惠更斯波浪理论
克里斯蒂安·惠更斯提出了惠更斯原理。 1678 年,他改变了我们对光及其特性的看法。您可能听说过光的直线理论,该理论指出光以直线传播。检查各种光学现象的最重要方法之一是惠更斯原理。原理是一种分析方法,可用于解决远场极限、近场衍射和反射中的波传播问题。
当你在房间里打开一扇窗户时,光线会通过它进入并在整个空间中传播。你知道为什么会这样吗?这是因为光具有波动字符,并在房间内向各个方向传播。让我们看一下惠更斯原理以更好地理解这一点。
惠更原理
Every point on a wavefront is a source of spherical wavelets that expand out at the speed of light in the forward direction. The wavefront is formed by the sum of these spherical wavelets.”
然而,这种解释并不能解释为什么首先会发生折射。其次,它无法解释光如何沿其路径传递能量。惠更斯原理,也称为惠更斯-菲涅耳原理,强调波的传播行为如下:
- 二次源产生的小波与原始源的小波相当。
- 新的波前由任何给定时间前向小波上的公切线确定。
- 球面小波的总和就是波前。
波前和波法线
考虑“空气”中的点光源“S”。该光源发出的光波向各个方向传播。如果“c”是空气中的光速,则每个波将在时间 t 内传播“ct”并到达半径为“ct”的球体表面。以源“S”为焦点。这种类型的表面被称为球面波表面。
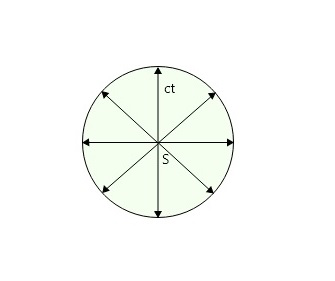
波面
波前是波同时到达的所有介质点的轨迹,因此所有点处于同一相位(见下图),例如,灯泡在有限距离处发出的光。当点光源位于其焦点时,平面波前从凸透镜中出现。此外,如果球面波前足够大,则表面的一小部分可以被认为是平面波前。例如,波前是由阳光引起的。线性源(例如狭缝)产生圆柱形波前。例如,光是由荧光管发出的。
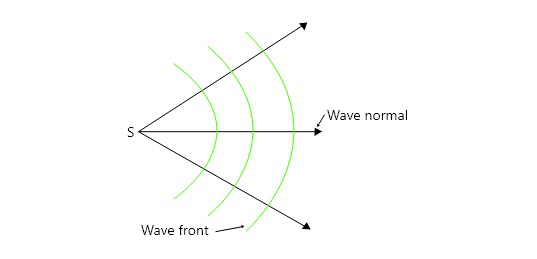
波前和波正常
波法线是在光传播方向上绘制到波前表面的垂线。换句话说,波前垂直于表面传输光能。
波正常
波前类型——波前分为三种类型,即
- 球面波前:考虑“S”点光源。 S产生的光波可以向任何方向移动。如果 c 是光速,那么每个波将在时间 t 后到达半径为 ct、中心为 S 的球体表面。这个球面被称为时间 t 的球面波前,它是从一个有限距离的点源推导出来的。例如,考虑一个灯泡在有限距离内发出的光。
- 平面波前:球面波前在距点源很远的距离处是如此巨大,以至于它的一小部分可以被认为是平面波前。它源自无限远的点源。例如,考虑由阳光引起的波前。
- 圆柱形波前:如果光源是线性的,即狭缝,那么我们得到一个圆柱形波前。它是从保持有限距离的线性源获得的。例如,光是由荧光管发出的。
惠更斯的球面波前构造
令 PQ 为在任何时刻由于点源 (S) 产生的球面波前的横截面。这可以称为初级波前。现在考虑 PQ 上的 A、B、C、D、E 点。它们充当二次源并根据惠更斯原理发出二次小波。
如果 c 是各向同性介质中的光速,则在时间 t 中,每个波将描述一个距离“ct”。以 A、B、C、D、E 为圆心,将跟踪每个半径 ct。每个圆圈将代表一个次级波前。
绘制到这些次级波阵面的公共切向表面(包络线)P'Q' 表示时间't' 之后波阵面的(新)位置。不存在向后移动的二次波。
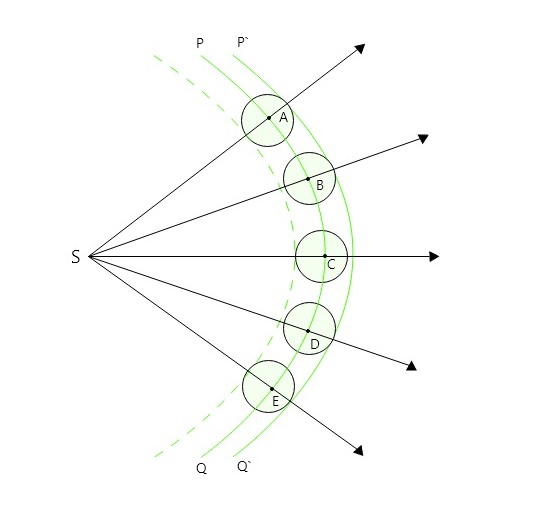
惠更斯球面波前
惠更斯的平面波前构造
令 PQ 是由于点源(S)在任何时刻和非常远的距离处垂直于纸面的平面波前,这可以称为主波前。现在考虑 PQ 上的 A、B、C、D 点。它们充当次级惠更斯源并根据惠更斯原理发出次级小波。
如果“c”是各向同性介质中的光速,那么在时间“t”中,每个波将描述一个距离“ct”。以 A、B、C、D 为中心,将跟踪每个半径为 'ct 的球体,每个球体将代表一个次级波前。绘制到这些次级波前的公共切面(包络线)即P'Q'代表时间't'之后波前的新位置。
向后移动的二次波不存在,因此用虚线表示。
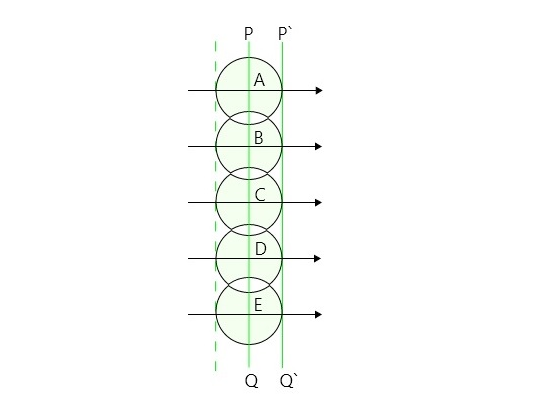
惠更斯平面波前
惠更原理的优点
- 它可以解释折射、干涉、反射、衍射等定律。
- 波动理论预测,光在光密介质中的速度小于光稀介质中的光速,这一点由福柯通过实验证明。
惠更原理的缺点
- 它无法解释光的直线传播。光的直线传播描述了光以直线传播。
- 它无法解释光的偏振现象以及拉曼效应、康普顿效应和光电效应等现象。后来修改为光是横波。
- 惠更斯假设存在一种假设的介质 [以太]。 Michelson 和 Morley 用他们基于光束干涉原理的设备进一步研究了假想的以太的性质。实验得出结论,当地球穿过它时,没有以太阻力。这个和其他实验证明以太不存在。
示例问题
问题1:陈述惠更斯光波理论的任何三个假设?
回答:
Assumptions of Huygens wave theory are as below:
- Light is propagated in form of longitudinal waves
- Different colors of light are due to different wavelengths of light waves.
- We feel sensation when light waves enter our eyes.
问题二:惠更斯光波理论的优缺点
回答:
Merits:
- This theory could explain the laws of reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, etc.
- According to this theory, the speed of light in a denser medium is less than that in a rarer medium. [This conclusion is in perfect agreement with the experimental results.]
Demerits:
- His theory could not explain rectilinear propagation of light.
- Huygens` assumed the presence of the hypothetical medium, ether.
- Experimentally it was proved that ether does not exist.
- This theory fails to explain the polarization of light phenomenon like Photoelectric effect, Compton effect and Raman effect.
问题 3:定义波前和波法线。
回答:
Wavefront: A locus containing all of the points of medium to which waves arrive at the same time, so that all of the points are in the same phase.
Wave normal: A wave normal is a perpendicular drawn to the surface of a wavefront at any point along the wavefront in the direction of light propagation.
问题 4:给出平面波前和球面波前的区别?
回答:
The difference between Plane and Spherical wavefront are: Plane Wavefront Spherical WavefrontIt is obtained from a point source of light kept at infinite distance. It is obtained from a point source of light kept at finite distance. The rays of light are parallel to each other. The rays of light are convergent or divergent in nature. It is plane in shape It is spherical in shape Radius of curvature is infinite Radius of curvature is finite Example: Wavefront due to sunlight. Example: light emitted by a bulb at a finite distance.
问题 5:解释圆柱波前是如何产生的并举例说明?
回答:
Cylindrical wavefront: In a cylindrical wavefront, all points are equidistant from the linear source and lie on the cylinder’s surface.
- If the source of light is linear i.e., a slit, then we get a cylindrical wavefront.
- It is obtained from linear source kept at finite distance.
Example: A little rectangular slit. A cylindrical wavefront is produced when light is transmitted through a fine rectangular slit. .