用Java实现自组织列表
自组织列表是一个列表,它根据实际或预期的访问模式修改元素的存储顺序。目标是实现一种排序,使最常查找的元素最接近以提高平均访问时间。此属性也称为引用位置,它将最常用的项目放在列表的开头。这增加了在列表开头找到项目的可能性,并且那些很少使用的元素被推到列表的后面。
重新排列节点的技术
在对列表中的元素进行排序时,元素的访问概率通常是事先不知道的。这导致了各种启发式方法的发展,以逼近最佳行为。用于对列表中的元素重新排序的基本启发式是,
1. 移到最前面的方法
这种技术将被评估的元素移动到列表的头部。
At the t-th item selection:
if item i is selected:
move item i to head of the list
2.计数法
在这种技术中,计算每个节点被搜索的次数,即每个节点保持一个单独的计数器变量,每次调用它时都会增加该变量。
init: count(i) = 0 for each item i
At t-th item selection:
if item i is searched:
count(i) = count(i) + 1
3.转置法
该技术涉及将访问的节点与其前任交换。
At the t-th item selection:
if item i is selected:
if i is not the head of list:
swap item i with item (i – 1)
Java
// Java Program to Implement Self organizing List
import java.util.Scanner;
class SelfOrganizingList {
private int[] list;
private int[] count;
private int size;
// Constructor
public SelfOrganizingList(int listSize)
{
list = new int[listSize];
count = new int[listSize];
size = 0;
}
// checks if list is empty
public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; }
// checks if list is full
public boolean isFull() { return size == list.length; }
// Makes list empty
public void makeEmpty()
{
int l = list.length;
list = new int[l];
count = new int[l];
size = 0;
}
// retunrs the size of list
public int getSize() { return size; }
// Function to insert element
public void insert(int val)
{
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Error : List full!");
return;
}
list[size] = val;
count[size] = 0;
size++;
}
// Function to remove element
public void remove(int pos)
{
pos--;
if (pos < 0 || pos >= size) {
System.out.println("Invalid position ");
return;
}
for (int i = pos; i < size - 1; i++) {
list[i] = list[i + 1];
count[i] = count[i + 1];
}
size--;
}
// Function to search for an element
public boolean search(int x)
{
boolean searchResult = false;
int pos = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (list[i] == x) {
searchResult = true;
pos = i;
break;
}
}
if (searchResult) {
count[pos]++;
int c = count[pos];
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
if (count[pos] > count[i]) {
for (int j = pos; j > i; j--) {
list[j] = list[j - 1];
count[j] = count[j - 1];
}
list[i] = x;
count[i] = c;
break;
}
}
}
return searchResult;
}
// prints list
public void printList()
{
System.out.print("\nList = ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
System.out.print(list[i] + " ");
System.out.print("\nCount = ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
System.out.print(count[i] + " ");
}
}
public class SelfOrganizingListTest {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("SelfOrganizingList Test\n");
// Creating object of class SelfOrganizingList
System.out.println("Enter size of list ");
SelfOrganizingList list
= new SelfOrganizingList(scan.nextInt());
char ch;
// Perform list operations
do {
System.out.println(
"\nSelfOrganizingList Operations\n");
System.out.println("1. insert ");
System.out.println("2. delete at position");
System.out.println("3. search");
System.out.println("4. check empty");
System.out.println("5. check full");
System.out.println("6. get size");
int choice = scan.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
System.out.println(
"Enter integer element to insert");
list.insert(scan.nextInt());
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(
"Enter position to delete");
list.remove(scan.nextInt());
break;
case 3:
System.out.println(
"Enter integer element to search");
System.out.println(
"Search Result : "
+ list.search(scan.nextInt()));
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("Empty status = "
+ list.isEmpty());
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("Full status = "
+ list.isFull());
break;
case 6:
System.out.println(
"Size = " + list.getSize() + " \n");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Wrong Entry \n ");
break;
}
// Display List
list.printList();
System.out.println(
"\nDo you want to continue (Type y or n) \n");
ch = scan.next().charAt(0);
} while (ch == 'Y' || ch == 'y');
}
}输出
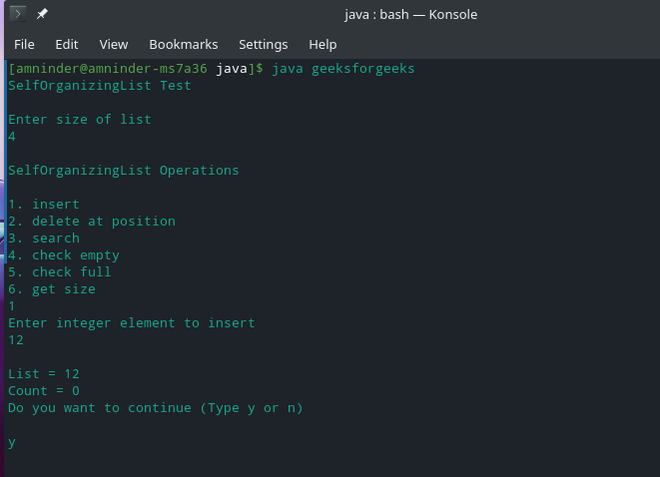
1.1 插入元素
在列表中插入元素: 12
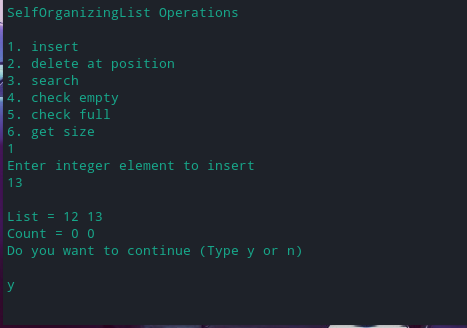
1.2 插入元素
在列表中插入元素: 13
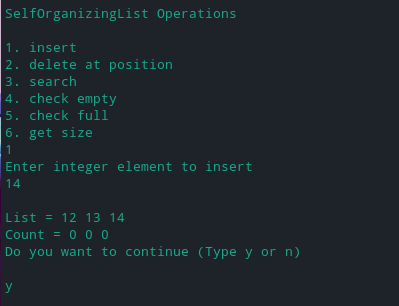
搜索元素
搜索元素 = 13