使用深度 Q 学习的 AI 驱动蛇游戏
简介:该项目基于强化学习,训练蛇吃环境中的食物。
下面给出了一个示例 gif,您可以了解我们将要构建的内容。
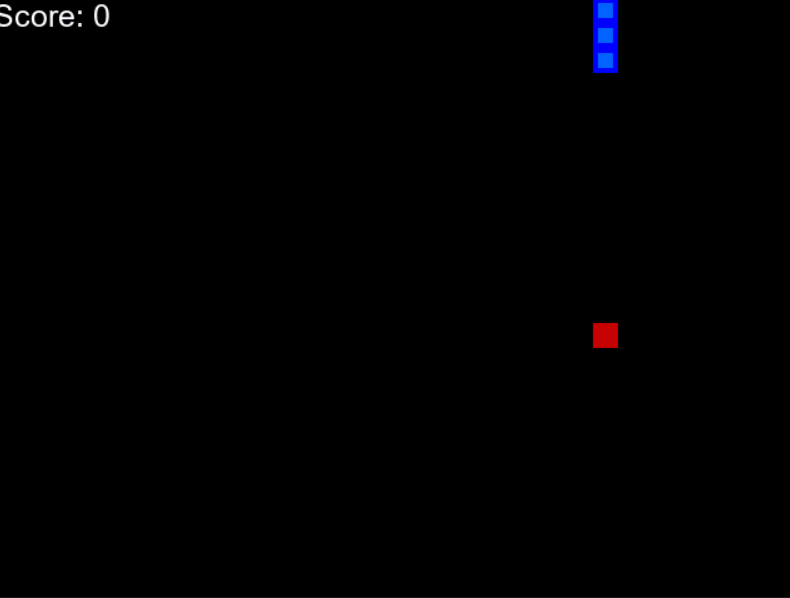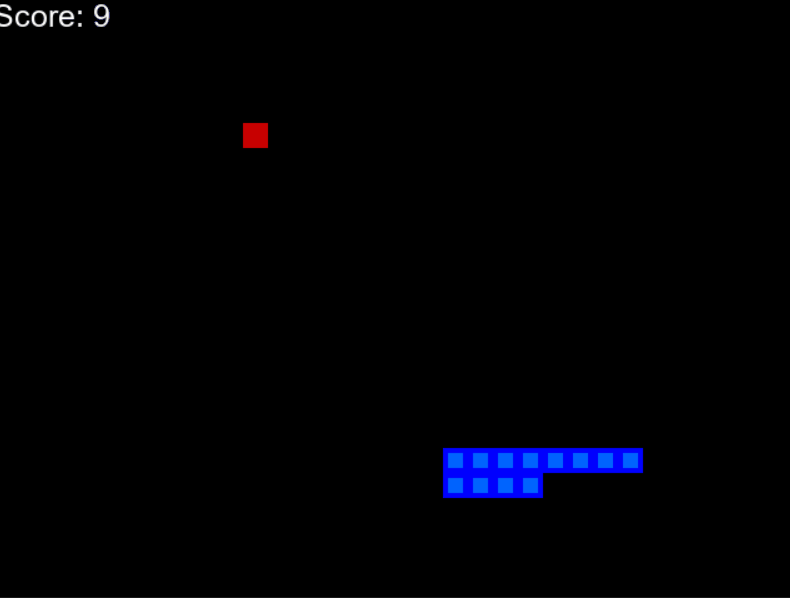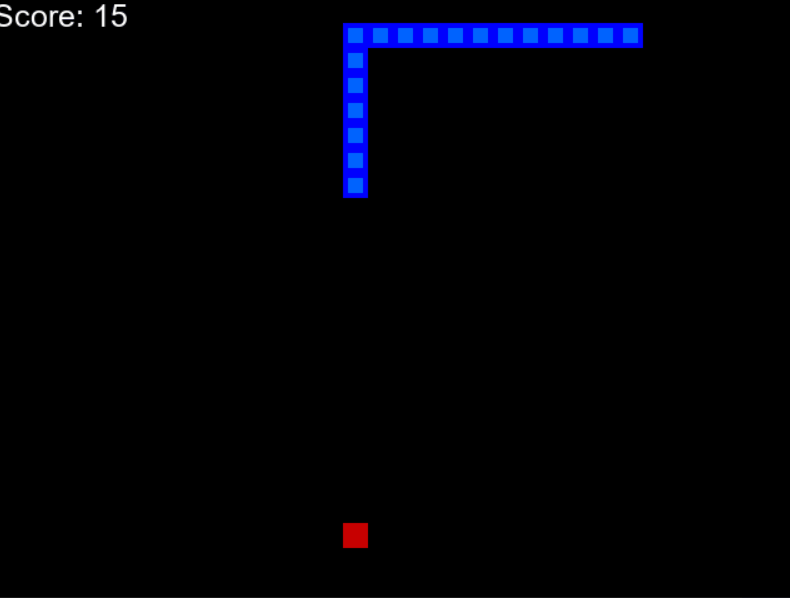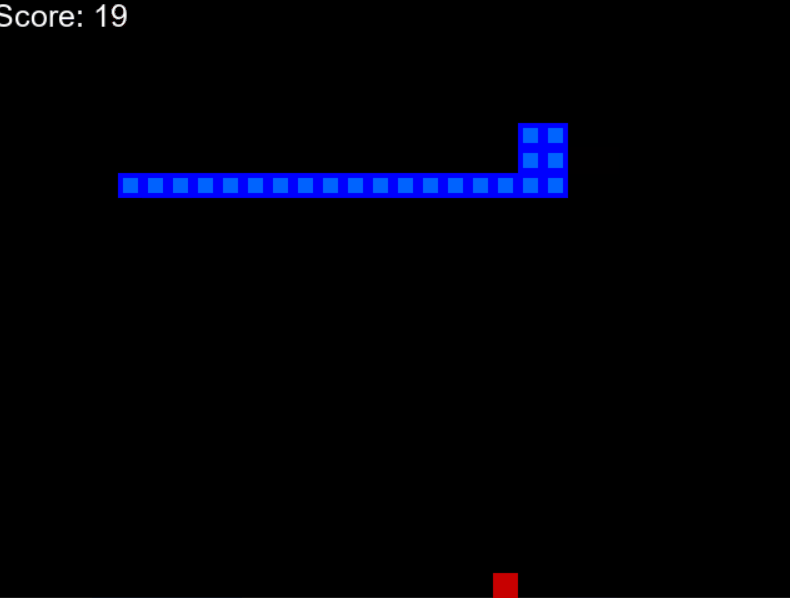
AI驱动的蛇
该项目的先决条件是:
- 强化学习
- 深度学习(密集神经网络)
- 小游戏
要了解我们如何使用 pygame 手动构建这个蛇 2D 动画模拟,请点击链接:https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/snake-game-in-python-using-pygame-module/
在构建基本的蛇游戏之后,现在我们将专注于如何将强化学习应用于它。
我们必须在这个项目中创建三个模块:
- 环境(我们刚刚构建的游戏)
- 模型(移动预测的强化模型)
- 代理(环境和模型之间的中介)

模块链接
算法:
我们在棋盘上随机放置了蛇和食物。
- 使用 11 个值计算蛇的状态。如果有任何条件为真,则将该值设置为零,否则设置一。

如何定义 11 个状态
基于当前的 Head 位置代理将计算 11 个状态值,如上所述。
- 获得这些状态后,代理会将其传递给模型并执行下一步操作。
- 执行下一个状态后计算奖励。奖励定义如下:
- 吃食物:+10
- 游戏结束:-10
- 其他:0
- 更新 Q 值(稍后将讨论)并训练模型。
- 在分析了算法之后,现在我们必须建立思想来继续编码这个算法。
该模型:

神经网络模型
该模型是使用 Pytorch 设计的,但您也可以根据自己的舒适度使用 TensorFlow。
我们正在使用具有11 大小输入层和具有 256 个神经元和3 个神经元输出的密集层的密集神经网络。您可以调整这些超参数以获得最佳结果。
模型如何工作?
- 游戏开始,Q值随机初始化。
- 系统获取当前状态 s。
- 它基于 s,随机或基于其神经网络执行一个动作。在训练的第一阶段,系统经常选择随机动作来最大化探索。后来,该系统越来越依赖其神经网络。
- 当 AI 选择并执行动作时,环境会给予奖励。然后,代理到达新状态并根据贝尔曼方程更新其 Q 值。你肯定在强化学习课程中涵盖了这个等式。如果没有,您可以参考 Q-learning Mathematics

贝尔曼方程
- 此外,对于每一步,它存储原始状态、动作、执行该动作后达到的状态、获得的奖励以及游戏是否结束。这些数据随后被采样以训练神经网络。此操作称为重放记忆。
- 重复最后两个操作,直到满足某个条件(例如:游戏结束)。
该项目的核心是您将要训练的模型,因为蛇将采取的动作的正确性完全取决于您构建的模型的质量。所以我想用部分代码向你解释这一点。
第一部分
1. Creating a class named Linear_Qnet for initializing the linear neural network.
2. The function forward is used to take the input(11 state vector) and pass it through the
Neural network and apply relu activation function and give the output back i.e the next
move of 1 x 3 vector size. In short, this is the prediction function that would be called by the agent.
3. The save function is used to save the trained model for future use.Python3
class Linear_QNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size):
super().__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.linear1(x))
x = self.linear2(x)
return x
def save(self, file_name='model_name.pth'):
model_folder_path = 'Path'
file_name = os.path.join(model_folder_path, file_name)
torch.save(self.state_dict(), file_name)C++
class QTrainer:
def __init__(self,model,lr,gamma):
#Learning Rate for Optimizer
self.lr = lr
#Discount Rate
self.gamma = gamma
#Linear NN defined above.
self.model = model
#optimizer for weight and biases updation
self.optimer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr = self.lr)
#Mean Squared error loss function
self.criterion = nn.MSELoss()
def train_step(self,state,action,reward,next_state,done):
state = torch.tensor(state,dtype=torch.float)
next_state = torch.tensor(next_state,dtype=torch.float)
action = torch.tensor(action,dtype=torch.long)
reward = torch.tensor(reward,dtype=torch.float)
#only one parameter to train, \
Hence convert to tuple of shape(1, x)
if(len(state.shape) == 1):
#(1, x)
state = torch.unsqueeze(state,0)
next_state = torch.unsqueeze(next_state,0)
action = torch.unsqueeze(action,0)
reward = torch.unsqueeze(reward,0)
done = (done, )
# 1. Predicted Q value with current state
pred = self.model(state)
target = pred.clone()
for idx in range(len(done)):
Q_new = reward[idx]
if not done[idx]:
Q_new = reward[idx] +
self.gamma * torch.max(self.model(next_state[idx]))
target[idx][torch.argmax(action).item()] = Q_new
# 2. Q_new = reward + gamma * max(next_predicted Qvalue)
#pred.clone()
#preds[argmax(action)] = Q_new
self.optimer.zero_grad()
loss = self.criterion(target,pred)
loss.backward() # backward propogation of loss
self.optimer.step()Python
def get_state(self, game):
head = game.snake[0]
point_l = Point(head.x - BLOCK_SIZE, head.y)
point_r = Point(head.x + BLOCK_SIZE, head.y)
point_u = Point(head.x, head.y - BLOCK_SIZE)
point_d = Point(head.x, head.y + BLOCK_SIZE)
dir_l = game.direction == Direction.LEFT
dir_r = game.direction == Direction.RIGHT
dir_u = game.direction == Direction.UP
dir_d = game.direction == Direction.DOWN
state = [
# Danger Straight
(dir_u and game.is_collision(point_u))or
(dir_d and game.is_collision(point_d))or
(dir_l and game.is_collision(point_l))or
(dir_r and game.is_collision(point_r)),
# Danger right
(dir_u and game.is_collision(point_r))or
(dir_d and game.is_collision(point_l))or
(dir_u and game.is_collision(point_u))or
(dir_d and game.is_collision(point_d)),
# Danger Left
(dir_u and game.is_collision(point_r))or
(dir_d and game.is_collision(point_l))or
(dir_r and game.is_collision(point_u))or
(dir_l and game.is_collision(point_d)),
# Move Direction
dir_l,
dir_r,
dir_u,
dir_d,
# Food Location
game.food.x < game.head.x, # food is in left
game.food.x > game.head.x, # food is in right
game.food.y < game.head.y, # food is up
game.food.y > game.head.y # food is down
]
return np.array(state, dtype=int)Python
def get_action(self, state):
# random moves: tradeoff explotation / exploitation
self.epsilon = 80 - self.n_game
final_move = [0, 0, 0]
if(random.randint(0, 200) < self.epsilon):
move = random.randint(0, 2)
final_move[move] = 1
else:
state0 = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float).cuda()
prediction = self.model(state0).cuda() # prediction by model
move = torch.argmax(prediction).item()
final_move[move] = 1
return final_movePython
def train_short_memory(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done):
self.trainer.train_step(state, action, reward, next_state, done)Python
def train_long_memory(self):
if (len(self.memory) > BATCH_SIZE):
mini_sample = random.sample(self.memory, BATCH_SIZE)
else:
mini_sample = self.memory
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = zip(*mini_sample)
self.trainer.train_step(states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones)Python
self.model.load_state_dict(torch.load('PATH'))第二部分
1. Initialising QTrainer class
∗ setting the learning rate for the optimizer.
* Gamma value that is the discount rate used in Bellman equation.
* initialising the Adam optimizer for updation of weight and biases.
* criterion is the Mean squared loss function.
2. Train_step function
* As you know that PyTorch work only on tensors, so we are converting all the input
to tensors.
* As discussed above we had a short memory training then we would only pass one value
of state, action, reward, move so we need to convert them into a vector, so we had used
unsqueezed function .
* Get the state from the model and calculate the new Q value using the below formula:
Q_new = reward + gamma * max(next_predicted Qvalue)
* calculate the mean squared error between the new Q value and previous Q value and
backpropogate that loss for weight updation. C++
class QTrainer:
def __init__(self,model,lr,gamma):
#Learning Rate for Optimizer
self.lr = lr
#Discount Rate
self.gamma = gamma
#Linear NN defined above.
self.model = model
#optimizer for weight and biases updation
self.optimer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr = self.lr)
#Mean Squared error loss function
self.criterion = nn.MSELoss()
def train_step(self,state,action,reward,next_state,done):
state = torch.tensor(state,dtype=torch.float)
next_state = torch.tensor(next_state,dtype=torch.float)
action = torch.tensor(action,dtype=torch.long)
reward = torch.tensor(reward,dtype=torch.float)
#only one parameter to train, \
Hence convert to tuple of shape(1, x)
if(len(state.shape) == 1):
#(1, x)
state = torch.unsqueeze(state,0)
next_state = torch.unsqueeze(next_state,0)
action = torch.unsqueeze(action,0)
reward = torch.unsqueeze(reward,0)
done = (done, )
# 1. Predicted Q value with current state
pred = self.model(state)
target = pred.clone()
for idx in range(len(done)):
Q_new = reward[idx]
if not done[idx]:
Q_new = reward[idx] +
self.gamma * torch.max(self.model(next_state[idx]))
target[idx][torch.argmax(action).item()] = Q_new
# 2. Q_new = reward + gamma * max(next_predicted Qvalue)
#pred.clone()
#preds[argmax(action)] = Q_new
self.optimer.zero_grad()
loss = self.criterion(target,pred)
loss.backward() # backward propogation of loss
self.optimer.step()
中介
- 从环境中获取蛇的当前状态。
Python
def get_state(self, game):
head = game.snake[0]
point_l = Point(head.x - BLOCK_SIZE, head.y)
point_r = Point(head.x + BLOCK_SIZE, head.y)
point_u = Point(head.x, head.y - BLOCK_SIZE)
point_d = Point(head.x, head.y + BLOCK_SIZE)
dir_l = game.direction == Direction.LEFT
dir_r = game.direction == Direction.RIGHT
dir_u = game.direction == Direction.UP
dir_d = game.direction == Direction.DOWN
state = [
# Danger Straight
(dir_u and game.is_collision(point_u))or
(dir_d and game.is_collision(point_d))or
(dir_l and game.is_collision(point_l))or
(dir_r and game.is_collision(point_r)),
# Danger right
(dir_u and game.is_collision(point_r))or
(dir_d and game.is_collision(point_l))or
(dir_u and game.is_collision(point_u))or
(dir_d and game.is_collision(point_d)),
# Danger Left
(dir_u and game.is_collision(point_r))or
(dir_d and game.is_collision(point_l))or
(dir_r and game.is_collision(point_u))or
(dir_l and game.is_collision(point_d)),
# Move Direction
dir_l,
dir_r,
dir_u,
dir_d,
# Food Location
game.food.x < game.head.x, # food is in left
game.food.x > game.head.x, # food is in right
game.food.y < game.head.y, # food is up
game.food.y > game.head.y # food is down
]
return np.array(state, dtype=int)
- 调用模型获取蛇的下一个状态
Python
def get_action(self, state):
# random moves: tradeoff explotation / exploitation
self.epsilon = 80 - self.n_game
final_move = [0, 0, 0]
if(random.randint(0, 200) < self.epsilon):
move = random.randint(0, 2)
final_move[move] = 1
else:
state0 = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float).cuda()
prediction = self.model(state0).cuda() # prediction by model
move = torch.argmax(prediction).item()
final_move[move] = 1
return final_move
注意:开发和探索之间存在权衡。开发包括根据目前观察到的数据做出假设为最佳的决定。探索是在不考虑之前的动作和奖励对的情况下随机做出决定。因此两者都是必要的,因为进行开发可能会导致代理无法探索整个环境,并且探索可能并不总是提供更好的奖励。
- 在环境中播放模型预测的步骤。
- 存储当前状态、执行的移动和奖励。
- 根据执行的移动和环境获得的奖励训练模型。 (训练短记忆)
Python
def train_short_memory(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done):
self.trainer.train_step(state, action, reward, next_state, done)
- 如果游戏因撞墙或身体而结束,则根据到目前为止执行的所有移动来训练模型并重置环境。 (训练长记忆)。以 1000 的批量大小进行训练。
Python
def train_long_memory(self):
if (len(self.memory) > BATCH_SIZE):
mini_sample = random.sample(self.memory, BATCH_SIZE)
else:
mini_sample = self.memory
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = zip(*mini_sample)
self.trainer.train_step(states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones)
训练模型需要大约 100 个时期才能获得更好的性能。查看我的训练进度。
输出:
- 要运行此游戏,请先在 anaconda 提示符或(任何平台)中创建一个环境。然后安装必要的模块,如 Pytorch(用于 DQ 学习模型)、Pygame(用于游戏的视觉效果)和其他基本模块。
- 然后在刚刚创建的环境中运行agent.py文件,然后开始训练,你会看到如下两个GUI,一个是训练进度,一个是AI驱动的snake game。
- 达到一定分数后可以退出游戏,刚刚训练好的模型会保存在models.py的save函数中定义的路径中。
将来,您只需更改 agent.py 文件中的代码即可使用此训练模型,如下所示:
Python
self.model.load_state_dict(torch.load('PATH'))
注意:注释掉所有训练函数调用。

培训进度

初步培训
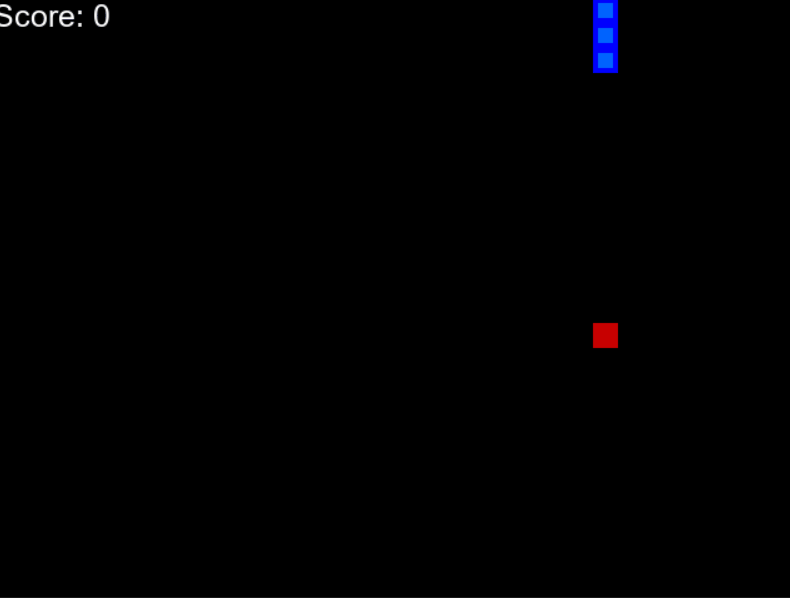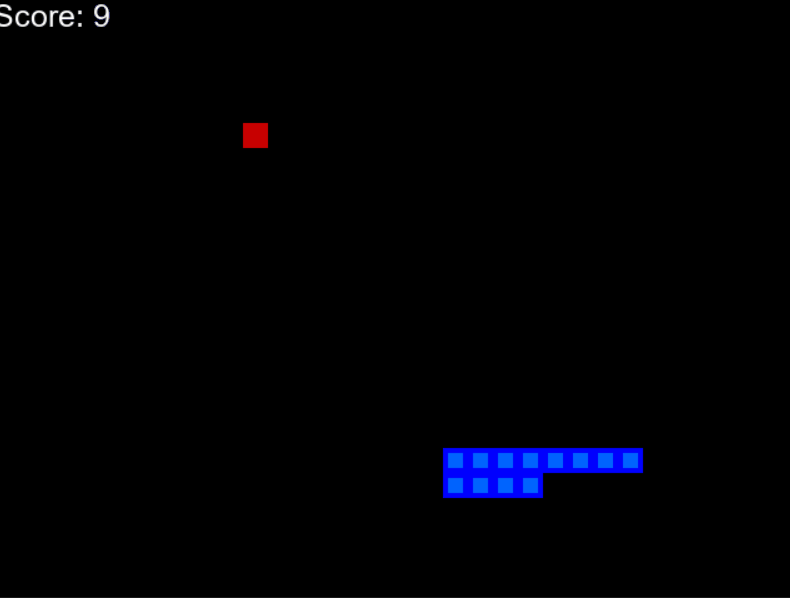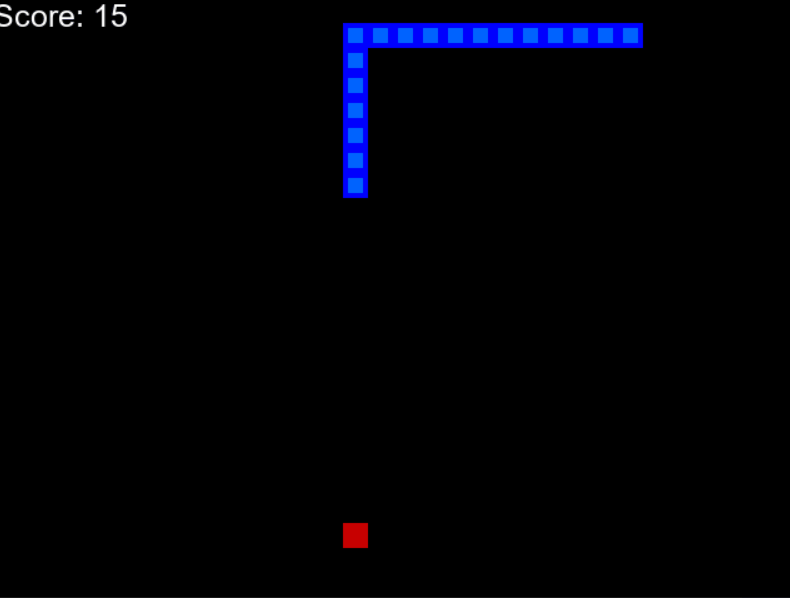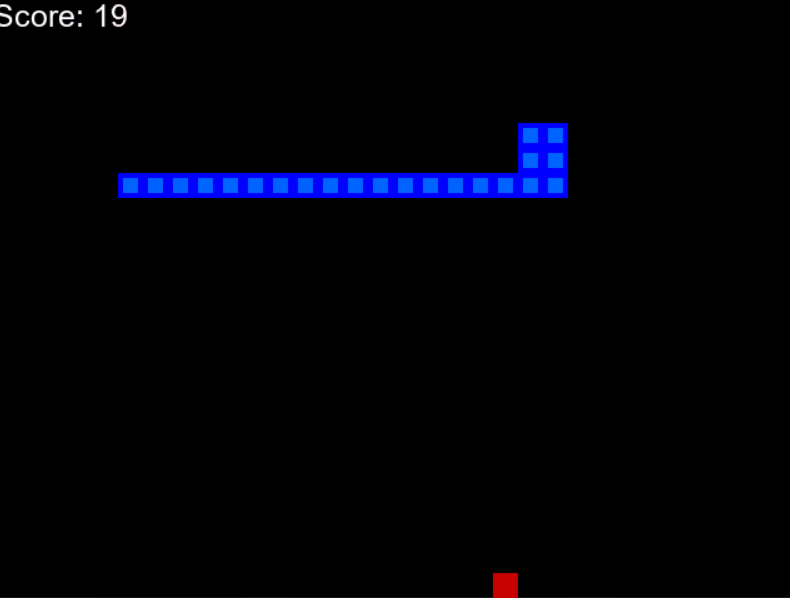
100个时代之后
源代码: https : //github.com/vedantgoswami/SnakeGameAI
应用:
该项目的目标是提出一个想法,即如何应用强化学习以及如何将其用于现实世界的应用程序,例如自动驾驶汽车(例如:AWS DeepRacer)、在装配线上训练机器人等等…
提示:
- 使用单独的环境并安装所有必需的模块。 (可以使用anaconda环境)
- 为了训练模型,您可以使用 GPU 进行更快的训练。