给定有向图,源顶点“ s”和目标顶点“ d”,打印从给定“ s”到“ d”的所有路径。
考虑以下有向图。令s为2,d为3。从2到3有4条不同的路径。
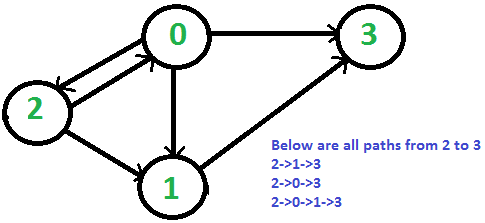
方法:
- 这个想法是对给定的有向图进行深度优先遍历。
- 从源开始DFS遍历。
- 继续将访问的顶点存储在数组或HashMap中,说“ path []”。
- 如果到达目标顶点,则打印path []的内容。
- 重要的是将path []中的当前顶点也标记为已访问,以使遍历不会以一个周期进行。
以下是上述想法的实现。
C++14
// C++ program to print all paths
// from a source to destination.
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// A directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
class Graph {
int V; // No. of vertices in graph
list* adj; // Pointer to an array containing adjacency lists
// A recursive function used by printAllPaths()
void printAllPathsUtil(int, int, bool[], int[], int&);
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
void addEdge(int u, int v);
void printAllPaths(int s, int d);
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v); // Add v to u’s list.
}
// Prints all paths from 's' to 'd'
void Graph::printAllPaths(int s, int d)
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
bool* visited = new bool[V];
// Create an array to store paths
int* path = new int[V];
int path_index = 0; // Initialize path[] as empty
// Initialize all vertices as not visited
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Call the recursive helper function to print all paths
printAllPathsUtil(s, d, visited, path, path_index);
}
// A recursive function to print all paths from 'u' to 'd'.
// visited[] keeps track of vertices in current path.
// path[] stores actual vertices and path_index is current
// index in path[]
void Graph::printAllPathsUtil(int u, int d, bool visited[],
int path[], int& path_index)
{
// Mark the current node and store it in path[]
visited[u] = true;
path[path_index] = u;
path_index++;
// If current vertex is same as destination, then print
// current path[]
if (u == d) {
for (int i = 0; i < path_index; i++)
cout << path[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
else // If current vertex is not destination
{
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to current vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
printAllPathsUtil(*i, d, visited, path, path_index);
}
// Remove current vertex from path[] and mark it as unvisited
path_index--;
visited[u] = false;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(1, 3);
int s = 2, d = 3;
cout << "Following are all different paths from " << s << " to " << d << endl;
g.printAllPaths(s, d);
return 0;
}
Java
// JAVA program to print all
// paths from a source to
// destination.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
// A directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
public class Graph {
// No. of vertices in graph
private int v;
// adjacency list
private ArrayList[] adjList;
// Constructor
public Graph(int vertices)
{
// initialise vertex count
this.v = vertices;
// initialise adjacency list
initAdjList();
}
// utility method to initialise
// adjacency list
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void initAdjList()
{
adjList = new ArrayList[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
adjList[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
// add edge from u to v
public void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
// Add v to u's list.
adjList[u].add(v);
}
// Prints all paths from
// 's' to 'd'
public void printAllPaths(int s, int d)
{
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[v];
ArrayList pathList = new ArrayList<>();
// add source to path[]
pathList.add(s);
// Call recursive utility
printAllPathsUtil(s, d, isVisited, pathList);
}
// A recursive function to print
// all paths from 'u' to 'd'.
// isVisited[] keeps track of
// vertices in current path.
// localPathList<> stores actual
// vertices in the current path
private void printAllPathsUtil(Integer u, Integer d,
boolean[] isVisited,
List localPathList)
{
if (u.equals(d)) {
System.out.println(localPathList);
// if match found then no need to traverse more till depth
return;
}
// Mark the current node
isVisited[u] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to current vertex
for (Integer i : adjList[u]) {
if (!isVisited[i]) {
// store current node
// in path[]
localPathList.add(i);
printAllPathsUtil(i, d, isVisited, localPathList);
// remove current node
// in path[]
localPathList.remove(i);
}
}
// Mark the current node
isVisited[u] = false;
}
// Driver program
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create a sample graph
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(1, 3);
// arbitrary source
int s = 2;
// arbitrary destination
int d = 3;
System.out.println(
"Following are all different paths from "
+ s + " to " + d);
g.printAllPaths(s, d);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Himanshu Shekhar. Python
# Python program to print all paths from a source to destination.
from collections import defaultdict
# This class represents a directed graph
# using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self, vertices):
# No. of vertices
self.V = vertices
# default dictionary to store graph
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
'''A recursive function to print all paths from 'u' to 'd'.
visited[] keeps track of vertices in current path.
path[] stores actual vertices and path_index is current
index in path[]'''
def printAllPathsUtil(self, u, d, visited, path):
# Mark the current node as visited and store in path
visited[u]= True
path.append(u)
# If current vertex is same as destination, then print
# current path[]
if u == d:
print path
else:
# If current vertex is not destination
# Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for i in self.graph[u]:
if visited[i]== False:
self.printAllPathsUtil(i, d, visited, path)
# Remove current vertex from path[] and mark it as unvisited
path.pop()
visited[u]= False
# Prints all paths from 's' to 'd'
def printAllPaths(self, s, d):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited =[False]*(self.V)
# Create an array to store paths
path = []
# Call the recursive helper function to print all paths
self.printAllPathsUtil(s, d, visited, path)
# Create a graph given in the above diagram
g = Graph(4)
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(0, 2)
g.addEdge(0, 3)
g.addEdge(2, 0)
g.addEdge(2, 1)
g.addEdge(1, 3)
s = 2 ; d = 3
print ("Following are all different paths from % d to % d :" %(s, d))
g.printAllPaths(s, d)
# This code is contributed by Neelam YadavC#
// C# program to print all
// paths from a source to
// destination.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// A directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
public class Graph {
// No. of vertices in graph
private int v;
// adjacency list
private List[] adjList;
// Constructor
public Graph(int vertices)
{
// initialise vertex count
this.v = vertices;
// initialise adjacency list
initAdjList();
}
// utility method to initialise
// adjacency list
private void initAdjList()
{
adjList = new List[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
adjList[i] = new List();
}
}
// add edge from u to v
public void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
// Add v to u's list.
adjList[u].Add(v);
}
// Prints all paths from
// 's' to 'd'
public void printAllPaths(int s, int d)
{
bool[] isVisited = new bool[v];
List pathList = new List();
// add source to path[]
pathList.Add(s);
// Call recursive utility
printAllPathsUtil(s, d, isVisited, pathList);
}
// A recursive function to print
// all paths from 'u' to 'd'.
// isVisited[] keeps track of
// vertices in current path.
// localPathList<> stores actual
// vertices in the current path
private void printAllPathsUtil(int u, int d,
bool[] isVisited,
List localPathList)
{
if (u.Equals(d)) {
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" ", localPathList));
// if match found then no need
// to traverse more till depth
return;
}
// Mark the current node
isVisited[u] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to current vertex
foreach(int i in adjList[u])
{
if (!isVisited[i]) {
// store current node
// in path[]
localPathList.Add(i);
printAllPathsUtil(i, d, isVisited,
localPathList);
// remove current node
// in path[]
localPathList.Remove(i);
}
}
// Mark the current node
isVisited[u] = false;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Create a sample graph
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(1, 3);
// arbitrary source
int s = 2;
// arbitrary destination
int d = 3;
Console.WriteLine("Following are all different"
+ " paths from " + s + " to " + d);
g.printAllPaths(s, d);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji 输出:
Following are all different paths from 2 to 3
2 0 1 3
2 0 3
2 1 3
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(V ^ V)。
时间复杂度是多项式。每个顶点都有v个顶点,可以从当前顶点访问这些顶点。 - 辅助空间: O(V ^ V)。
为了存储路径,需要V ^ V空间。