拐点
考虑下图中给出的两个函数,而这两个函数看起来很相似。它们的不同之处在于它们的弯曲,注意其中一个看起来向上打开,另一个看起来向下闭合。这种趋势称为凹度,第一个图形向上凹,第二个图形向下凹。寻找这些趋势有助于我们生成函数的曲线。
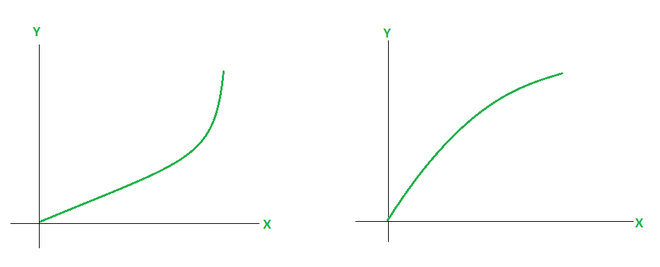
凹
如果该函数的图形位于在区间的任何点上绘制的任何切线之上,则称该函数在区间上是凹的。类似地,如果函数的图形位于在区间的任何点上绘制的任何切线下方,则称该函数是向下凹的。直观地说,凹度与增长率有关。众所周知,导数为我们提供了变化率,这意味着它们告诉我们函数是增加还是减少。凹度与变化率的变化率有关,即必然与双导有关。
在上图中,第一个函数以递增速率增加,而第二个函数以递减速率递增。从第一个函数中的事实也可以看出,切线变得越来越陡峭,反之亦然,对于第二个函数。下图显示了类似的场景,但具有递减函数。
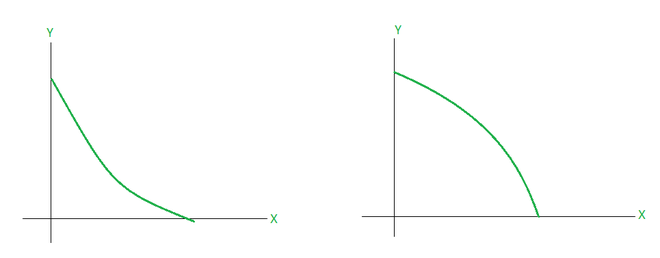
为了总结这些观察结果,下图显示了所有这些不同情况的综合比较。

为了形式化上述观察,
Concavity Test:
Consider a function f(x) which is differentiable and has derivatives and double derivatives as f’ and f” on the interval I.
- f(x) is considered concave up if f”(x) > 0 for all the points in the interval I.
- (x) is considered concave down if f”(x) < 0 for all the points in the interval I.
拐点
有时在函数轨迹中,函数从向上凹到向下凹,反之亦然。现在,当函数经历这样的变化时,会有一个特定的点作为边界。这意味着如果在此点之前函数是凹的,那么在此点之后函数将与此相反。这个点称为拐点。该图显示了这一点。
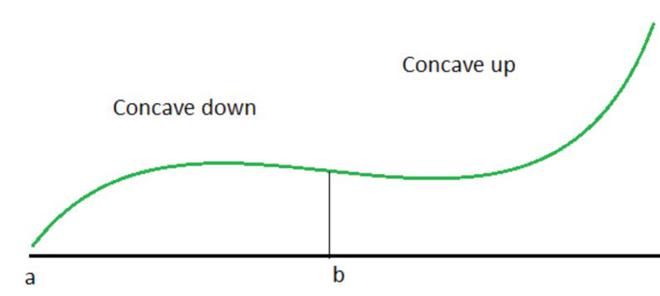
从几何上讲,此时绘制的切线既不在图形上方,也不在图形下方。切线在这一点与函数的图形相交。
Point of inflection is the point where function goes from being concave upwards to concave downwards and vice-versa. Let’s say f(x) is the function which has a point x = c as it’s inflection point. Then,
f”(c) = 0 or f”(c) does not exist.
请注意,当 f”(c) = 0 时,这意味着 x = c 基本上是 f'(x) = 0 的临界点。因此,在这种情况下,可能存在三种情况:
- 情况(i): f”(x)的符号在拐点处由正变为负。这意味着函数从向上凹变为向下凹。
- 情况(ii): f”(x)的符号在拐点处由负变为正。这意味着函数从向下凹变为向上凹。
- 情况(iii):符号不变,这意味着在整个函数中二阶导数已经为零。在这种情况下,拐点将不存在。
这三种情况表明,如果某个点的二阶导数为零,则该点不一定是拐点。
Inflection Point Test
Consider a function f(x), to determine the inflection points.
- Find f”(x).
- Solve the equation f”(x) = 0 and find all the critical points of f'(x).
- Use the number line to see at which points the double derivative changes sign.
让我们看看这些概念的一些示例问题。
示例问题
问题1:找出给定函数在区间[0,1]之间的凹度。
f(x) = x 2 + 4
解决方案:
To check for the concavity, let’s look at the second derivative of the function..
f(x) = x2 + 4
Differentiating w.r.t x,
f'(x) = 2x
Differentiating w.r.t x again,
f”(x) = 2 > 0
This is greater than zero, the function is concave upwards in the given interval.
问题2:找出给定函数在区间[2,4]之间的凹度。
f(x) = x 3 + 4
解决方案:
To check for the concavity, let’s look at the second derivative of the function..
f(x) = x3
Differentiating w.r.t x,
f'(x) = 3x2
Differentiating w.r.t x again,
f”(x) = 6x > 0
This is greater than zero, the function is concave upwards in the given interval.
问题 3:找出给定函数的拐点。
f(x) = x 3
解决方案:
To check for the point of inflection., let’s look at the second derivative of the function..
f(x) = x3 + 4
Differentiating w.r.t x,
f'(x) = 3x2
Differentiating w.r.t x again,
f”(x) = 6x = 0
Solving f”(x) = 0, it shows that x = 0 is the critical point of f'(x).
Now let’s check the value of f”(x) before and after the critical point.
for x < 0, f”(x) < 0.
for x > 0, f”(x) > 0.
Thus, the function changes from concave downward to concave upward. Thus, x = 0 is the inflection point.
问题 4:找出给定函数的拐点。
f(x) = x 3 + x 2 + 3
解决方案:
To check for the point of inflection., let’s look at the second derivative of the function..
f(x) = x3 + x2 + 3
Differentiating w.r.t x,
f'(x) = 3x2 + 2x
Differentiating w.r.t x again,
f”(x) = 6x + 2 = 0
Solving f”(x) = 0, it shows that x = ![]() is the critical point of f'(x).
is the critical point of f'(x).
Now let’s check the value of f”(x) before and after the critical point.
for x < -1, f”(x) < 0.
for x > 0, f”(x) > 0.
Thus, the function changes from concave downward to concave upward. Thus, x = ![]() is the inflection point.
is the inflection point.
问题 5:找出给定函数的拐点。
f(x) = x 4 – 2x 2 + 3x
解决方案:
To check for the point of inflection., let’s look at the second derivative of the function..
f(x) = x4 – 2x2 + 3x
Differentiating w.r.t x,
f'(x) = 4x3 – 4x + 3
Differentiating w.r.t x again,
f”(x) = 12x2 – 4x + 3= 0
Solving f”(x) = 0, it shows that x = ![]() is the critical point of f'(x).
is the critical point of f'(x).
Now let’s check the value of f”(x) before and after the critical point.
for x < -1, f”(x) < 0.
for x > 0, f”(x) > 0.
Thus, the function changes from concave downward to concave upward. Thus, x = ![]() is the inflection point.
is the inflection point.
问题 6:找出区间 [0,1] 的给定函数的拐点。
f(x) = ![]()
解决方案:
To check for the point of inflection., let’s look at the second derivative of the function..
f(x) = ![]()
Differentiating w.r.t x,
f'(x) = ![]()
⇒ f'(x) = ![]()
Differentiating w.r.t x again,
f”(x) = ![]()
Solving f”(x) = 0 for the given interval. There is no solution to this equation in the given interval.
Thus, inflection point does not exist in [0,1].