使用Python将 CSV 转换为 JSON
CSV(或逗号分隔值)文件以表格格式表示数据,具有多行和多列。 CSV 文件的一个示例可以是 Excel 电子表格。这些文件的扩展名为 .csv,例如 geeksforgeeks .csv 。在这个示例文件中,每一行将代表数据集的一条记录,每一列将表示一个唯一的特征变量。
另一方面, JSON(或 JavaScript 对象表示法)是一种类似字典的表示法,可以通过在Python中导入 JSON 包来使用。每条记录(或行)都保存为单独的字典,列名作为字典的键。所有这些记录作为字典都保存在嵌套字典中以组成整个数据集。它以扩展名 .json 存储,例如 geeksforgeeks .json
Refer to the below articles to understand the basics of JSON and CSV.
- Working With JSON Data in Python
- Working with CSV file in Python.
将 CSV 转换为 JSON
我们将创建一个包含多个字典的 JSON 文件,每个字典代表 CSV 文件中的一条记录(行),其中指定的列是 Key。
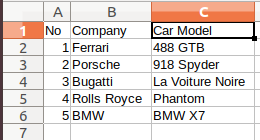
使用的示例 CSV 文件:
Python3
import csv
import json
# Function to convert a CSV to JSON
# Takes the file paths as arguments
def make_json(csvFilePath, jsonFilePath):
# create a dictionary
data = {}
# Open a csv reader called DictReader
with open(csvFilePath, encoding='utf-8') as csvf:
csvReader = csv.DictReader(csvf)
# Convert each row into a dictionary
# and add it to data
for rows in csvReader:
# Assuming a column named 'No' to
# be the primary key
key = rows['No']
data[key] = rows
# Open a json writer, and use the json.dumps()
# function to dump data
with open(jsonFilePath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as jsonf:
jsonf.write(json.dumps(data, indent=4))
# Driver Code
# Decide the two file paths according to your
# computer system
csvFilePath = r'Names.csv'
jsonFilePath = r'Names.json'
# Call the make_json function
make_json(csvFilePath, jsonFilePath)输出: