净水
水通过水净化系统中的运河或冗长的管道输送,其中包含来自河流和湖泊的各种污染物和悬浮颗粒。河水通常用于为城市提供饮用水和餐饮用水。这种水不适合饮用或用餐,因为它含有高浓度的悬浮污染物和潜在的有害微生物,包括细菌和细菌。以下阶段组成水净化系统流程:
什么是净水?
Water purification is the process of removing unwanted chemical compounds, organic and inorganic elements, and biological pollutants from water.
蒸馏(将液体转化为蒸气以将其冷凝回液体形式)和去离子也是该过程的一部分(通过提取溶解的盐来去除离子)。水过滤的主要目标之一是生产安全的饮用水。水净化还满足医疗、制药、化学和工业应用中对清洁和饮用水的要求。在净化过程中,悬浮颗粒、寄生虫、细菌、藻类、病毒和真菌等污染物的浓度会降低。水净化有多种规模,从大型(例如,整个城市)到小型(例如,单个家庭)。
大多数社区依靠天然水体进行水净化和日常使用。这些资源通常分为地下水或地表水,包括地下含水层、小溪、溪流、河流和湖泊。由于最近的技术发展,海洋和咸海也被用作饮用和家庭用水的替代水源。
净水系统
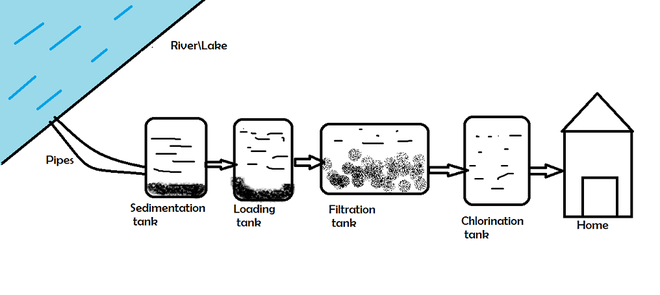
如以下四个阶段所述,供水被净化,以分别到达我们的家庭:
第一阶段:使用运河或长管道从河流和湖泊中收集水。
第 2 阶段:将其置于沉淀池中,使所有固体颗粒沉淀。当悬浮材料和物质沉到容器底部时,第二阶段开始。水保持不受干扰的时间越长,就越多的固体将由于重力而落到容器地板上。沉积过程必须在广大的沉积盆地中连续发生,以供社区供水。在过滤和消毒过程之前,需要这种简单、低成本的应用程序作为预处理步骤。
Sedimentation tank: The water from the river or lake is first filtered by the sedimentation tank. The water is allowed to sit for a while here. Many suspended solids settle to the bottom of the tank during this time.
第 3 阶段:将其转移到装载罐,所有分散的颗粒都可以在那里沉降。
Loading tank: Water is supplied to the loading tank from the sedimentation tank. Alum (phitkari) is added to the water in the loading tank. Clay particles in water are negatively charged colloidal particles. In the sedimentation tank, they do not settle. When alum is introduced, however, the positively charged aluminium ions in alum neutralize the negatively charged particles. As a result, suspended clay particles become heavy, loaded with aluminium ions, and settle to the bottom of the tank.
第 4 阶段:然后将水泵入三层过滤罐。此时胶体颗粒已落到供水底部,干净的水已准备好进行进一步处理。由于清水中存在微小的溶解颗粒,例如灰尘、寄生虫、化学物质、病毒和细菌,因此需要进行过滤。在过滤过程中,水会穿过大小和含量不同的物理颗粒。沙子、砾石和木炭是一些最常用的材料。
Filtration tank: The water is routed through a filtration tank after insoluble solids and other suspended pollutants have been removed. There are three layers in the filtering tank. Coarse gravel is placed at the bottom of the tank. Fine gravel is placed over it, and a thick layer of fine sand is laid on top of the gravel. These sand and gravel layers operate as filters. At the bottom, filthy water is added. All of the contaminants in the water are retained as the water climbs above, and only pure water leaves the tank at the top.
第 5 阶段:过滤后的水随后被送入氯化池进行消毒,在此与氯片结合以消除水中的微生物。餐饮水处理过程的最后一步是在供水中添加消毒剂,例如氯。自 1800 年代后期以来,就开始使用氯。一氯胺是一种用于水处理的氯。这与可能污染游泳池周围室内空气质量的类型不同。消毒作用是氧化和去除有机物,从而阻止寄生虫、病毒和细菌在饮用水中传播。
Chlorination tank: The water from the filtration tank is pumped into the chlorination tank, where it is bleached or treated with additional germicides to eliminate microorganisms. As a result, the water purification system has reached its conclusion, and pure water is now available for drinking and other human use.
某市餐饮\饮用水供应
经过上述程序获得的水不含任何污染物和微生物,并分配给我们的家庭饮用。
示例问题
问题 1:溶液和常规混合物之间的主要区别是什么?
回答:
In general, mixtures are heterogeneous, with a border separation between distinct substituents. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures in which there is no obvious separation between the various ingredients.
问题2:这两种纯物质有什么区别?给出每种类型的示例。
回答:
There are two sorts of pure substances:
- A pure substance formed up of atoms of the same type. Sulphur is a good example.
- A pure substance formed up of molecules of the same type. Water is good example.
问题 3:给出区分金属和非金属的两种物理性质。
回答:
Non-metals are neither malleable or ductile, whereas metals are.
问题4:你怎么知道给你的无色液体是纯净水?
回答:
Ans. We can test this by evaporating the colourless liquid provided. The colourless liquid is pure water if nothing is left behind.
问题 5:给出你认为水是化合物而不是混合物的两个理由。
回答:
Below are the reasons for water is a compound.
- Physical methods cannot split water into its constituents, hydrogen and oxygen.
- When water is created by burning hydrogen in oxygen, heat and light are released.
问题 6:给出糖在水中的溶液与糖和沙子的混合物具有相同的一个特性,以及一个没有的特性。
回答:
- Similarity: Physical procedures can be used to separate the mixture into its constituents in both circumstances is same.
- Difference: In a mixture of sugar and water, no separation is visible, however in a mixture of sand and sand, separation is visible.