of entries for vector B :
5
Enter 5 (int, double) pairs
9 21.0
10 44.5
6 13.22
71 30.0
63 99.0
Output:
Vector A = (2, 20.0) (4, 66.0) (5, 12.2) (11, 100.0) (19, 23.1)
Vector B = (6, 13.22) (9, 21.0) (10, 44.5) (63, 99.0) (71, 30.0)
A dot B = 0.0
A + B = (2, 20.0) (4, 66.0) (5, 12.2) (6, 13.22) (9, 21.0) (10, 44.5) (11, 100.0) (19, 23.1) (63, 99.0) (71, 30.0)方法
为了有效地存储稀疏向量,我们只将向量的非零值与索引一起存储。 pair 的第一个元素将是稀疏向量元素(非零)的索引,第二个元素将是实际元素。
我们使用 TreeMap 作为索引值对的向量。使用 TreeMap 的优点是,地图根据其键的自然顺序进行排序。这被证明是一种排序和存储键值对的有效方法。
执行
Java
// importing generic packages
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class SparseVector {
// TreeMap is used to maintain sorted order
private TreeMap st;
private int size;
// Constructor
public SparseVector(int size)
{
this.size = size;
// assigning empty TreeMap
st = new TreeMap();
}
// Function to insert a (index, value) pair
public void put(int i, double value)
{
// checking if index(i) is out of bounds
if (i < 0 || i >= size)
throw new RuntimeException(
"\nError : Out of Bounds\n");
// if value is zero, don't add to that index &
// remove any previously held value
if (value == 0.0)
st.remove(i);
// if value is non-zero add index-value pair to
// TreeMap
else
st.put(i, value);
}
// Function to get value for an index
public double get(int i)
{
// checking if index(i) is out of bounds
if (i < 0 || i >= size)
throw new RuntimeException(
"\nError : Out of Bounds\n");
// if index is valid, return value at index
if (st.containsKey(i))
return st.get(i);
// if index not found, it means the value is zero as
// only non-zero entries are added to the Map
else
return 0.0;
}
// Function to get size of the vector
public int size() { return size; }
// Function to get dot product of two vectors
public double dot(SparseVector b)
{
SparseVector a = this;
// Dot product of Sparse Vectors whose lengths are
// different is not possible
if (a.size != b.size)
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error : Vector lengths are not same");
double sum = 0.0;
// Traversing each sorted vector and getting
// product of consequent entries of the vectors
if (a.st.size() <= b.st.size()) {
for (Map.Entry entry :
a.st.entrySet())
if (b.st.containsKey(entry.getKey()))
sum += a.get(entry.getKey())
* b.get(entry.getKey());
}
// Traversing each sorted vector and getting
// product of consequent entries of the vectors
else {
for (Map.Entry entry :
b.st.entrySet())
if (a.st.containsKey(entry.getKey()))
sum += a.get(entry.getKey())
* b.get(entry.getKey());
}
return sum;
}
// Function to get sum of two vectors
public SparseVector plus(SparseVector b)
{
SparseVector a = this;
// Addition of Sparse Vectors whose lengths are
// different is not possible
if (a.size != b.size)
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error : Vector lengths are not same");
// creating new empty Sparse Vector object
SparseVector c = new SparseVector(size);
// Traversing and adding the two vectors a & b and
// constructing resultant Sparse Vector c
for (Map.Entry entry :
a.st.entrySet())
c.put(entry.getKey(), a.get(entry.getKey()));
for (Map.Entry entry :
b.st.entrySet())
c.put(entry.getKey(),
b.get(entry.getKey())
+ c.get(entry.getKey()));
return c;
}
// Function toString() for printing vector
public String toString()
{
String s = "";
for (Map.Entry entry :
st.entrySet())
s += "(" + entry.getKey() + ", "
+ st.get(entry.getKey()) + ") ";
return s;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(
"Enter size of Sparse Vectors : ");
// Size of the two Sparse Vector
int n = scan.nextInt();
// sparse vector a and b
SparseVector A = new SparseVector(n);
SparseVector B = new SparseVector(n);
// store key, value pairs
System.out.println(
"Enter number of entries for Vector A :");
int n1 = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter " + n1
+ " (int, double) pairs :");
for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++)
A.put(scan.nextInt(), scan.nextDouble());
System.out.println(
"Enter number of entries for vector B :");
int n2 = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter " + n2
+ " (int, double) pairs :");
for (int i = 0; i < n2; i++)
B.put(scan.nextInt(), scan.nextDouble());
System.out.println("\nVector A = " + A);
System.out.println("Vector B = " + B);
System.out.println("\nA dot B = " + A.dot(B));
System.out.println("A + B = " + A.plus(B));
}
} 输出