在Python中将文本文件转换为 JSON
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种数据交换格式,它是人类可读的文本,用于传输数据,尤其是在 Web 应用程序和服务器之间。 JSON 文件将类似于Python中的嵌套字典。要将文本文件转换为 JSON, Python中有一个json模块。该模块内置Python标准模块,因此无需外部安装。
请参阅下表以了解序列化 JSON 即编码 JSON 的过程。
| Python object | JSON object |
|---|---|
| dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str | string |
| int, long, float | numbers |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
为了处理文件中的数据流, Python中的 JSON 库使用dump()函数将Python对象转换为各自的 JSON 对象,因此可以轻松地将数据写入文件。
句法:
json.dump()
可以将各种参数传递给此方法。它们有助于提高 JSON 文件的可读性。他们是 :
- dict object:保存键值对的字典。
- indent :适合可读性的缩进(一个数值)。
- separator :对象必须如何相互分离,值必须如何与其键分离。 “、”、“:”、“;”、“.”等符号被使用
- sort_keys :如果设置为 true,则键按升序排序
这里的想法是将文本的内容作为键值对存储在字典中,然后将其转储到 JSON 文件中。下面解释一个简单的例子。文本文件包含一个人的详细信息。 text1.txt 文件如下所示:
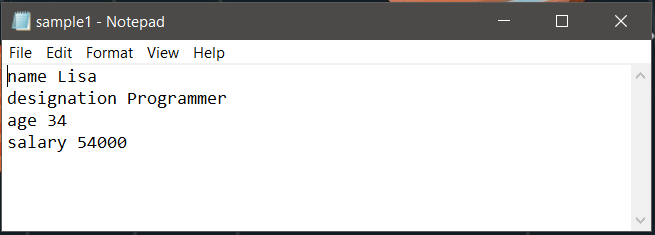
现在要将其转换为 JSON 文件,可以使用以下代码:
# Python program to convert text
# file to JSON
import json
# the file to be converted to
# json format
filename = 'data.txt'
# dictionary where the lines from
# text will be stored
dict1 = {}
# creating dictionary
with open(filename) as fh:
for line in fh:
# reads each line and trims of extra the spaces
# and gives only the valid words
command, description = line.strip().split(None, 1)
dict1[command] = description.strip()
# creating json file
# the JSON file is named as test1
out_file = open("test1.json", "w")
json.dump(dict1, out_file, indent = 4, sort_keys = False)
out_file.close()
执行上述代码时,如果给定名称中存在 JSON 文件,则将其写入,否则,在目标路径中创建一个新文件并将内容写入其中。
输出:
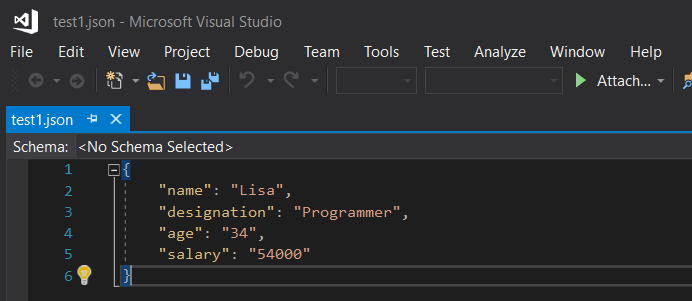
注意下面的代码行:
command, description = line.strip().split(None, 1)这里 split(None, 1) 用于修剪键值对之间的所有多余空格,并且 '1' 表示在一行中只拆分一次。这可确保在键值对中,值中的空格不会被删除,并且这些单词不会被拆分。只有键与其值分开。
如果文本文件中存储了多条记录,如何转换?
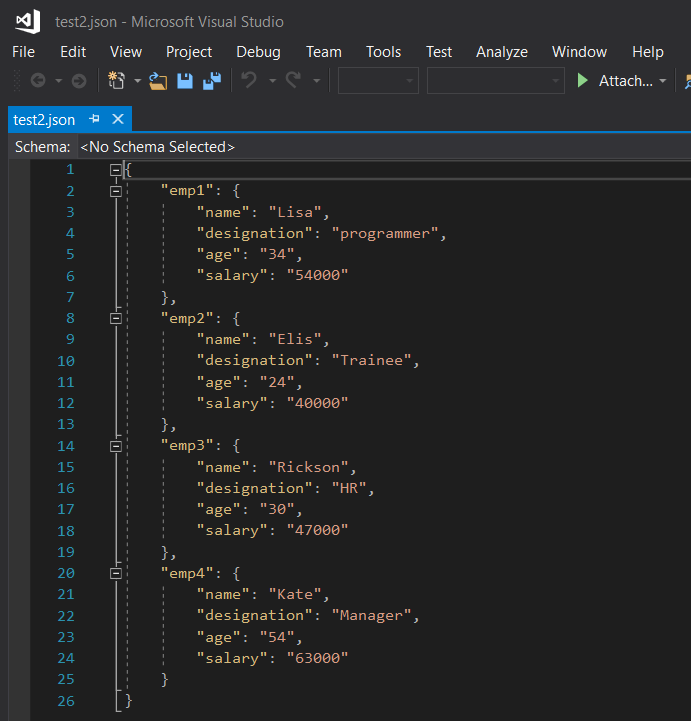
让我们考虑以下文本文件,它是包含 4 行的员工记录。
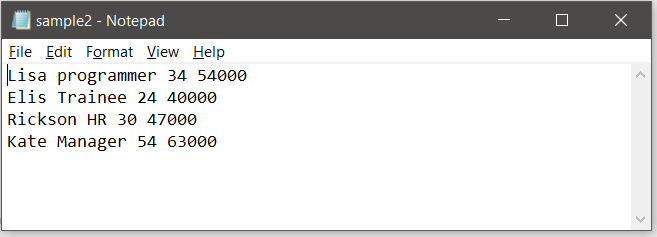
这个想法是将每个员工的详细信息转换为一个中间字典,并将其附加到一个主要的结果字典中。对于每个中间字典,都会创建一个唯一的 id,并将其用作键。因此,这里的员工 id 和一个中间字典为要转储的结果字典创建了一个键值对。
# Python program to convert text
# file to JSON
import json
# the file to be converted
filename = 'data.txt'
# resultant dictionary
dict1 = {}
# fields in the sample file
fields =['name', 'designation', 'age', 'salary']
with open(filename) as fh:
# count variable for employee id creation
l = 1
for line in fh:
# reading line by line from the text file
description = list( line.strip().split(None, 4))
# for output see below
print(description)
# for automatic creation of id for each employee
sno ='emp'+str(l)
# loop variable
i = 0
# intermediate dictionary
dict2 = {}
while i与每列关联的属性存储在一个名为'fields'的单独列表中。在上面的代码中,每一行都根据空格进行分割,并转换成字典。每次执行print(attributes)行时,它都会如下所示。
['Lisa', 'programmer', '34', '54000']
['Elis', 'Trainee', '24', '40000']
['Rickson', 'HR', '30', '47000']
['Kate', 'Manager', '54', '63000']
此代码创建的 JSON 文件如下所示: