用于单链表递归选择排序的Python程序 - 交换节点链接
给定一个包含n 个节点的单链表。问题是使用递归选择排序技术对列表进行排序。该方法应该涉及交换节点链接而不是交换节点数据。
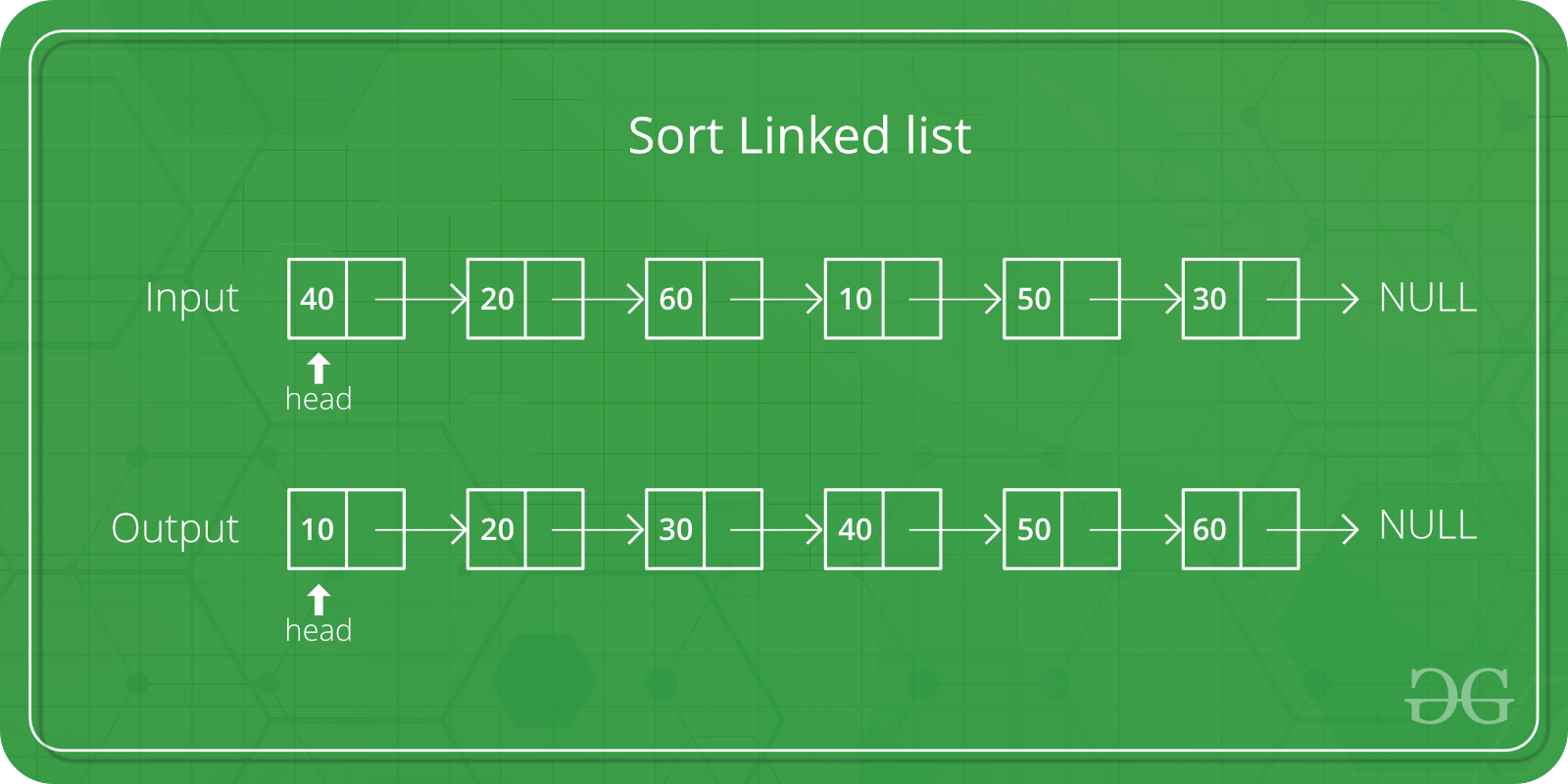
例子:
Input: 10 -> 12 -> 8 -> 4 -> 6
Output: 4 -> 6 -> 8 -> 10 -> 12 在选择排序中,我们首先找到最小元素,将其与开始节点交换,并为剩余的列表递归。下面是链表这些步骤的递归实现。
recurSelectionSort(head)
if head->next == NULL
return head
Initialize min = head
Initialize beforeMin = NULL
Initialize ptr = head
while ptr->next != NULL
if min->data > ptr->next->data
min = ptr->next
beforeMin = ptr
ptr = ptr->next
if min != head
swapNodes(&head, head, min, beforeMin)
head->next = recurSelectionSort(head->next)
return head
swapNodes(head_ref, currX, currY, prevY)
head_ref = currY
prevY->next = currX
Initialize temp = currY->next
currY->next = currX->next
currX->next = temp swapNodes(head_ref, currX, currY, prevY)基于此处讨论的方法,但已针对本文的实施进行了相应修改。
Python
# Python implementation of recursive
# selection sort for singly linked
# list | Swapping node links
# Linked List node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Function to swap nodes 'currX' and
# 'currY' in a linked list without
# swapping data
def swapNodes(head_ref, currX,
currY, prevY):
# Make 'currY' as new head
head_ref = currY
# Adjust links
prevY.next = currX
# Swap next pointers
temp = currY.next
currY.next = currX.next
currX.next = temp
return head_ref
# Function to sort the linked list using
# recursive selection sort technique
def recurSelectionSort(head):
# If there is only a single node
if (head.next == None)8:
return head
# 'min' - pointer to store the node
# having minimum data value
min = head
# 'beforeMin' - pointer to store node
# previous to 'min' node
beforeMin = None
ptr = head
# Traverse the list till the last node
while (ptr.next != None):
# if true, then update 'min' and
# 'beforeMin'
if (ptr.next.data < min.data) :
min = ptr.next
beforeMin = ptr
ptr = ptr.next
# if 'min' and 'head' are not same,
# swap the head node with the 'min' node
if (min != head):
head = swapNodes(head, head,
min, beforeMin)
# Recursively sort the remaining list
head.next =
recurSelectionSort(head.next)
return head
# Function to sort the given linked list
def sort(head_ref):
# If list is empty
if ((head_ref) == None):
return None
# Sort the list using recursive
# selection sort technique
head_ref = recurSelectionSort(head_ref)
return head_ref
# Function to insert a node at the
# beginning of the linked list
def push(head_ref, new_data):
# Allocate node
new_node = Node(0)
# Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data
# Link the old list to the
# new node
new_node.next = (head_ref)
# Move the head to point to the
# new node
(head_ref) = new_node
return head_ref
# Function to print the linked list
def printList(head):
while (head != None):
print(head.data , end = " ")
head = head.next
# Driver code
head = None
# Create linked list 10.12.8.4.6
head = push(head, 6)
head = push(head, 4)
head = push(head, 8)
head = push(head, 12)
head = push(head, 10)
print("Linked list before sorting:")
printList(head)
# sort the linked list
head = sort(head)
print("Linked list after sorting:")
printList(head)
# This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu输出:
Linked list before sorting:
10 12 8 4 6
Linked list after sorting:
4 6 8 10 12时间复杂度: O(n 2 )
辅助空间: O(n)
请参阅关于单链表递归选择排序的完整文章 |交换节点链接以获取更多详细信息!