用于查找链表长度的Python程序
编写一个函数来计算给定单链表中的节点数。
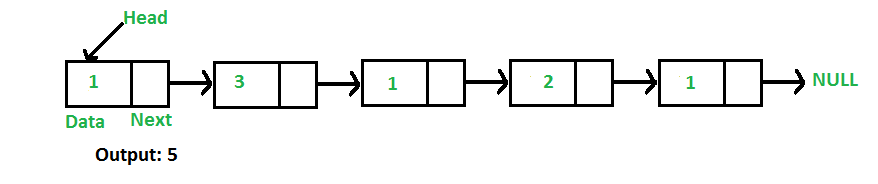
例如,对于链表 1->3->1->2->1,函数应该返回 5。
迭代解决方案:
1) Initialize count as 0
2) Initialize a node pointer, current = head.
3) Do following while current is not NULL
a) current = current -> next
b) count++;
4) Return count 以下是上述算法的迭代实现,用于查找给定单链表中的节点数。
Python
# A complete working Python program to
# find the length of a Linked List
# iteratively
# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
# Assign data
self.data = data
# Initialize next as null
self.next = None
# Linked List class contains a Node object
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# This function is in LinkedList class.
# It inserts a new node at the beginning
# of Linked List.
def push(self, new_data):
# 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
# Put in the data
new_node = Node(new_data)
# 3. Make next of new Node as head
new_node.next = self.head
# 4. Move the head to point to the new Node
self.head = new_node
# This function counts number of nodes in
# Linked List iteratively, given 'node'
# as starting node.
def getCount(self):
# Initialise temp
temp = self.head
count = 0 # Initialise count
# Loop while end of linked list is
# not reached
while (temp):
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return count
# Code execution starts here
if __name__=='__main__':
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(1)
llist.push(3)
llist.push(1)
llist.push(2)
llist.push(1)
print ("Count of nodes is :",
llist.getCount())Python
# A complete working Python program to
# find the length of a Linked List
# recursively
# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
# Assign data
self.data = data
# Initialize next as null
self.next = None
# Linked List class contains a Node object
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# This function is in LinkedList class.
# It inserts a new node at the beginning
# of Linked List.
def push(self, new_data):
# 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
# Put in the data
new_node = Node(new_data)
# 3. Make next of new Node as head
new_node.next = self.head
# 4. Move the head to point to the new Node
self.head = new_node
# This function counts number of nodes in
# Linked List recursively, given 'node'
# as starting node.
def getCountRec(self, node):
# Base case
if (not node):
return 0
else:
return 1 + self.getCountRec(node.next)
# A wrapper over getCountRec()
def getCount(self):
return self.getCountRec(self.head)
# Code execution starts here
if __name__=='__main__':
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(1)
llist.push(3)
llist.push(1)
llist.push(2)
llist.push(1)
print ("Count of nodes is :",
llist.getCount())输出:
count of nodes is 5递归解决方案:
int getCount(head)
1) If head is NULL, return 0.
2) Else return 1 + getCount(head->next)以下是上述算法的递归实现,用于查找给定单链表中的节点数。
Python
# A complete working Python program to
# find the length of a Linked List
# recursively
# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
# Assign data
self.data = data
# Initialize next as null
self.next = None
# Linked List class contains a Node object
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# This function is in LinkedList class.
# It inserts a new node at the beginning
# of Linked List.
def push(self, new_data):
# 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
# Put in the data
new_node = Node(new_data)
# 3. Make next of new Node as head
new_node.next = self.head
# 4. Move the head to point to the new Node
self.head = new_node
# This function counts number of nodes in
# Linked List recursively, given 'node'
# as starting node.
def getCountRec(self, node):
# Base case
if (not node):
return 0
else:
return 1 + self.getCountRec(node.next)
# A wrapper over getCountRec()
def getCount(self):
return self.getCountRec(self.head)
# Code execution starts here
if __name__=='__main__':
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(1)
llist.push(3)
llist.push(1)
llist.push(2)
llist.push(1)
print ("Count of nodes is :",
llist.getCount())
输出:
Count of nodes is 5有关详细信息,请参阅有关查找链表长度(迭代和递归)的完整文章!