通过旋转 Array 然后从原始 Array 减少它来使最小为 0 的迭代计数
给定一个数组arr[]。任务是找到使数组中的最小元素为0所需的迭代次数。在一次迭代中,将数组左旋转一并减去原始数组和旋转数组的对应元素。
例子:
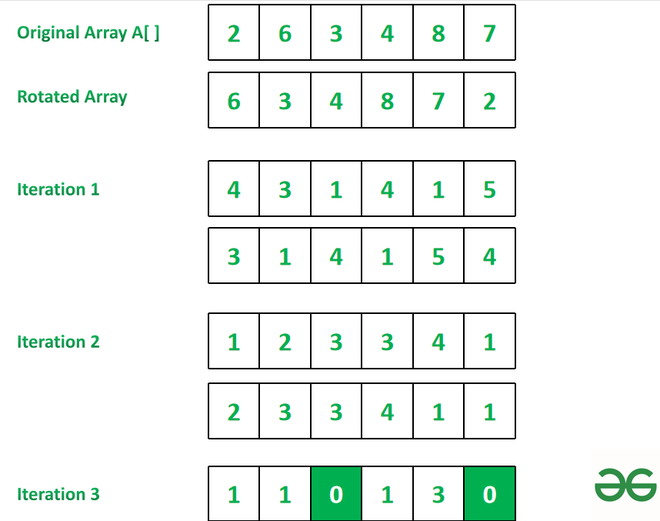
Input: arr[] = { 2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7 }
Output: 3
Explanation: Refer to the image below for explanation.
Input: arr[] = { 4, 10, 12, 3, 9, 7 }
Output: 5
朴素方法:解决此问题的最简单方法是使用贪婪方法。
- 只需弹出数组的第一个元素并将其附加到末尾,然后对相应的元素执行减法。
- 类似地,对结果数组执行相同的操作,直到我们得到数组中的最小元素为零,并返回迭代计数。
下面是上述方法的实现
C++
// C++ program for above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find no of iterations.
int minZero(vector& A, int n)
{
// Initialize count c = 0.
int c = 0;
// if zero is already present
// in array return c.
if (*min_element(A.begin(), A.end()) == 0)
return c;
// Iterate till minimum
// in array becomes zero.
while (*min_element(A.begin(), A.end()) != 0) {
// Copy array element to A1
vector A1 = A;
// Pop first element and
// append it to last
int x = A[0];
A.erase(A.begin());
A.push_back(x);
// Perform subtraction
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
A[i] = abs(A[i] - A1[i]);
// Increment count by 1
c += 1;
}
// Return value of count c
return c;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Original array
vector arr = { 2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7 };
// Calling method minZero
int x = minZero(arr, arr.size());
// Print the result
cout << (x);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rakeshsahni Java
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find no of iterations.
static int minZero(Vector A, int n)
{
// Initialize count c = 0.
int c = 0;
// if zero is already present
// in array return c.
if (Collections.min(A) == 0)
return c;
// Iterate till minimum
// in array becomes zero.
while (Collections.min(A) != 0) {
// Copy array element to A1
Vector A1 = (Vector) A.clone();
// Pop first element and
// append it to last
int x = A.get(0);
A.remove(0);
A.add(x);
// Perform subtraction
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
A.set(i, Math.abs(A.get(i) - A1.get(i)));
// Increment count by 1
c += 1;
}
// Return value of count c
return c;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Original array
Integer []arr = { 2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7 };
Vector v = new Vector();
Collections.addAll(v, arr);
// Calling method minZero
int x = minZero(v, arr.length);
// Print the result
System.out.print(x);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Python3
# Python program for above approach
# Function to find no of iterations.
def minZero(A, n):
# Initialize count c = 0.
c = 0
# if zero is already present
# in array return c.
if min(A) == 0:
return c
# Iterate till minimum
# in array becomes zero.
while min(A) != 0:
# Copy array element to A1
A1 = A[:]
# Pop first element and
# append it to last
x = A.pop(0)
A.append(x)
# Perform subtraction
for i in range(n):
A[i] = abs(A[i]-A1[i])
# Increment count by 1
c += 1
# Return value of count c
return c
# Driver Code
# Original array
arr = [2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7]
# Calling method minZero
x = minZero(arr, len(arr))
# Print the result
print(x)C#
// C# program for above approach
using System;
using System.Linq;
class GFG{
// Function to find no of iterations
static int minZero(int []A, int n)
{
// Initialize count c = 0
int c = 0;
// If 0 already in array return c
if (A.Min()== 0)
return c;
// Iterate till we get zero in array
while (A.Min() != 0) {
// Assign first element in x
int x = (int)A[0];
// Loop to subtract consecutive element
for (int i = 0; i < (n - 1); i++) {
A[i] = Math.Abs((int)A[i] - (int)A[i + 1]);
}
A[n - 1] = Math.Abs((int)A[n - 1] - x);
// Increment count c
c += 1;
}
// Return c
return c;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Original array
int []arr = { 2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7 };
// Length of array
int N = arr.Length;
// calling function
int x = minZero(arr, N);
// print the result
Console.Write(x);
}
}
// This code is contributed by avijitmondal1998Javascript
C++
// C++ program for above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find no of iterations
int minZero(int A[], int n)
{
// Initialize count c = 0
int c = 0;
// If 0 already in array return c
if (*min_element(A + 0, A + n - 1) == 0)
return c;
// Iterate till we get zero in array
while (*min_element(A + 0, A + n - 1) != 0) {
// Assign first element in x
int x = A[0];
// Loop to subtract consecutive element
for (int i = 0; i < (n - 1); i++) {
A[i] = abs(A[i] - A[i + 1]);
}
A[n - 1] = abs(A[n - 1] - x);
// Increment count c
c += 1;
}
// Return c
return c;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Original array
int arr[] = { 2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7 };
// Length of array
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// calling function
int x = minZero(arr, N);
// print the result
cout << (x);
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp. Java
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find no of iterations
static int minZero(int A[], int n)
{
// Initialize count c = 0
int c = 0;
// If 0 already in array return c
if (Arrays.stream(A).min().getAsInt()== 0)
return c;
// Iterate till we get zero in array
while (Arrays.stream(A).min().getAsInt() != 0) {
// Assign first element in x
int x = A[0];
// Loop to subtract consecutive element
for (int i = 0; i < (n - 1); i++) {
A[i] = Math.abs(A[i] - A[i + 1]);
}
A[n - 1] = Math.abs(A[n - 1] - x);
// Increment count c
c += 1;
}
// Return c
return c;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Original array
int arr[] = { 2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7 };
// Length of array
int N = arr.length;
// calling function
int x = minZero(arr, N);
// print the result
System.out.print(x);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# Python program for above approach
# Function to find no of iterations
def minZero(A, n):
# Initialize count c = 0
c = 0
# If 0 already in array return c
if min(A) == 0:
return c
# Iterate till we get zero in array
while min(A) != 0:
# Assign first element in x
x = A[0]
# Loop to subtract consecutive element
for i in range(n-1):
A[i] = abs(A[i]-A[i + 1])
A[n-1] = abs(A[n-1]-x)
# Increment count c
c += 1
# Return c
return c
# Driver Code
# Original array
arr = [2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7]
# Length of array
N = len(arr)
# calling function
x = minZero(arr, N)
# print the result
print(x)C#
// C# program for above approach
using System;
using System.Linq;
class GFG{
// Function to find no of iterations
static int minZero(int []A, int n)
{
// Initialize count c = 0
int c = 0;
// If 0 already in array return c
if (A.Min()== 0)
return c;
// Iterate till we get zero in array
while (A.Min() != 0) {
// Assign first element in x
int x = (int)A[0];
// Loop to subtract consecutive element
for (int i = 0; i < (n - 1); i++) {
A[i] = Math.Abs((int)A[i] - (int)A[i + 1]);
}
A[n - 1] = Math.Abs((int)A[n - 1] - x);
// Increment count c
c += 1;
}
// Return c
return c;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Original array
int []arr = { 2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7 };
// Length of array
int N = arr.Length;
// calling function
int x = minZero(arr, N);
// print the result
Console.Write(x);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Samim Hossain Mondal.Javascript
输出
3时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
高效方法:空间优化方法是一种基于逻辑和实现的方法。请按照以下步骤解决给定的问题。
- 将数组的第一个元素存储在变量x中。
- 现在找到连续元素之间的绝对差异。
- 替换索引0的结果。
- 从变量x中减去最后一个元素并存储它。
- 计算迭代次数并重复这些步骤。
- 返回计数作为最终答案。
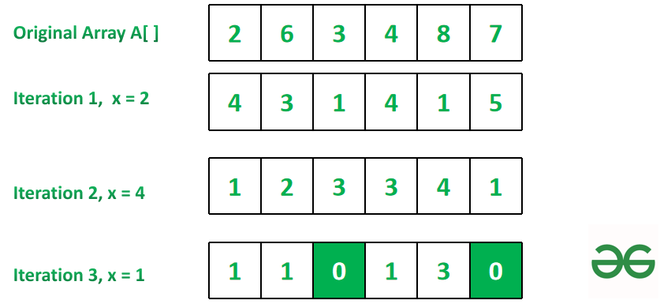
下面是上述方法的实现
C++
// C++ program for above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find no of iterations
int minZero(int A[], int n)
{
// Initialize count c = 0
int c = 0;
// If 0 already in array return c
if (*min_element(A + 0, A + n - 1) == 0)
return c;
// Iterate till we get zero in array
while (*min_element(A + 0, A + n - 1) != 0) {
// Assign first element in x
int x = A[0];
// Loop to subtract consecutive element
for (int i = 0; i < (n - 1); i++) {
A[i] = abs(A[i] - A[i + 1]);
}
A[n - 1] = abs(A[n - 1] - x);
// Increment count c
c += 1;
}
// Return c
return c;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Original array
int arr[] = { 2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7 };
// Length of array
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// calling function
int x = minZero(arr, N);
// print the result
cout << (x);
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp.
Java
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find no of iterations
static int minZero(int A[], int n)
{
// Initialize count c = 0
int c = 0;
// If 0 already in array return c
if (Arrays.stream(A).min().getAsInt()== 0)
return c;
// Iterate till we get zero in array
while (Arrays.stream(A).min().getAsInt() != 0) {
// Assign first element in x
int x = A[0];
// Loop to subtract consecutive element
for (int i = 0; i < (n - 1); i++) {
A[i] = Math.abs(A[i] - A[i + 1]);
}
A[n - 1] = Math.abs(A[n - 1] - x);
// Increment count c
c += 1;
}
// Return c
return c;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Original array
int arr[] = { 2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7 };
// Length of array
int N = arr.length;
// calling function
int x = minZero(arr, N);
// print the result
System.out.print(x);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Python3
# Python program for above approach
# Function to find no of iterations
def minZero(A, n):
# Initialize count c = 0
c = 0
# If 0 already in array return c
if min(A) == 0:
return c
# Iterate till we get zero in array
while min(A) != 0:
# Assign first element in x
x = A[0]
# Loop to subtract consecutive element
for i in range(n-1):
A[i] = abs(A[i]-A[i + 1])
A[n-1] = abs(A[n-1]-x)
# Increment count c
c += 1
# Return c
return c
# Driver Code
# Original array
arr = [2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7]
# Length of array
N = len(arr)
# calling function
x = minZero(arr, N)
# print the result
print(x)
C#
// C# program for above approach
using System;
using System.Linq;
class GFG{
// Function to find no of iterations
static int minZero(int []A, int n)
{
// Initialize count c = 0
int c = 0;
// If 0 already in array return c
if (A.Min()== 0)
return c;
// Iterate till we get zero in array
while (A.Min() != 0) {
// Assign first element in x
int x = (int)A[0];
// Loop to subtract consecutive element
for (int i = 0; i < (n - 1); i++) {
A[i] = Math.Abs((int)A[i] - (int)A[i + 1]);
}
A[n - 1] = Math.Abs((int)A[n - 1] - x);
// Increment count c
c += 1;
}
// Return c
return c;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Original array
int []arr = { 2, 6, 3, 4, 8, 7 };
// Length of array
int N = arr.Length;
// calling function
int x = minZero(arr, N);
// print the result
Console.Write(x);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Samim Hossain Mondal.
Javascript
输出
3时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)