递归:
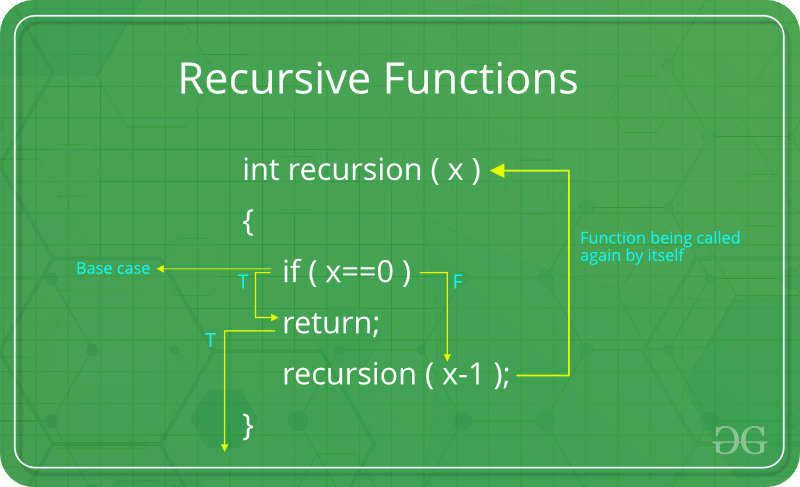
用编程术语,可以将递归函数定义为直接或间接调用自身的例程。
使用递归算法,可以很容易地解决某些问题。河内塔(TOH)就是这样的编程活动之一。尝试为TOH编写迭代算法。而且,每个递归程序都可以使用迭代方法编写(请参阅Lipschutz的参考数据结构)。
数学递归有助于轻松解决一些难题。
例如,一个例行面试问题,
在N人的聚会中,每个人只会与对方握手一次。总共会发生多少次握手?
解决方案:
可以用不同的方式(图,递归等)来解决它。让我们看看如何以递归的方式来解决它。
有N个人。每个人只能握手一次。考虑到第N个人,他必须与(N-1)个人握手。现在,问题减少到(N-1)个人的小情况。假定T N为总握手,则可以递归地公式化。
T N =(N-1)+ T N-1 [T 1 = 0,即最后一个人已经与每个人握手]
递归求解可得出算术级数,该算术级数可计算为N(N-1)/ 2。
练习:在N对夫妇的聚会中,只有一个性别(男性或女性)可以与每一个人握手。会发生多少握手?
通常,递归程序会导致较差的时间复杂度。一个例子是斐波那契数列。使用递归计算第n个斐波那契数的时间复杂度约为1.6 n 。这意味着同一台计算机花费下一个斐波纳契数的时间将近60%。递归斐波那契算法具有重叠的子问题。还有其他技术,例如动态编程,可以改善这种重叠算法。
但是,很少有算法(例如合并排序,快速排序等)可以使用递归来实现最佳时间复杂度。
基本情况:
递归函数的一项关键要求是终止点或基本情况。每个递归程序都必须具有基本大小写,以确保该函数将终止。缺少基本情况会导致意外的行为。
编写递归函数的不同方法
函数调用自身:(直接方式)
我们大多数人都知道编写递归程序的至少两种不同方式。下面给出的是河内代码塔。这是直接调用的示例。
C++
#include
using namespace std;
// Assuming n-th disk is bottom disk (count down)
void tower(int n, char sourcePole,
char destinationPole, char auxiliaryPole)
{
// Base case (termination condition)
if(0 == n)
return;
// Move first n-1 disks from source pole
// to auxiliary pole using destination as
// temporary pole
tower(n - 1, sourcePole, auxiliaryPole,
destinationPole);
// Move the remaining disk from source
// pole to destination pole
cout << "Move the disk "<< n << " from " <<
sourcePole <<" to "<< destinationPole << endl;
// Move the n-1 disks from auxiliary (now source)
// pole to destination pole using source pole as
// temporary (auxiliary) pole
tower(n - 1, auxiliaryPole, destinationPole,
sourcePole);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
tower(3, 'S', 'D', 'A');
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10 C
#include
// Assuming n-th disk is bottom disk (count down)
void tower(int n, char sourcePole, char destinationPole, char auxiliaryPole)
{
// Base case (termination condition)
if(0 == n)
return;
// Move first n-1 disks from source pole
// to auxiliary pole using destination as
// temporary pole
tower(n-1, sourcePole, auxiliaryPole,
destinationPole);
// Move the remaining disk from source
// pole to destination pole
printf("Move the disk %d from %c to %c\n",
n,sourcePole, destinationPole);
// Move the n-1 disks from auxiliary (now source)
// pole to destination pole using source pole as
// temporary (auxiliary) pole
tower(n-1, auxiliaryPole, destinationPole,
sourcePole);
}
int main()
{
tower(3, 'S', 'D', 'A');
return 0;
} Java
// Assuming n-th disk is
// bottom disk (count down)
class GFG {
static void tower(int n, char sourcePole,
char destinationPole, char auxiliaryPole)
{
// Base case (termination condition)
if (0 == n)
return;
// Move first n-1 disks from source pole
// to auxiliary pole using destination as
// temporary pole
tower(n - 1, sourcePole, auxiliaryPole,
destinationPole);
// Move the remaining disk from source
// pole to destination pole
System.out.printf("Move the disk %d from %c to %c\n",
n, sourcePole, destinationPole);
// Move the n-1 disks from auxiliary (now source)
// pole to destination pole using source pole as
// temporary (auxiliary) pole
tower(n - 1, auxiliaryPole, destinationPole, sourcePole);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
tower(3, 'S', 'D', 'A');
}
}
// This code is contributed by Smitha Dinesh Semwal.Python3
# Assuming n-th disk is
# bottom disk (count down)
def tower(n, sourcePole, destinationPole, auxiliaryPole):
# Base case (termination condition)
if(0 == n):
return
# Move first n-1 disks
# from source pole
# to auxiliary pole
# using destination as
# temporary pole
tower(n-1, sourcePole, auxiliaryPole, destinationPole)
# Move the remaining
# disk from source
# pole to destination pole
print("Move the disk",sourcePole,"from",sourcePole,"to",destinationPole)
# Move the n-1 disks from
# auxiliary (now source)
# pole to destination pole
# using source pole as
# temporary (auxiliary) pole
tower(n-1, auxiliaryPole, destinationPole,sourcePole)
# Driver code
tower(3, 'S', 'D', 'A')C#
// Assuming n-th disk is bottom disk
// (count down)
using System;
class GFG {
static void tower(int n, char sourcePole,
char destinationPole,
char auxiliaryPole)
{
// Base case (termination condition)
if (0 == n)
return;
// Move first n-1 disks from source
// pole to auxiliary pole using
// destination as temporary pole
tower(n - 1, sourcePole, auxiliaryPole,
destinationPole);
// Move the remaining disk from source
// pole to destination pole
Console.WriteLine("Move the disk " + n
+ "from " + sourcePole + "to "
+ destinationPole);
// Move the n-1 disks from auxiliary
// (now source) pole to destination
// pole using source pole as temporary
// (auxiliary) pole
tower(n - 1, auxiliaryPole,
destinationPole, sourcePole);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
tower(3, 'S', 'D', 'A');
}
}
// This code is contributed by Anant Agarwal.PHP
Javascript
C++
void recursive(int data)
{
static callDepth;
if(callDepth > MAX_DEPTH)
return;
// Increase call depth
callDepth++;
// do other processing
recursive(data);
// do other processing
// Decrease call depth
callDepth--;
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56C
void recursive(int data)
{
static callDepth;
if(callDepth > MAX_DEPTH)
return;
// Increase call depth
callDepth++;
// do other processing
recursive(data);
// do other processing
// Decrease call depth
callDepth--;
}Java
static void recursive(int data)
{
static callDepth;
if(callDepth > MAX_DEPTH)
return;
// Increase call depth
callDepth++;
// do other processing
recursive(data);
// do other processing
// Decrease call depth
callDepth--;
}
// This code is contributed by divyeh072019Python3
def recursive(data):
callDepth = 0
if(callDepth > MAX_DEPTH):
return;
# Increase call depth
callDepth+=1
# do other processing
recursive(data);
# do other processing
# Decrease call depth
callDepth -= 1
# This code is contributed by Pratham76C#
static void recursive(int data)
{
static callDepth;
if(callDepth > MAX_DEPTH)
return;
// Increase call depth
callDepth++;
// do other processing
recursive(data);
// do other processing
// Decrease call depth
callDepth--;
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07输出 :
Move the disk 1 from S to D
Move the disk 2 from S to A
Move the disk 1 from D to A
Move the disk 3 from S to D
Move the disk 1 from A to S
Move the disk 2 from A to D
Move the disk 1 from S to D TOH的时间复杂度可以通过制定移动次数来计算。
我们需要将前N-1个磁盘从“源”移到“辅助”,再从“辅助”移到“目标”,即前N-1个磁盘需要移动两次。最后一个磁盘从“源”移动到“目标”。从数学上讲,它可以递归定义。
M N = 2M N-1 + 1。
我们可以很容易地解决上述递归关系(2 N -1),它是指数关系。
使用相互函数调用进行递归:(间接方式)
间接调用。虽然至少之实践,一个函数[FUNA()]可以调用另一个函数[funB()],它依次调用[FUNA()]前一函数。在这种情况下,两个功能都应具有基本情况。
防御性编程:
我们可以将防御性编码技术与递归相结合,以实现应用程序的优美功能。通常,在安全关键型应用程序(例如飞行控制,健康监控等)中不允许进行递归编程。但是,可以使用静态计数技术来避免不受控制的调用(在安全关键型系统中不能使用,可以在软实时系统中使用) 。
C++
void recursive(int data)
{
static callDepth;
if(callDepth > MAX_DEPTH)
return;
// Increase call depth
callDepth++;
// do other processing
recursive(data);
// do other processing
// Decrease call depth
callDepth--;
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C
void recursive(int data)
{
static callDepth;
if(callDepth > MAX_DEPTH)
return;
// Increase call depth
callDepth++;
// do other processing
recursive(data);
// do other processing
// Decrease call depth
callDepth--;
}
Java
static void recursive(int data)
{
static callDepth;
if(callDepth > MAX_DEPTH)
return;
// Increase call depth
callDepth++;
// do other processing
recursive(data);
// do other processing
// Decrease call depth
callDepth--;
}
// This code is contributed by divyeh072019
Python3
def recursive(data):
callDepth = 0
if(callDepth > MAX_DEPTH):
return;
# Increase call depth
callDepth+=1
# do other processing
recursive(data);
# do other processing
# Decrease call depth
callDepth -= 1
# This code is contributed by Pratham76
C#
static void recursive(int data)
{
static callDepth;
if(callDepth > MAX_DEPTH)
return;
// Increase call depth
callDepth++;
// do other processing
recursive(data);
// do other processing
// Decrease call depth
callDepth--;
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07
callDepth深度取决于函数堆栈帧大小和最大堆栈大小。
使用函数指针进行递归:(间接方式)
递归还可以使用函数指针来实现。一个示例是POSIX投诉系统中的信号处理程序。如果处理程序导致触发同一事件(由于调用该处理程序而导致该事件),则该函数将重新输入。