增加和减少间隔
导数是衡量变量变化率的方法。当谈到函数和微积分时,导数为我们提供了大量关于函数形状和图形的信息。它们提供有关函数增加或减少的区域的信息。它们对于找出函数获得的最大值和最小值也很有用。通过从导数中收集的信息绘制函数的图形可以帮助我们找出有关函数行为的极限和其他信息。
衍生品
导数是函数上的一个点,它为我们提供了函数在该特定点的变化率的度量。从几何上讲,它们为我们提供了有关该点切线斜率的信息。此信息可用于找出函数增加或减少的区间或区域。一旦知道了这样的间隔,就不太难找出函数图中的山谷和山丘。下图显示了函数f(x) 及其增加和减少的区间。
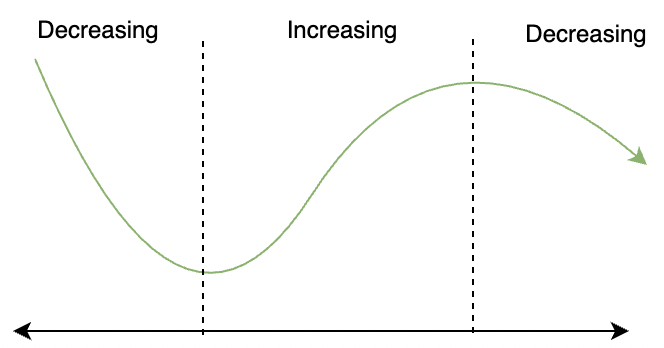
For a function f(x). For an interval I defined in its domain.
- The function f(x) is said to be increasing in an interval I if for every a < b, f(a) ≤ f(b).
- The function f(x) is said to be decreasing in an interval I if for every a < b, f(a) ≥ f(b).
The function is called strictly increasing if for every a < b, f(a) < f(b). Similar definition holds for strictly decreasing case.
增加和减少间隔
目标是在不查看函数图的情况下识别这些区域。为此,让我们看一下这些区域中函数的导数。这些导数只不过是该曲线上切线的斜率这一事实已经确定。下图显示了这条曲线上不同点的切线斜率。

请注意,在函数减小的区域中,曲线的斜率对于函数增加的区域实际上是负值和正值。峰谷处的斜率为零。所以,正式地说。
Let’s say f(x) is a function continuous on [a, b] and differentiable in the interval (a, b).
- If f'(c) > 0 for all c in (a, b), then f(x) is said to be increasing in the interval.
- If f'(c) < 0 for all c in (a, b), then f(x) is said to be decreasing in the interval.
- If f'(c) = 0 for all c in (a, b), then f(x) is said to be constant in the interval.
关键点
在上图中,请注意函数何时从减少到增加或从增加到减少。有山谷或山峰。这些谷和峰是函数的极值点,因此称为极值。从图中可以很明显地看出,在这些点上,函数的导数变为零。该函数在这些点处达到其最小值和最大值。
Note: A function can have any number of critical points. While all the critical points do not necessarily give maximum and minimum value of the function. But every critical point is valley that is a minimum point in local region.
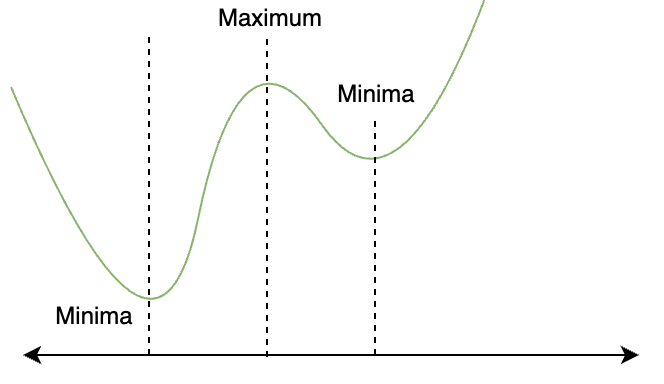
上图中,存在三个极值,其中两个是极小值,但只有一个全局极大值和全局极小值。所以在形式上,
For a function f(x), a point x = c is extrema if,
f'(c) = 0
识别递增和递减区间
从上图中可以清楚地看出,函数的每个极值都是其导数改变符号的点。也就是说,函数要么从增加变为减少,反之亦然。在寻找函数增加或减少的区域时,必须环顾极端情况。对于任何函数f(x) 和给定的区间,需要遵循以下步骤来找出这些区间:
- 检查函数在给定区间内是否可微且连续。
- 求解方程 f'(x) = 0,这个方程的解给了我们极值。
- 对于极值点 x = c,查看该点附近的区域并检查导数的符号以找出函数增加或减少的区间。
让我们看一些与这些概念相关的示例问题。
示例问题
问题1:对于给定的函数,判断它在区域[-1,1]中是增加还是减少
f(x) = e x
解决方案:
To analyze any function, first step is to look for critical points.
f(x) = ex
f'(x) = ex …. (1)
Solving the equation f'(x) = 0
ex = 0
There is no critical point for this function in the given region. That means that in the given region, this function must be either monotonically increasing or monotonically decreasing. For that, check the derivative of the function in this region.
f'(x) > 0 in the interval [0,1].
Thus, the function is increasing.
问题2:对于给定的函数,判断它在区域[2,4]中是增加还是减少
f(x) = x 2 – x – 4
解决方案:
To analyze any function, first step is to look for critical points.
f(x) = x2 – x – 4
f'(x) = 2x – 1 …. (1)
Solving the equation f'(x) = 0
2x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = 0.5
The critical point is outside the region of interest. That means that in the given region, this function must be either monotonically increasing or monotonically decreasing. For that, check the derivative of the function in this region.
f'(x) > 0 in the interval [2,4].
Thus, the function is increasing.
问题 3:找到给定函数增加或减少的区域。
f(x) = 3x + 4
解决方案:
To analyze any function, first step is to look for critical points.
f(x) = 3x + 4
f'(x) = 3
This equation is not zero for any x. That means the derivative of this function is constant through it’s domain.
Since f'(x) > 0 for all the values of x.
The function is monotonically increasing over it’s domain.
问题 4:找出给定函数增加或减少的区域。
f(x) = x 2 + 4x + 4
解决方案:
To analyze any function, first step is to look for critical points.
f(x) = x2 + 4x + 4
f'(x) = 2x + 4 …. (1)
Solving the equation f'(x) = 0
2x + 4 = 0
⇒ x = -2
Thus, at x =-2 the derivative this function changes its sign. Check for the sign of derivative in its vicinity.
at x = -1
f'(x) = 2(-1) + 4 = 2 > 0
This means for x > -2 the function is increasing.
at x = -3
f'(x) = 2(-3) + 4 = -2 < 0
For x < -2, the function is decreasing.
问题 5:找出给定函数增加或减少的区域。
f(x) = x 2 + 3x
解决方案:
To analyze any function, first step is to look for critical points.
f(x) = x2 + 3x
f'(x) = 2x + 3 …. (1)
Solving the equation f'(x) = 0
2x + 3 = 0
⇒ x = -1.5
Thus, at x =-1.5 the derivative this function changes its sign. Check for the sign of derivative in its vicinity.
at x = -1
f'(x) = 2(-1) + 3 = 1 > 0
This means for x > -1.5 the function is increasing.
at x = -3
f'(x) = 2(-3) + 3 = -3 < 0
For x < -1.5, the function is decreasing.
问题 6:找出给定函数增加或减少的区域。
f(x) = e x + e -x
解决方案:
To analyze any function, first step is to look for critical points.
f(x) = ex + e-x
f'(x) = ex – e-x …. (1)
Solving the equation f'(x) = 0
ex – e-x= 0
⇒ ex = e-x
⇒ e2x = 1
⇒ e2x = e0
Comparing both sides of the equation,
⇒2x = 0
⇒x = 0
Thus, at x = 0 the derivative this function changes its sign. Check for the sign of derivative in its vicinity.
at x = 1
f'(x) = e1 – e-1 > 0
This means for x > 0 the function is increasing.
at x = –1
f'(x) = e-1 – e1 < 0
For x < 0, the function is decreasing.