R 编程中的二比例 Z 检验
两比例 z 检验用于比较两个观察到的比例。例如,假设有两组人:
- A组肺癌:n = 500
- B组,健康个体:n = 500
每组吸烟人数如下:
- A 组肺癌:n = 500, 490 吸烟者,p A = 490/500 = 98
- B 组,健康个体:n = 500,400 名吸烟者,p B = 400/500 = 80
在此设置中:
- 吸烟者的总比例为 p = frac(490+400) 500 + 500 = 89
- 非吸烟者的总体比例为 q = 1 – p = 11
所以我们想知道,这两组个体中吸烟者的比例是否相同?
二比例 Z 检验的公式
检验统计量(也称为 z 检验)可以计算如下:
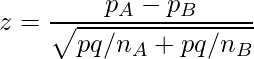
where,
pA: the proportion observed in group A with size nA
pB: the proportion observed in group B with size nB
p and q: the overall proportions
R中的实现
在 R 语言中,用于执行 z 测试的函数是prop.test() 。
Syntax:
prop.test(x, n, p = NULL, alternative = “two.sided”, correct = TRUE)
Parameters:
x = number of successes and failures in data set.
n = size of data set.
p = probabilities of success. It must be in the range of 0 to 1.
alternative = a character string specifying the alternative hypothesis.
correct = a logical indicating whether Yates’ continuity correction should be applied where possible.
示例 1:
假设我们有两组学生 A 和 B。A 组有 400 名学生和 342 名女学生的早班。 B组晚班400人,女学生290人。使用 5% 的 alpha 级别。我们想知道,这两组学生中女性的比例是否相同?这里让我们使用prop.test() 。
# prop Test in R
prop.test(x = c(342, 290),
n = c(400, 400))
输出:
2-sample test for equality of proportions with continuity correction
data: c(342, 290) out of c(400, 400)
X-squared = 19.598, df = 1, p-value = 9.559e-06
alternative hypothesis: two.sided
95 percent confidence interval:
0.07177443 0.18822557
sample estimates:
prop 1 prop 2
0.855 0.725
- 它返回一个 p 值
- 备择假设
- 95% 置信区间
- 成功的概率
因此作为结果检验的 p 值为 9.558674e-06 大于 alpha 的显着性水平。这是0.05。这意味着两个比例之间没有区别。现在,如果您想测试 A(p A ) 组中观察到的女性比例是否小于 B(p B ) 组中观察到的女性比例,那么命令是:
# prop Test in R
prop.test(x = c(342, 290),
n = c(400, 400),
alternative = "less")
输出:
2-sample test for equality of proportions with continuity correction
data: c(342, 290) out of c(400, 400)
X-squared = 19.598, df = 1, p-value = 1
alternative hypothesis: less
95 percent confidence interval:
-1.0000000 0.1792664
sample estimates:
prop 1 prop 2
0.855 0.725
如果要测试 A 组中观察到的女性比例(p A )是否大于组中观察到的女性比例(p B ),则命令为:
# prop Test in R
prop.test(x = c(342, 290),
n = c(400, 400),
alternative = "greater")
输出:
2-sample test for equality of proportions with continuity correction
data: c(342, 290) out of c(400, 400)
X-squared = 19.598, df = 1, p-value = 4.779e-06
alternative hypothesis: greater
95 percent confidence interval:
0.08073363 1.00000000
sample estimates:
prop 1 prop 2
0.855 0.725
示例 2:
ABC 公司生产平板电脑。为了质量控制,测试了两组片剂。在第一组中,700 人中有 32 人被发现存在某种缺陷。在第二组中,400 人中有 30 人被发现存在某种缺陷。两组之间的差异是否显着?使用 5% 的 alpha 级别。这里让我们使用prop.test() 。
# prop Test in R
prop.test(x = c(32, 30),
n = c(700, 400))
输出:
2-sample test for equality of proportions with continuity correction
data: c(32, 30) out of c(700, 400)
X-squared =3.5725, df = 1, p-value = 0.05874
alternative hypothesis: two.sided
95 percent confidence interval:
-0.061344109 0.002772681
sample estimates:
prop 1 prop 2
0.04571429 0.07500000
- 它返回一个 p 值
- 备择假设
- 95% 置信区间
- 成功的概率
因此作为结果检验的 p 值为 0.0587449 大于 alpha 的显着性水平,即 0.05。这意味着两个比例之间没有显着差异。现在如果要测试第一组观察到的缺陷比例是否小于第二组观察到的缺陷比例,那么命令是:
# prop Test in R
prop.test(x = c(32, 30),
n = c(700, 400),
alternative = "less")
输出:
2-sample test for equality of proportions with continuity correction
data: c(32, 30) out of c(700, 400)
X-squared = 3.5725, df = 1, p-value = 0.02937
alternative hypothesis: less
95 percent confidence interval:
-1.000000000 -0.002065656
sample estimates:
prop 1 prop 2
0.04571429 0.07500000
如果要测试第一组观察到的缺陷比例是否大于第二组观察到的缺陷比例,那么命令是:
# prop.test() in R
prop.test(x = c(32, 30),
n = c(700, 400),
alternative = "greater")
输出:
2-sample test for equality of proportions with continuity correction
data: c(32, 30) out of c(700, 400)
X-squared = 3.5725, df = 1, p-value = 0.9706
alternative hypothesis: greater
95 percent confidence interval:
-0.05650577 1.00000000
sample estimates:
prop 1 prop 2
0.04571429 0.07500000