Java中的ConcurrentHashMap
先决条件: ConcurrentMap
JDK 1.5 引入的ConcurrentHashMap类属于Java.util.concurrent包,它实现了 ConcurrentMap 以及 Serializable 接口。 ConcurrentHashMap 是 HashMap 的增强,因为我们知道在我们的应用程序中处理线程时 HashMap 不是一个好的选择,因为性能方面的 HashMap 达不到标准。
ConcurrentHashMap的关键点:
- ConcurrentHashMap 带下划线的数据结构是 Hashtable。
- ConcurrentHashMap 类是线程安全的,即多个线程可以对单个对象进行操作而不会产生任何复杂性。
- 一次任何数量的线程都适用于读取操作,而不会锁定 HashMap 中不存在的 ConcurrentHashMap 对象。
- 在 ConcurrentHashMap 中,根据并发级别将 Object 分成若干个段。
- ConcurrentHashMap 的默认并发级别为 16。
- 在 ConcurrentHashMap 中,一次任意数量的线程都可以执行检索操作,但对于对象中的更新,线程必须锁定线程想要操作的特定段。这种类型的锁定机制称为分段锁定或桶锁定。因此,线程一次可以执行 16 个更新操作。
- 在 ConcurrentHashMap 中无法将空对象作为键或值插入。
宣言:
public class ConcurrentHashMap
这里, K是键对象类型, V是值对象类型。
ConcurrentHashMap 的层次结构
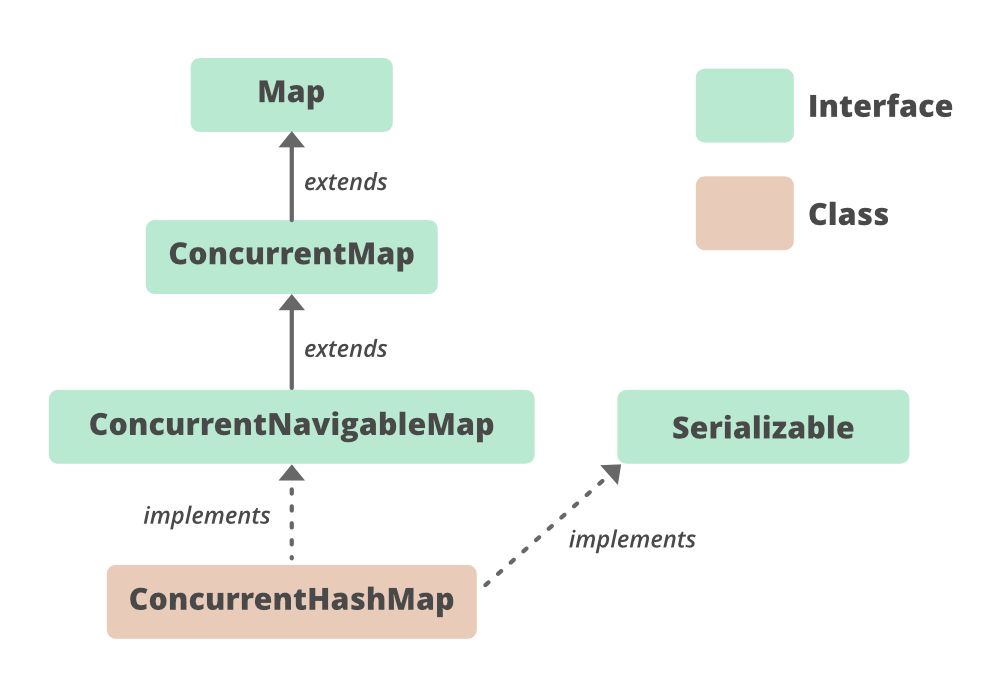
它实现了 Serializable 、 ConcurrentMap
ConcurrentHashMap 的构造函数
- 并发级别:它是并发更新地图的线程数。该实现执行内部大小调整以尝试容纳这么多线程。
- Load-Factor:这是一个阈值,用于控制调整大小。
- 初始容量:由实现最初提供的一定数量的元素的容纳。如果这个map的容量是10,这意味着它可以存储10个条目。
1. ConcurrentHashMap() :创建一个具有默认初始容量 (16)、负载因子 (0.75) 和 concurrencyLevel (16) 的新空映射。
ConcurrentHashMap
2. ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) :使用指定的初始容量、默认加载因子 (0.75) 和 concurrencyLevel (16) 创建一个新的空映射。
ConcurrentHashMap
3. ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) :使用指定的初始容量和负载因子以及默认的 concurrencyLevel (16) 创建一个新的空映射。
ConcurrentHashMap
4. ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) :使用指定的初始容量、负载因子和并发级别创建一个新的空映射。
ConcurrentHashMap
5. ConcurrentHashMap(Map m) :创建一个与给定映射具有相同映射的新映射。
ConcurrentHashMap
例子:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate working of ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class ConcurrentHashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create an instance of
// ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap m
= new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// Insert mappings using
// put method
m.put(100, "Hello");
m.put(101, "Geeks");
m.put(102, "Geeks");
// Here we cant add Hello because 101 key
// is already present in ConcurrentHashMap object
m.putIfAbsent(101, "Hello");
// We can remove entry because 101 key
// is associated with For value
m.remove(101, "Geeks");
// Now we can add Hello
m.putIfAbsent(103, "Hello");
// We cant replace Hello with For
m.replace(101, "Hello", "For");
System.out.println(m);
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate adding
// elements to the ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class AddingElementsToConcuurentHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap my_cmmap
= new ConcurrentHashMap();
// Adding elements to the map
// using put() method
my_cmmap.put("1", "1");
my_cmmap.put("2", "1");
my_cmmap.put("3", "1");
my_cmmap.put("4", "1");
my_cmmap.put("5", "1");
my_cmmap.put("6", "1");
// Printing the map
System.out.println("Mappings of my_cmmap : "
+ my_cmmap);
// create another concurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap new_chm
= new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// copy mappings from my_cmmap to new_chm
new_chm.putAll(my_cmmap);
// Displaying the new map
System.out.println("New mappings are: " + new_chm);
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate removing
// elements from ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class RemoveElementsFromConcurrentHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating ConcurrentHashMap
Map my_cmmap
= new ConcurrentHashMap();
// Adding elements to the map
// using put() method
my_cmmap.put("1", "1");
my_cmmap.put("2", "1");
my_cmmap.put("3", "1");
my_cmmap.put("4", "1");
my_cmmap.put("5", "1");
my_cmmap.put("6", "1");
// Printing the map
System.out.println("Map: " + my_cmmap);
System.out.println();
// Removing the mapping
// with existing key 6
// using remove() method
String valueRemoved = my_cmmap.remove("6");
// Printing the map after remove()
System.out.println(
"After removing mapping with key 6:");
System.out.println("Map: " + my_cmmap);
System.out.println("Value removed: "
+ valueRemoved);
System.out.println();
// Removing the mapping
// with non-existing key 10
// using remove() method
valueRemoved = my_cmmap.remove("10");
// Printing the map after remove()
System.out.println(
"After removing mapping with key 10:");
System.out.println("Map: " + my_cmmap);
System.out.println("Value removed: "
+ valueRemoved);
System.out.println();
// Now clear the map using clear()
my_cmmap.clear();
// Print the clea Map
System.out.println("Map after use of clear(): "
+ my_cmmap);
}
} Java
// Java Program Demonstrate accessing
// elements of ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class AccessingElementsOfConcurrentHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create an instance of ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap chm
= new ConcurrentHashMap();
// insert mappings using put method
chm.put(100, "Geeks");
chm.put(101, "for");
chm.put(102, "Geeks");
chm.put(103, "Contribute");
// Displaying the HashMap
System.out.println("The Mappings are: ");
System.out.println(chm);
// Display the value of 100
System.out.println("The Value associated to "
+ "100 is : " + chm.get(100));
// Getting the value of 103
System.out.println("The Value associated to "
+ "103 is : " + chm.get(103));
}
} Java
// Java Program for traversing a
// ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class TraversingConcurrentHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create an instance of ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap chmap
= new ConcurrentHashMap();
// Add elements using put()
chmap.put(8, "Third");
chmap.put(6, "Second");
chmap.put(3, "First");
chmap.put(11, "Fourth");
// Create an Iterator over the
// ConcurrentHashMap
Iterator >
itr = chmap.entrySet().iterator();
// The hasNext() method is used to check if there is
// a next element The next() method is used to
// retrieve the next element
while (itr.hasNext()) {
ConcurrentHashMap.Entry entry
= itr.next();
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey()
+ ", Value = "
+ entry.getValue());
}
}
} {100=Hello, 102=Geeks, 103=Hello}
ConcurrentHashMap 的基本操作
1.添加元素
要将映射插入 ConcurrentHashMap,我们可以使用 put() 或 putAll() 方法。下面的示例代码解释了这两种方法。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate adding
// elements to the ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class AddingElementsToConcuurentHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap my_cmmap
= new ConcurrentHashMap();
// Adding elements to the map
// using put() method
my_cmmap.put("1", "1");
my_cmmap.put("2", "1");
my_cmmap.put("3", "1");
my_cmmap.put("4", "1");
my_cmmap.put("5", "1");
my_cmmap.put("6", "1");
// Printing the map
System.out.println("Mappings of my_cmmap : "
+ my_cmmap);
// create another concurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap new_chm
= new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// copy mappings from my_cmmap to new_chm
new_chm.putAll(my_cmmap);
// Displaying the new map
System.out.println("New mappings are: " + new_chm);
}
}
Mappings of my_cmmap : {1=1, 2=1, 3=1, 4=1, 5=1, 6=1}
New mappings are: {1=1, 2=1, 3=1, 4=1, 5=1, 6=1}
2. 移除元素
要删除映射,我们可以使用 ConcurrentHashmap 类的 remove(Object key) 方法。如果映射中不存在该键,则此函数不执行任何操作。要清除整个地图,我们可以使用 clear() 方法。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate removing
// elements from ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class RemoveElementsFromConcurrentHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating ConcurrentHashMap
Map my_cmmap
= new ConcurrentHashMap();
// Adding elements to the map
// using put() method
my_cmmap.put("1", "1");
my_cmmap.put("2", "1");
my_cmmap.put("3", "1");
my_cmmap.put("4", "1");
my_cmmap.put("5", "1");
my_cmmap.put("6", "1");
// Printing the map
System.out.println("Map: " + my_cmmap);
System.out.println();
// Removing the mapping
// with existing key 6
// using remove() method
String valueRemoved = my_cmmap.remove("6");
// Printing the map after remove()
System.out.println(
"After removing mapping with key 6:");
System.out.println("Map: " + my_cmmap);
System.out.println("Value removed: "
+ valueRemoved);
System.out.println();
// Removing the mapping
// with non-existing key 10
// using remove() method
valueRemoved = my_cmmap.remove("10");
// Printing the map after remove()
System.out.println(
"After removing mapping with key 10:");
System.out.println("Map: " + my_cmmap);
System.out.println("Value removed: "
+ valueRemoved);
System.out.println();
// Now clear the map using clear()
my_cmmap.clear();
// Print the clea Map
System.out.println("Map after use of clear(): "
+ my_cmmap);
}
}
Map: {1=1, 2=1, 3=1, 4=1, 5=1, 6=1}
After removing mapping with key 6:
Map: {1=1, 2=1, 3=1, 4=1, 5=1}
Value removed: 1
After removing mapping with key 10:
Map: {1=1, 2=1, 3=1, 4=1, 5=1}
Value removed: null
Map after use of clear(): {}
3. 访问元素
我们可以使用 get() 方法访问 ConcurrentHashMap 的元素,下面给出了这个例子。
Java
// Java Program Demonstrate accessing
// elements of ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class AccessingElementsOfConcurrentHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create an instance of ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap chm
= new ConcurrentHashMap();
// insert mappings using put method
chm.put(100, "Geeks");
chm.put(101, "for");
chm.put(102, "Geeks");
chm.put(103, "Contribute");
// Displaying the HashMap
System.out.println("The Mappings are: ");
System.out.println(chm);
// Display the value of 100
System.out.println("The Value associated to "
+ "100 is : " + chm.get(100));
// Getting the value of 103
System.out.println("The Value associated to "
+ "103 is : " + chm.get(103));
}
}
The Mappings are:
{100=Geeks, 101=for, 102=Geeks, 103=Contribute}
The Value associated to 100 is : Geeks
The Value associated to 103 is : Contribute
4. 遍历
我们可以使用 Iterator 接口来遍历 Collection Framework 的任何结构。由于迭代器使用一种类型的数据,我们使用 Entry< ? , ? > 将两种不同的类型解析为兼容的格式。然后使用 next() 方法打印 ConcurrentHashMap 的元素。
Java
// Java Program for traversing a
// ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class TraversingConcurrentHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create an instance of ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap chmap
= new ConcurrentHashMap();
// Add elements using put()
chmap.put(8, "Third");
chmap.put(6, "Second");
chmap.put(3, "First");
chmap.put(11, "Fourth");
// Create an Iterator over the
// ConcurrentHashMap
Iterator >
itr = chmap.entrySet().iterator();
// The hasNext() method is used to check if there is
// a next element The next() method is used to
// retrieve the next element
while (itr.hasNext()) {
ConcurrentHashMap.Entry entry
= itr.next();
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey()
+ ", Value = "
+ entry.getValue());
}
}
}
Key = 3, Value = First
Key = 6, Value = Second
Key = 8, Value = Third
Key = 11, Value = Fourth
ConcurrentHashMap 的方法
- K - 地图上键的类型。
- V – 映射中映射的值的类型。
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| clear() | Removes all of the mappings from this map. |
| compute(K key, BiFunction remappingFunction) | Attempts to compute a mapping for the specified key and its current mapped value (or null if there is no current mapping). |
| computeIfAbsent(K key, Function mappingFunction) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value, attempts to compute its value using the given mapping function and enters it into this map unless null. |
| computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction remappingFunction) | If the value for the specified key is present, attempts to compute a new mapping given the key and its current mapped value. |
| contains(Object value) | Tests if some keymaps into the specified value in this table. |
| containsKey(Object key) | Tests if the specified object is a key in this table. |
| containsValue(Object value) | Returns true if this map maps one or more keys to the specified value. |
| elements() | Returns an enumeration of the values in this table. |
| entrySet() | Returns a Set view of the mappings contained in this map. |
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object with this map for equality. |
| forEach(long parallelismThreshold, BiConsumer action) | Performs the given action for each (key, value). |
| forEach(long parallelismThreshold, BiFunction transformer, Consumer action) | Performs the given action for each non-null transformation of each (key, value). |
| forEachEntry(long parallelismThreshold, Consumer> action) | Performs the given action for each entry. |
| forEachEntry(long parallelismThreshold, Function | Performs the given action for each non-null transformation of each entry. |
| forEachKey(long parallelismThreshold, Consumer action) | Performs the given action for each key. |
| forEachKey(long parallelismThreshold, Function transformer, Consumer action) | Performs the given action for each non-null transformation of each key. |
| forEachValue(long parallelismThreshold, Consumer action) | Performs the given action for each value. |
| forEachValue(long parallelismThreshold, Function transformer, Consumer action) | Performs the given action for each non-null transformation of each value. |
| get(Object key) | Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or null if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
| getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or the given default value if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this Map, i.e., the sum of, for each key-value pair in the map, key.hashCode() ^ value.hashCode(). |
| keys() | Returns an enumeration of the keys in this table. |
| keySet() | Returns a Set view of the keys contained in this map. |
| keySet(V mappedValue) | Returns a Set view of the keys in this map, using the given common mapped value for any additions (i.e., Collection.add(E) and Collection.addAll(Collection)). |
| mappingCount() | Returns the number of mappings. |
| merge(K key, V value, BiFunction remappingFunction) | If the specified key is not already associated with a (non-null) value, associates it with the given value. |
| newKeySet() | Creates a new Set backed by a ConcurrentHashMap from the given type to Boolean.TRUE. |
| newKeySet(int initialCapacity) | Creates a new Set backed by a ConcurrentHashMap from the given type to Boolean.TRUE. |
| put(K key, V value) | Maps the specified key to the specified value in this table. |
| putAll(Map m) | Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this one. |
| putIfAbsent(K key, V value) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value, associates it with the given value. |
| reduce(long parallelismThreshold, BiFunction transformer, BiFunction reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all (key, value) pairs using the given reducer to combine values, or null if none. |
| reduceEntries(long parallelismThreshold, BiFunction | Returns the result of accumulating all entries using the given reducer to combine values, or null if none. |
| reduceEntries(long parallelismThreshold, Function | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all entries using the given reducer to combine values, or null if none. |
| reduceEntriesToDouble(long parallelismThreshold, ToDoubleFunction | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all entries using the given reducer to combine values, and the given basis as an identity value. |
| reduceEntriesToInt(long parallelismThreshold, ToIntFunction | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all entries using the given reducer to combine values, and the given basis as an identity value. |
| reduceEntriesToLong(long parallelismThreshold, ToLongFunction | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all entries using the given reducer to combine values, and the given basis as an identity value. |
| reduceKeys(long parallelismThreshold, BiFunction reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating all keys using the given reducer to combine values, or null if none. |
| reduceKeys(long parallelismThreshold, Function transformer, BiFunction reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all keys using the given reducer to combine values, or null if none. |
| reduceKeysToDouble(long parallelismThreshold, ToDoubleFunction transformer, double basis, DoubleBinaryOperator reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all keys using the given reducer to combine values, and the given basis as an identity value. |
| reduceKeysToInt(long parallelismThreshold, ToIntFunction transformer, int basis, IntBinaryOperator reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all keys using the given reducer to combine values, and the given basis as an identity value. |
| reduceKeysToLong(long parallelismThreshold, ToLongFunction transformer, long basis, LongBinaryOperator reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all keys using the given reducer to combine values, and the given basis as an identity value. |
| reduceToDouble(long parallelismThreshold, ToDoubleBiFunction transformer, double basis, DoubleBinaryOperator reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all (key, value) pairs using the given reducer to combine values, and the given basis as an identity value. |
| reduceToInt(long parallelismThreshold, ToIntBiFunction transformer, int basis, IntBinaryOperator reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all (key, value) pairs using the given reducer to combine values, and the given basis as an identity value. |
| reduceToLong(long parallelismThreshold, ToLongBiFunction transformer, long basis, LongBinaryOperator reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all (key, value) pairs using the given reducer to combine values, and the given basis as an identity value. |
| reduceValues(long parallelismThreshold, BiFunction reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating all values using the given reducer to combine values, or null if none. |
| reduceValues(long parallelismThreshold, Function transformer, BiFunction reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all values using the given reducer to combine values, or null if none. |
| reduceValuesToDouble(long parallelismThreshold, ToDoubleFunction transformer, double basis, DoubleBinaryOperator reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all values using the given reducer to combine values, and the given basis as an identity value. |
| reduceValuesToInt(long parallelismThreshold, ToIntFunction transformer, int basis, IntBinaryOperator reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all values using the given reducer to combine values, and the given basis as an identity value. |
| reduceValuesToLong(long parallelismThreshold, ToLongFunction transformer, long basis, LongBinaryOperator reducer) | Returns the result of accumulating the given transformation of all values using the given reducer to combine values, and the given basis as an identity value. |
| remove(Object key) | Removes the key (and its corresponding value) from this map. |
| remove(Object key, Object value) | Removes the entry for a key only if currently mapped to a given value. |
| replace(K key, V value) | Replaces the entry for a key only if currently mapped to some value. |
| replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) | Replaces the entry for a key only if currently mapped to a given value. |
| search(long parallelismThreshold, BiFunction searchFunction) | Returns a non-null result from applying the given search function on each (key, value), or null if none. |
| searchEntries(long parallelismThreshold, Function | Returns a non-null result from applying the given search function on each entry, or null if none. |
| searchKeys(long parallelismThreshold, Function searchFunction) | Returns a non-null result from applying the given search function on each key, or null if none. |
| searchValues(long parallelismThreshold, Function searchFunction) | Returns a non-null result from applying the given search function on each value, or null if none. |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this map. |
| values() | Returns a Collection view of the values contained in this map. |
在类Java.util.AbstractMap 中声明的方法 METHOD DESCRIPTIONclone() Returns a shallow copy of this AbstractMap instance: the keys and values themselves are not cloned. isEmpty() Returns true if this map contains no key-value mappings. size() Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map.
在接口Java .util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap 中声明的方法 METHOD DESCRIPTIONforEach(BiConsumer action) Performs the given action for each entry in this map until all entries have been processed or the action throws an exception. replaceAll(BiFunction function) Replaces each entry’s value with the result of invoking the given function on that entry until all entries have been processed or the function throws an exception.
必读: HashMap 和 ConcurrentHashMap 的区别
ConcurrentHashMap 与 Hashtable
哈希表
- Hashtable是 Map 数据结构的一种实现
- 这是一个遗留类,其中所有方法都使用 synchronized 关键字在 Hashtable 实例上同步。
- 线程安全,因为它的方法是同步的
并发哈希映射
- ConcurrentHashMap实现了 Map 数据结构,也像 Hashtable 一样提供线程安全。
- 它通过将完整的哈希表数组划分为段或部分并允许并行访问这些段来工作。
- 锁定在哈希图存储桶级别的粒度要细得多。
- 当您的应用程序需要非常高的并发性时,请使用ConcurrentHashMap 。
- 它是线程安全的,无需同步整个地图。
- 在使用段级别或存储桶级别的锁定完成写入时,读取可能会非常快。
- 在对象级别没有锁定。
- 如果一个线程尝试修改它而另一个线程正在对其进行迭代,则 ConcurrentHashMap 不会引发ConcurrentModificationException 。
- ConcurrentHashMap 不允许 NULL 值,因此在ConcurrentHashMap中键不能为空
- 如果一个线程尝试修改 ConcurrentHashMap,而另一个线程正在对其进行迭代,则 ConcurrentHashMap 不会引发ConcurrentModificationException 。
| Properties | Hashtable | ConcurrentHashMap |
|---|---|---|
| Creation | Map ht = new Hashtable(); | Map chm = new ConcurrentHashMap(); |
| Is Null Key Allowed ? | No | No |
| Is Null Value Allowed ? | No | No (does not allow either null keys or values) |
| Is Thread Safe ? | Yes | Yes, Thread safety is ensured by having separate locks for separate buckets, resulting in better performance. Performance is further improved by providing read access concurrently without any blocking. |
| Performance | Slow due to synchronization overhead. | Faster than Hashtable. ConcurrentHashMap is a better choice when there are more reads than writes. |
| Iterator | Hashtable uses enumerator to iterate the values of Hashtable object. Enumerations returned by the Hashtable keys and elements methods are not fail-fast. | Fail-safe iterator: Iterator provided by the ConcurrentHashMap is fail-safe, which means it will not throw ConcurrentModificationException. |
结论:
如果需要线程安全的高并发实现,则建议使用ConcurrentHashMap代替Hashtable 。
参考: Java : Java