以朱莉娅为背景的作品
Julia 中的集合是元素的集合,就像数组、字典等其他集合一样。集合与数组不同,因为集合是唯一元素的无序集合,而元素的顺序在数组中被严格记住。此外,数组和字典可能包含重复值,但集合不能。集合中的每个元素都必须是唯一的。集合是可变的数据类型,这意味着它的值可以被更改、删除、覆盖等。
集合可以包含任何数据类型的元素。就像其他集合一样,在 Julia 中,在元素声明之前定义集合的数据类型并不是强制性的。 Julia 会自动分析元素并定义 Set 的数据类型。 Julia 不允许单独访问集合的元素,因为它是无序集合,因此任何元素都没有固定索引。

创建一个集合
可以使用预定义的关键字Set()创建 Julia 中的集合。此关键字接受放置在方括号 ([]) 中的元素,并通过根据元素的数据类型定义其数据类型来创建一个集合。
句法:
Set_name = Set([Value1, Value2, Value3, ....]) Julia
# Julia program to illustrate
# the use of Sets
# Creating an empty set
Set1 = Set()
println("Empty Set: ", Set1)
# Creating a set with Integer values
Set2 = Set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 2, 4, 6])
println(Set2)
# Creating a set with mixed datatypes
Set3 = Set([1, 2, 3, "Hello", "Geeks"])
println(Set3)Julia
# Julia program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
Set1 = Set(["Geeks", "For", "Geeks"])
println("\nInitial set:")
println(Set1)
# Accessing element using
# for loop
println("\nElements of set: ")
for i in Set1
println(i)
end
# Checking the element
# using in keyword
println(in("For", Set1))Python
# Julia program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
Set1 = Set(["Hello", "Geeks", 10])
println("\nInitial set:")
println(Set1)
# Adding an element to the set
Set1 = push !(Set1, "Welcome")
println("\nSet after adding one element:\n", Set1)
# Adding a range of elements
# using for loop
for i in 1:5
push !(Set1, i)
end
println("\nSet after adding range of elements:\n", Set1)Python
# Julia program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
Set1 = Set(["Hello", "Geeks", 10])
println("\nSet1:")
println(Set1)
# Creating another set
Set2 = Set([1, 2, 3, 4])
println("\nSet2:")
println(Set2)
# Performing Merge using union operation
println("\nMerged Set after union Operation:")
println(union(Set1, Set2))
# Existing set after union operation
println("\nSet1 after union operation:")
println(Set1)Python3
# Sets taken from previous example
# Performing Merge using union ! operation
println("\nMerged Set after union ! Operation:")
println(union !(Set1, Set2))
# Existing set after union ! operation
println("\nSet1 after union ! operation:")
println(Set1)Python
# Julia program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
Set1 = Set(["Hello", "Geeks", 1, 2, 3])
println("\nSet1:")
println(Set1)
# Creating another set
Set2 = Set([1, 2, 3, 4, "Geeks"])
println("\nSet2:")
println(Set2)
# Performing intersection using 'intersect' operation
println("\nSet after intersect Operation:")
println(intersect(Set1, Set2))
# Existing set after intersect operation
println("\nSet1 after intersect operation:")
println(Set1)Python3
# Performing intersection using 'intersect !' operation
println("\nSet after intersect ! Operation:")
println(intersect !(Set1, Set2))
# Existing set after intersect ! operation
println("\nSet1 after intersect ! operation:")
println(Set1)Python
# Julia program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
Set1 = Set(["Hello", "Geeks", 1, 2, 3])
println("\nSet1:")
println(Set1)
# Creating another set
Set2 = Set([1, 2, 3, 4, "Geeks"])
println("\nSet2:")
println(Set2)
# Finding Difference using 'setdiff' operation
println("\nSet after 'setdiff' Operation:")
println(setdiff(Set1, Set2))
# Existing set after 'setdiff' operation
println("\nSet1 after 'setdiff' operation:")
println(Set1)Python3
# Finding Difference using 'setdiff !' operation
println("\nSet after 'setdiff !' Operation:")
println(setdiff !(Set1, Set2))
# Existing set after 'setdiff !' operation
println("\nSet1 after 'setdiff !' operation:")
println(Set1)Python
# Julia program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
Set1 = Set(["Hello", "Geeks", 1, 2, 3])
println("\nInitial set:")
println(Set1)
# Removing an element from the set
Set1 = delete !(Set1, "Hello")
println("\nSet after deleting one element:\n", Set1)
# Deleting whole set
for i in Set1
Set1 = delete !(Set1, i)
end
println("\nEmpty set after deleting all elements:\n", Set1)输出:

访问 Set 中的元素
集合项不能通过引用索引值来访问,因为集合是无序的,这些项没有固定的索引。但是您可以使用 for 循环遍历集合项,或者使用in()关键字询问集合中是否存在指定值。
朱莉娅
# Julia program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
Set1 = Set(["Geeks", "For", "Geeks"])
println("\nInitial set:")
println(Set1)
# Accessing element using
# for loop
println("\nElements of set: ")
for i in Set1
println(i)
end
# Checking the element
# using in keyword
println(in("For", Set1))
输出:

集合的方法
添加新元素:
集是 Julia 中的可变类型集合,因此,可以使用某些预定义的关键字来修改它们的值。 Julia 允许使用'push!'在集合中添加新元素命令。向集合中添加元素与在数组中添加元素非常相似,唯一的区别是,与数组不同,集合中的元素不能添加到特定索引上,因为集合是无序的。
句法:
push!(Set_name, Value)Python
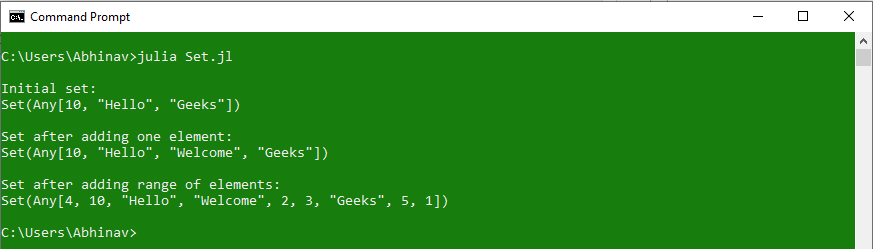
# Julia program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
Set1 = Set(["Hello", "Geeks", 10])
println("\nInitial set:")
println(Set1)
# Adding an element to the set
Set1 = push !(Set1, "Welcome")
println("\nSet after adding one element:\n", Set1)
# Adding a range of elements
# using for loop
for i in 1:5
push !(Set1, i)
end
println("\nSet after adding range of elements:\n", Set1)
输出:
集合并集:
Julia 允许使用“union”关键字合并两个集合的元素。联合运算将两个集合都作为参数,并将结果作为具有两个集合元素的另一个集合。除非返回值存储在两个集合中的任何一个中,否则这两个集合的实际值不会改变。 union函数的另一个变体是union! .这两个关键字执行类似的操作,但唯一的区别是union!函数将用新的合并集覆盖现有集。
句法:
union(Set1, Set2)
or
union!(Set1, Set2)示例 1:执行联合操作
Python
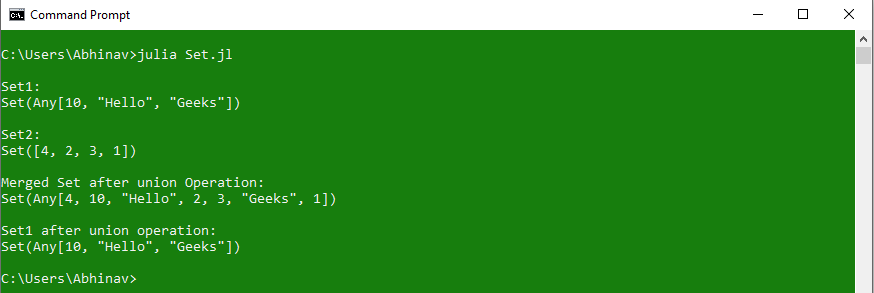
# Julia program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
Set1 = Set(["Hello", "Geeks", 10])
println("\nSet1:")
println(Set1)
# Creating another set
Set2 = Set([1, 2, 3, 4])
println("\nSet2:")
println(Set2)
# Performing Merge using union operation
println("\nMerged Set after union Operation:")
println(union(Set1, Set2))
# Existing set after union operation
println("\nSet1 after union operation:")
println(Set1)
输出:
示例 2:执行联合!手术
Python3
# Sets taken from previous example
# Performing Merge using union ! operation
println("\nMerged Set after union ! Operation:")
println(union !(Set1, Set2))
# Existing set after union ! operation
println("\nSet1 after union ! operation:")
println(Set1)
输出:
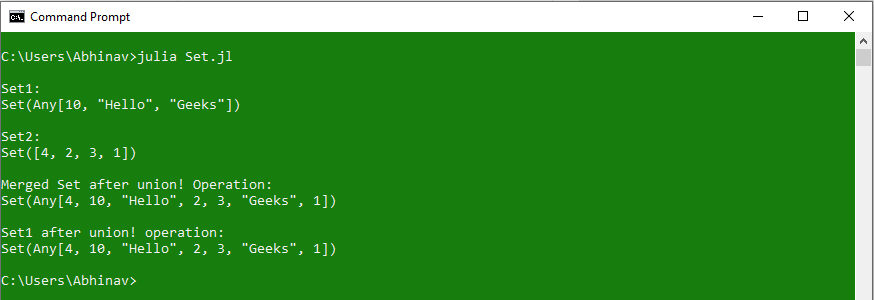
从上面的代码可以看出, union!运算符在执行合并操作后更新了 Set1 的现有内容,但联合运算符不对现有集合进行任何更改,仅执行合并操作。
集合的交集
Julia 允许使用“intersect”关键字查找两个集合的共同元素。交集运算将两个集合都作为参数,并将结果作为另一个集合给出,该集合具有两个集合的共同元素。除非返回值存储在两个集合中的任何一个中,否则这两个集合的实际值不会改变。相交函数还有另一种变体,即相交! .这两个关键字执行类似的操作,但唯一的区别是相交!函数将用新的相交集覆盖现有集。
句法:
intersect(Set1, Set2)
or
intersect!(Set1, Set2)示例 1:执行相交操作
Python
# Julia program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
Set1 = Set(["Hello", "Geeks", 1, 2, 3])
println("\nSet1:")
println(Set1)
# Creating another set
Set2 = Set([1, 2, 3, 4, "Geeks"])
println("\nSet2:")
println(Set2)
# Performing intersection using 'intersect' operation
println("\nSet after intersect Operation:")
println(intersect(Set1, Set2))
# Existing set after intersect operation
println("\nSet1 after intersect operation:")
println(Set1)
输出:

示例 2:执行相交!手术
Python3
# Performing intersection using 'intersect !' operation
println("\nSet after intersect ! Operation:")
println(intersect !(Set1, Set2))
# Existing set after intersect ! operation
println("\nSet1 after intersect ! operation:")
println(Set1)
输出:

从上面的代码可以看出,相交!运算符在执行交集后更新了 Set1 的现有内容,但交集运算符不对现有集合做任何更改,只执行交集。
两组之间的差异
Julia 允许使用“setdiff”关键字在两个集合之间查找不同的元素。该运算符将两个集合都作为参数,并将结果作为具有两个集合的不同元素的另一个集合给出。除非返回值存储在两个集合中的任何一个中,否则这两个集合的实际值不会改变。 setdiff函数的另一个变体是setdiff! .这两个关键字执行类似的操作,但唯一的区别是setdiff!函数将用新集合覆盖现有集合。
句法:
setdiff(Set1, Set2)
or
setdiff!(Set1, Set2)示例 1:执行 setdiff 操作
Python
# Julia program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
Set1 = Set(["Hello", "Geeks", 1, 2, 3])
println("\nSet1:")
println(Set1)
# Creating another set
Set2 = Set([1, 2, 3, 4, "Geeks"])
println("\nSet2:")
println(Set2)
# Finding Difference using 'setdiff' operation
println("\nSet after 'setdiff' Operation:")
println(setdiff(Set1, Set2))
# Existing set after 'setdiff' operation
println("\nSet1 after 'setdiff' operation:")
println(Set1)
输出:

示例 2:执行 setdiff!手术
Python3
# Finding Difference using 'setdiff !' operation
println("\nSet after 'setdiff !' Operation:")
println(setdiff !(Set1, Set2))
# Existing set after 'setdiff !' operation
println("\nSet1 after 'setdiff !' operation:")
println(Set1)
输出:

从上面的代码可以看出, setdiff!运算符在执行操作后更新了 Set1 的现有内容,但setdiff运算符不会对现有集合进行任何更改,而仅给出不同元素的集合。
从 Set 中移除元素:
从集合中移除元素是一项相当容易的任务。 Julia 提供了一个预定义的关键字“删除!”从集合中删除特定元素。就像添加过程一样,由于其无序性质,不可能从任何特定索引中删除元素。确切的元素将被传递给删除!函数作为参数,以便将其从集合中删除。
句法:
delete!(Set_name, value)Python
# Julia program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
Set1 = Set(["Hello", "Geeks", 1, 2, 3])
println("\nInitial set:")
println(Set1)
# Removing an element from the set
Set1 = delete !(Set1, "Hello")
println("\nSet after deleting one element:\n", Set1)
# Deleting whole set
for i in Set1
Set1 = delete !(Set1, i)
end
println("\nEmpty set after deleting all elements:\n", Set1)
输出:

设置方法
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| intersect() | Used to construct the intersection of the specified sets |
| intersect!() | Used to intersect all passed in sets and overwrite s with the result |
| issetequal() | Used to determine whether the two specified sets a and b have the same elements or not |
| setdiff() | Used to returns the elements which are in first set but not in second set |
| setdiff!() | Used to remove each element of set s which are also in the specified iterable |
| symdiff() | Used to construct the symmetric difference of elements in the passed in sets |
| symdiff!() | Used to construct the symmetric difference of the passed in sets, and overwrite the specified set s with the result |
| union() | Used to construct the union of the specified sets |
| union!() | Used to construct the union of passed in sets and overwrite s with the result |