给定一个NXM区域。您有无数个大小为2 i X 2 i的图块,其中i = 0、1、2,…依此类推。任务是找到用瓷砖填充给定区域所需的最小瓷砖数量。
例子:
输入:N = 5,M =6。输出:9 5 X 6的区域至少可以覆盖9个图块。 1 X 1的6个图块2 X 2的2个图块,4 X 4的1个图块。 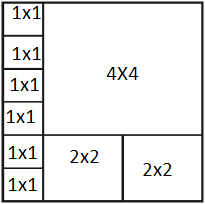 输入:N = 10,M =5。输出:14
输入:N = 10,M =5。输出:14
想法是将给定区域划分为最接近的2 i X 2 i 。
让我们将问题分为几个案例:
情况1:如果N为奇数而M为偶数,则用M个1 X 1的图块填充行或列。然后计算N / 2 XM / 2面积大小的最小图块数。同样,如果M为奇数而N为偶数,则将N添加到我们的答案中,并找到N / 2 XM / 2区域的最小图块数。
情况2:如果N和M都为奇数,则填充一行和一列,因此将N + M – 1添加到答案中,并找到填充N / 2 XM / 2区域所需的最小图块数。
情况3:如果N和M均为偶数,请计算填充N / 2 XM / 2区域所需的最小块数。因为将两个尺寸减半不会改变所需的图块数量。
以下是此方法的实现:
C++
#include
using namespace std;
int minTiles(int n, int m)
{
// base case, when area is 0.
if (n == 0 || m == 0)
return 0;
// If n and m both are even, calculate tiles for n/2 x m/2
// Halving both dimensions doesn't change the number of tiles
else if (n%2 == 0 && m%2 == 0)
return minTiles(n/2, m/2);
// If n is even and m is odd
// Use a row of 1x1 tiles
else if (n%2 == 0 && m%2 == 1)
return (n + minTiles(n/2, m/2));
// If n is odd and m is even
// Use a column of 1x1 tiles
else if (n%2 == 1 && m%2 == 0)
return (m + minTiles(n/2, m/2));
// If n and m are odd
// add row + column number of tiles
else
return (n + m - 1 + minTiles(n/2, m/2));
}
// Driven Program
int main()
{
int n = 5, m = 6;
cout << minTiles(n, m) << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java code for Minimum tiles of
// sizes in powers of two to cover
// whole area
class GFG {
static int minTiles(int n, int m)
{
// base case, when area is 0.
if (n == 0 || m == 0)
return 0;
// If n and m both are even,
// calculate tiles for n/2 x m/2
// Halving both dimensions doesn't
// change the number of tiles
else if (n % 2 == 0 && m % 2 == 0)
return minTiles(n / 2, m / 2);
// If n is even and m is odd
// Use a row of 1x1 tiles
else if (n % 2 == 0 && m % 2 == 1)
return (n + minTiles(n / 2, m / 2));
// If n is odd and m is even
// Use a column of 1x1 tiles
else if (n % 2 == 1 && m % 2 == 0)
return (m + minTiles(n / 2, m / 2));
// If n and m are odd
// add row + column number of tiles
else
return (n + m - 1 + minTiles(n / 2, m / 2));
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int n = 5, m = 6;
System.out.println(minTiles(n, m));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Anant Agarwal.Python3
def minTiles(n, m):
# base case, when area is 0.
if n == 0 or m == 0:
return 0
# If n and m both are even, calculate
# tiles for n/2 x m/2
# Halfing both dimensions doesn't
# change the number of tiles
elif n%2 == 0 and m%2 == 0:
return minTiles(int(n/2), int(m/2))
# If n is even and m is odd
# Use a row of 1x1 tiles
elif n % 2 == 0 and m % 2 == 1:
return (n + minTiles(int(n/2), int(m/2)))
# If n is odd and m is even
# Use a column of 1x1 tiles
elif n % 2 == 1 and m % 2 == 0:
return (m + minTiles(int(n/2), int(m/2)))
# If n and m are odd add
# row + column number of tiles
else:
return (n + m - 1 + minTiles(int(n/2), int(m/2)))
# Driven Program
n = 5
m = 6
print (minTiles(n, m))
# This code is contributed
# by Shreyanshi Arun.C#
// C# code for Minimum tiles of
// sizes in powers of two to cover
// whole area
using System;
class GFG {
static int minTiles(int n, int m)
{
// base case, when area is 0.
if (n == 0 || m == 0)
return 0;
// If n and m both are even,
// calculate tiles for n/2 x m/2
// Halving both dimensions doesn't
// change the number of tiles
else if (n % 2 == 0 && m % 2 == 0)
return minTiles(n / 2, m / 2);
// If n is even and m is odd
// Use a row of 1x1 tiles
else if (n % 2 == 0 && m % 2 == 1)
return (n + minTiles(n / 2, m / 2));
// If n is odd and m is even
// Use a column of 1x1 tiles
else if (n % 2 == 1 && m % 2 == 0)
return (m + minTiles(n / 2, m / 2));
// If n and m are odd
// add row + column number of tiles
else
return (n + m - 1 + minTiles(n / 2, m / 2));
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int n = 5, m = 6;
Console.WriteLine(minTiles(n, m));
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.PHP
输出:
9