Pandas DataFrame 中的转换函数
Python是一种用于进行数据分析的出色语言,主要是因为以数据为中心的Python包的奇妙生态系统。 Pandas 就是其中之一,它使导入和分析数据变得更加容易。在本文中,我们使用“ nba.csv ”文件下载 CSV,请单击此处。 
将 pandas 对象强制转换为指定的 dtype
DataFrame.astype()函数用于将 pandas 对象转换为指定的 dtype。 astype()函数还提供将任何合适的现有列转换为分类类型的能力。
代码 #1:转换权重列数据类型。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Making data frame from the csv file
df = pd.read_csv("nba.csv")
# Printing the first 10 rows of
# the data frame for visualization
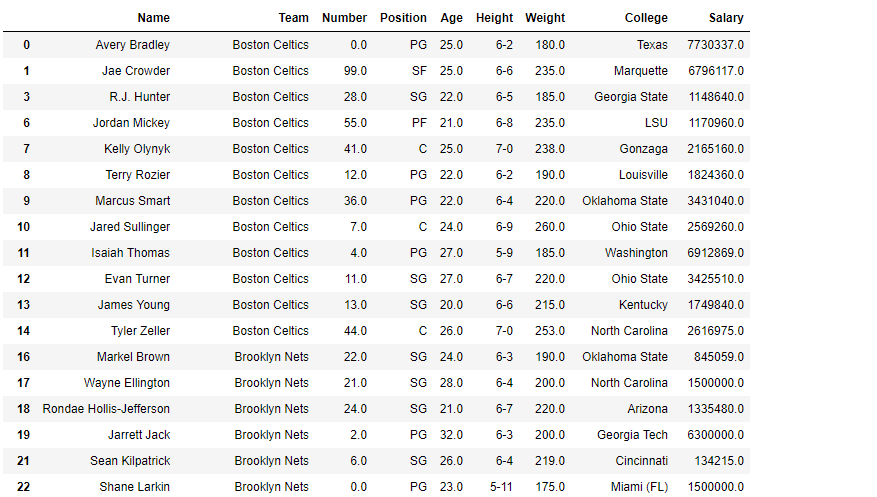
df[:10]

由于数据有一些“nan”值,所以为了避免任何错误,我们将删除所有包含任何nan值的行。
# drop all those rows which
# have any 'nan' value in it.
df.dropna(inplace = True)
# let's find out the data type of Weight column
before = type(df.Weight[0])
# Now we will convert it into 'int64' type.
df.Weight = df.Weight.astype('int64')
# let's find out the data type after casting
after = type(df.Weight[0])
# print the value of before
before
# print the value of after
after
输出: 

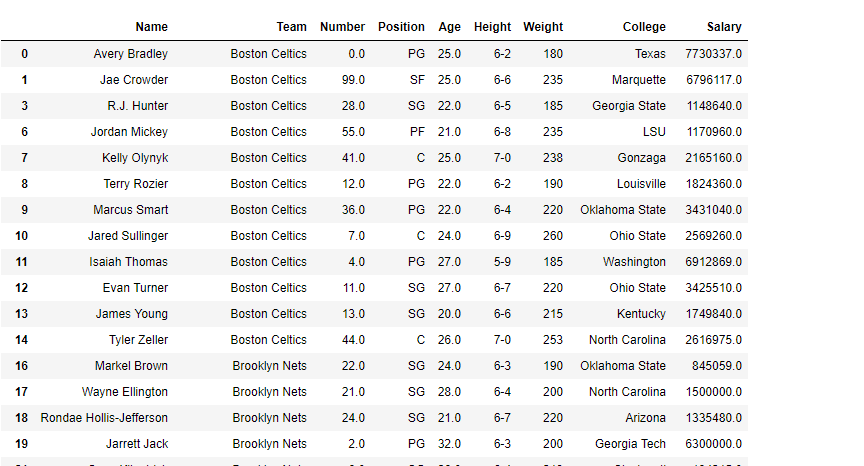
# print the data frame and see
# what it looks like after the change
df
为输入对象列推断更好的数据类型
DataFrame.infer_objects()函数尝试为输入对象列推断更好的数据类型。此函数尝试对对象类型化列进行软转换,使非对象列和不可转换列保持不变。推理规则与正常的 Series/DataFrame 构造期间相同。
代码 #1:使用infer_objects()函数来推断更好的数据类型。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":["sofia", 5, 8, 11, 100],
"B":[2, 8, 77, 4, 11],
"C":["amy", 11, 4, 6, 9]})
# Print the dataframe
print(df)
输出 : 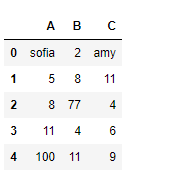
让我们看看数据框中每一列的dtype(数据类型)。
# to print the basic info
df.info()
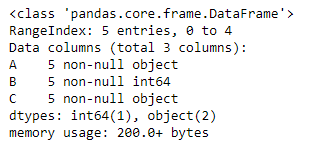
正如我们在输出中看到的,第一列和第三列是object类型。而第二列是int64类型。现在切片数据框并从中创建一个新的数据框。
# slice from the 1st row till end
df_new = df[1:]
# Let's print the new data frame
df_new
# Now let's print the data type of the columns
df_new.info()
输出 : 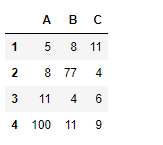
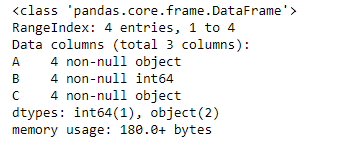
正如我们在输出中看到的,列“A”和“C”是对象类型,即使它们包含整数值。所以,让我们试试infer_objects()函数。
# applying infer_objects() function.
df_new = df_new.infer_objects()
# Print the dtype after applying the function
df_new.info()
输出 : 
现在,如果我们查看每一列的 dtype,我们可以看到列“A”和“C”现在是int64类型。
检测缺失值
DataFrame.isna()函数用于检测缺失值。它返回一个布尔值相同大小的对象,指示值是否为 NA。 NA 值,例如 None 或 numpy.NaN,被映射到 True 值。其他所有内容都映射到 False 值。空字符串” 或 numpy.inf 等字符不被视为 NA 值(除非您设置 pandas.options.mode.use_inf_as_na = True)。
代码 #1:使用isna()函数检测数据帧中的缺失值。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the dataframe
df = pd.read_csv("nba.csv")
# Print the dataframe
df
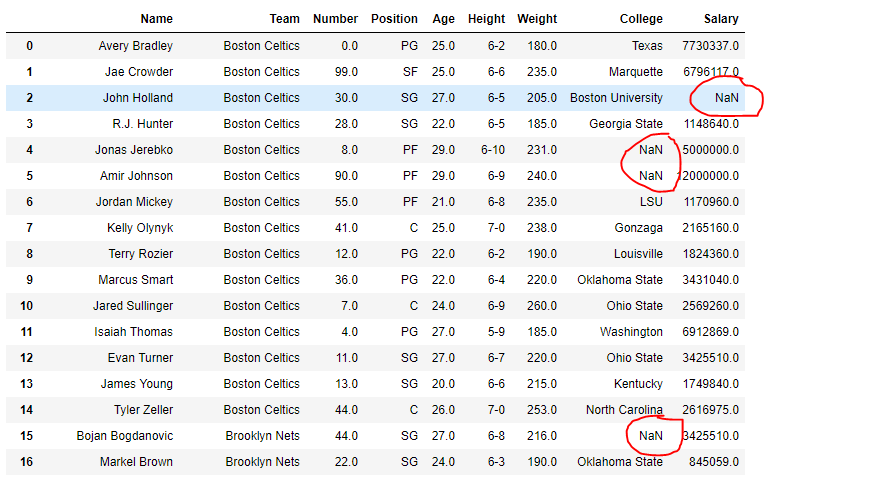
让我们使用isna()函数来检测缺失值。
# detect the missing values
df.isna()
输出 : 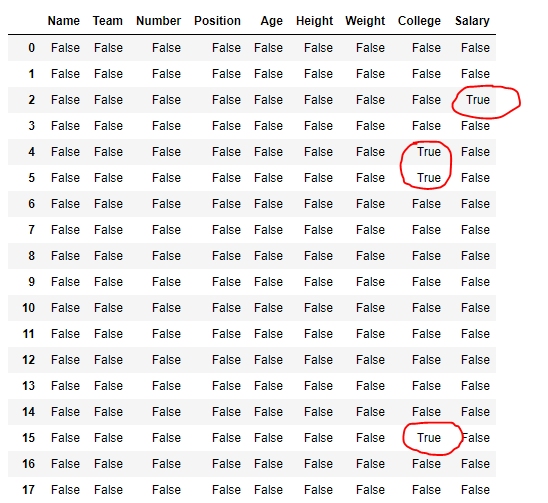
在输出中,对应于缺失值的单元格包含真值,否则为假。
检测现有/非缺失值
DataFrame.notna()函数检测数据框中的现有/非缺失值。该函数返回一个与应用它的对象大小相同的布尔对象,指示每个单独的值是否为na值。所有非缺失值都映射为 true,缺失值映射为 false。
代码 #1:使用notna()函数查找数据框中的所有非缺失值。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the first dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[14, 4, 5, 4, 1],
"B":[5, 2, 54, 3, 2],
"C":[20, 20, 7, 3, 8],
"D":[14, 3, 6, 2, 6]})
# Print the dataframe
print(df)
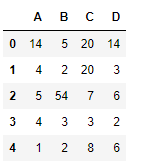
让我们使用dataframe.notna()函数来查找数据框中的所有非缺失值。
# find non-na values
df.notna()
输出 : 
正如我们在输出中看到的那样,数据帧中的所有非缺失值都已映射为 true。没有错误值,因为数据框中没有缺失值。
DataFrame中的转换方法
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| DataFrame.convert_objects() | Attempt to infer better dtype for object columns. |
| DataFrame.copy() | Return a copy of this object’s indices and data. |
| DataFrame.bool() | Return the bool of a single element PandasObject. |