给定N个具有奇数值的节点的二叉树。任务是检查树的所有节点是否可以表示为两个质数之和。
例子:
Input:
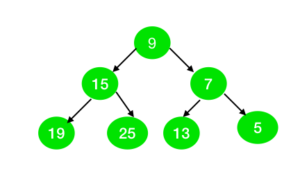
Output: Yes
Explanation:
All the nodes in the tree can be represented as the sum of two prime numbers as:
9 = 2 + 7
15 = 2 +13
7 = 2 + 5
19 = 2 + 17
25 = 2 + 23
13 = 11 + 2
5 = 2 + 3
Input:
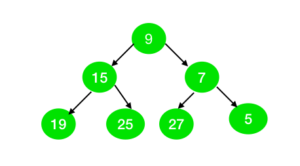
Output: No
Explanation:
The node with value 27 cannot be represented as the sum of two prime numbers.
方法:
- 这个想法是使用哥德巴赫的弱猜想,它指出大于5的每个奇数都可以表示为三个素数的总和。
- 要将奇数(例如N )表示为两个质数之和,请将一个质数固定为2 ,如果(N – 2)也是质数,则N可以表示为两个质数之和。
- 检查树中所有节点的上述条件。如果任何节点不符合上述条件,则打印“否”,否则打印“是”。
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to create array to mark
// whether element are prime or not
void spf_array(int arr[], int N)
{
int i = 0;
// Initially we set same value in
// array as a index of array.
for (i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
arr[i] = i;
}
// Mark all even elements as 2
for (i = 2; i <= N; i = i + 2) {
arr[i] = 2;
}
// Mark all the multiple of prime
// numbers as a non-prime
for (i = 3; i * i <= N; i++) {
if (arr[i] == i) {
int j = 0;
for (j = i * i; j <= N;
j = j + i) {
if (arr[j] == j) {
arr[j] = i;
}
}
}
}
}
// Tree Node
struct node {
int val;
node* left;
node* right;
};
// Funtion to create node of tree
node* newnode(int i)
{
node* temp = NULL;
temp = new node();
temp->val = i;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Function to check whether the
// tree is prime or not
int prime_tree(node* root, int arr[])
{
int a = -1;
if (root != NULL) {
// If element is not the sum of
// two prime then return 0
if (root->val <= 3
|| arr[root->val - 2]
!= root->val - 2) {
return 0;
}
}
if (root->left != NULL) {
a = prime_tree(root->left, arr);
// If a is 0 then we don't need
// to check further
if (a == 0) {
return 0;
}
}
if (root->right != NULL) {
a = prime_tree(root->right, arr);
// If a is 0 then we don't need
// to check further
if (a == 0) {
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Tree
node* root = newnode(9);
root->right = newnode(7);
root->right->right = newnode(5);
root->right->left = newnode(13);
root->left = newnode(15);
root->left->left = newnode(19);
root->left->right = newnode(25);
// Number of nodes in the tree
int n = 50;
// Declare spf[] to store
// prime numbers
int brr[n + 1];
int i = 0;
// Find prime numbers in spf[]
spf_array(brr, n + 1);
// Function Call
if (prime_tree(root, brr)) {
cout << "Yes" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "No" << endl;
}
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to create array to mark
// whether element are prime or not
static void spf_array(int arr[], int N)
{
int i = 0;
// Initially we set same value in
// array as a index of array.
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
arr[i] = i;
}
// Mark all even elements as 2
for(i = 2; i <= N; i = i + 2)
{
arr[i] = 2;
}
// Mark all the multiple of prime
// numbers as a non-prime
for(i = 3; i * i <= N; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == i)
{
int j = 0;
for(j = i * i; j <= N;
j = j + i)
{
if (arr[j] == j)
{
arr[j] = i;
}
}
}
}
}
// Tree Node
static class node
{
int val;
node left;
node right;
};
// Funtion to create node of tree
static node newnode(int i)
{
node temp = null;
temp = new node();
temp.val = i;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to check whether
// the tree is prime or not
static int prime_tree(node root, int arr[])
{
int a = -1;
if (root != null)
{
// If element is not the sum
// of two prime then return 0
if (root.val <= 3 ||
arr[root.val - 2] !=
root.val - 2)
{
return 0;
}
}
if (root.left != null)
{
a = prime_tree(root.left, arr);
// If a is 0 then we don't
// need to check further
if (a == 0)
{
return 0;
}
}
if (root.right != null)
{
a = prime_tree(root.right, arr);
// If a is 0 then we don't
// need to check further
if (a == 0)
{
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given Tree
node root = newnode(9);
root.right = newnode(7);
root.right.right = newnode(5);
root.right.left = newnode(13);
root.left = newnode(15);
root.left.left = newnode(19);
root.left.right = newnode(25);
// Number of nodes in the tree
int n = 50;
// Declare spf[] to store
// prime numbers
int []brr = new int[n + 1];
int i = 0;
// Find prime numbers in spf[]
spf_array(brr, n);
// Function Call
if (prime_tree(root, brr) == 1)
{
System.out.print("Yes" + "\n");
}
else
{
System.out.print("No" + "\n");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rohit_ranjanPython3
# Python3 program for the above approach
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.val = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to create array to mark
# whether element are prime or not
def spf_array(arr, N):
# Initially we set same value in
# array as a index of array.
for i in range(1, N + 1):
arr[i] = i
# Mark all even elements as 2
for i in range(2, N + 1, 2):
arr[i] = 2
# Mark all the multiple of prime
# numbers as a non-prime
for i in range(3, N + 1):
if i * i > N:
break
if (arr[i] == i):
for j in range(2 * i, N, i):
if arr[j] == j:
arr[j] = i
return arr
# Function to check whether the
# tree is prime or not
def prime_tree(root, arr):
a = -1
if (root != None):
# If element is not the sum of
# two prime then return 0
if (root.val <= 3 or
arr[root.val - 2] != root.val - 2):
return 0
if (root.left != None):
a = prime_tree(root.left, arr)
# If a is 0 then we don't need
# to check furthe
if (a == 0):
return 0
if (root.right != None):
a = prime_tree(root.right, arr)
# If a is 0 then we don't need
# to check further
if (a == 0):
return 0
return 1
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Given Tree
root = Node(9);
root.right = Node(7);
root.right.right = Node(5);
root.right.left = Node(13);
root.left = Node(15);
root.left.left = Node(19);
root.left.right = Node(25);
# Number of nodes in the tree
n = 50
# Declare spf[] to store
# prime numbers
arr = [0] * (n + 2)
# Find prime numbers in spf[]
brr = spf_array(arr, n + 1);
# Function Call
if (prime_tree(root, brr)):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to create array to mark
// whether element are prime or not
static void spf_array(int []arr, int N)
{
int i = 0;
// Initially we set same value in
// array as a index of array.
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
arr[i] = i;
}
// Mark all even elements as 2
for(i = 2; i <= N; i = i + 2)
{
arr[i] = 2;
}
// Mark all the multiple of prime
// numbers as a non-prime
for(i = 3; i * i <= N; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == i)
{
int j = 0;
for(j = i * i; j <= N;
j = j + i)
{
if (arr[j] == j)
{
arr[j] = i;
}
}
}
}
}
// Tree Node
class node
{
public int val;
public node left;
public node right;
};
// Funtion to create node of tree
static node newnode(int i)
{
node temp = null;
temp = new node();
temp.val = i;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to check whether
// the tree is prime or not
static int prime_tree(node root, int []arr)
{
int a = -1;
if (root != null)
{
// If element is not the sum
// of two prime then return 0
if (root.val <= 3 ||
arr[root.val - 2] !=
root.val - 2)
{
return 0;
}
}
if (root.left != null)
{
a = prime_tree(root.left, arr);
// If a is 0 then we don't
// need to check further
if (a == 0)
{
return 0;
}
}
if (root.right != null)
{
a = prime_tree(root.right, arr);
// If a is 0 then we don't
// need to check further
if (a == 0)
{
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Given Tree
node root = newnode(9);
root.right = newnode(7);
root.right.right = newnode(5);
root.right.left = newnode(13);
root.left = newnode(15);
root.left.left = newnode(19);
root.left.right = newnode(25);
// Number of nodes in the tree
int n = 50;
// Declare spf[] to store
// prime numbers
int []brr = new int[n + 1];
// Find prime numbers in spf[]
spf_array(brr, n);
// Function Call
if (prime_tree(root, brr) == 1)
{
Console.Write("Yes" + "\n");
}
else
{
Console.Write("No" + "\n");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey输出:
Yes
时间复杂度: O(N * log(log N))
辅助空间: O(N)