给定一个无向,不加权的图,并以两个节点作为源和目标,任务是打印给定源和目标之间最短长度的所有路径。
例子:
Input: source = 0, destination = 5
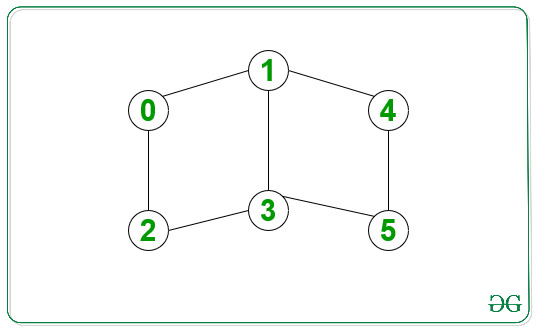
Output:
0 -> 1 -> 3 -> 5
0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 5
0 -> 1 -> 4 -> 5
Explanation:
All the above paths are of length 3, which is the shortest distance between 0 and 5.
Input: source = 0, destination = 4

Output:
0 -> 1 -> 4
方法:要做图形的广度优先遍历(BFS)。步骤如下:
- 从源顶点开始BFS遍历。
- 在执行BFS时,存储到其他每个节点的最短距离,并且还为每个节点维护父向量。
- 将源节点的父节点设为“ -1” 。对于每个节点,它将存储距离源节点最短距离的所有父节点。
- 使用父数组恢复所有路径。在任何时候,我们都会在路径数组中推送一个顶点,然后调用其所有父对象。
- 如果在上述步骤中遇到“ -1”,则表示已找到路径,并且可以将其存储在paths数组中。
下面是上述方法的实现:
cpp14
// Cpp program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to form edge between
// two vertices src and dest
void add_edge(vector adj[],
int src, int dest)
{
adj[src].push_back(dest);
adj[dest].push_back(src);
}
// Function which finds all the paths
// and stores it in paths array
void find_paths(vector >& paths,
vector& path,
vector parent[],
int n, int u)
{
// Base Case
if (u == -1) {
paths.push_back(path);
return;
}
// Loop for all the parents
// of the given vertex
for (int par : parent[u]) {
// Insert the current
// vertex in path
path.push_back(u);
// Recursive call for its parent
find_paths(paths, path, parent,
n, par);
// Remove the current vertex
path.pop_back();
}
}
// Function which performs bfs
// from the given souce vertex
void bfs(vector adj[],
vector parent[],
int n, int start)
{
// dist will contain shortest distance
// from start to every other vertex
vector dist(n, INT_MAX);
queue q;
// Insert source vertex in queue and make
// its parent -1 and distance 0
q.push(start);
parent[start] = { -1 };
dist[start] = 0;
// Untill Queue is empty
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + 1) {
// A shorter distance is found
// So erase all the previous parents
// and insert new parent u in parent[v]
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1;
q.push(v);
parent[v].clear();
parent[v].push_back(u);
}
else if (dist[v] == dist[u] + 1) {
// Another candidate parent for
// shortes path found
parent[v].push_back(u);
}
}
}
}
// Function which prints all the paths
// from start to end
void print_paths(vector adj[],
int n, int start, int end)
{
vector > paths;
vector path;
vector parent[n];
// Function call to bfs
bfs(adj, parent, n, start);
// Function call to find_paths
find_paths(paths, path, parent, n, end);
for (auto v : paths) {
// Since paths contain each
// path in reverse order,
// so reverse it
reverse(v.begin(), v.end());
// Print node for the current path
for (int u : v)
cout << u << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of vertices
int n = 6;
// array of vectors is used
// to store the graph
// in the form of an adjacency list
vector adj[n];
// Given Graph
add_edge(adj, 0, 1);
add_edge(adj, 0, 2);
add_edge(adj, 1, 3);
add_edge(adj, 1, 4);
add_edge(adj, 2, 3);
add_edge(adj, 3, 5);
add_edge(adj, 4, 5);
// Given source and destination
int src = 0;
int dest = n - 1;
// Function Call
print_paths(adj, n, src, dest);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python program for the above approach
# Function to form edge between
# two vertices src and dest
from typing import List
from sys import maxsize
from collections import deque
def add_edge(adj: List[List[int]],
src: int, dest: int) -> None:
adj[src].append(dest)
adj[dest].append(src)
# Function which finds all the paths
# and stores it in paths array
def find_paths(paths: List[List[int]], path: List[int],
parent: List[List[int]], n: int, u: int) -> None:
# Base Case
if (u == -1):
paths.append(path.copy())
return
# Loop for all the parents
# of the given vertex
for par in parent[u]:
# Insert the current
# vertex in path
path.append(u)
# Recursive call for its parent
find_paths(paths, path, parent, n, par)
# Remove the current vertex
path.pop()
# Function which performs bfs
# from the given souce vertex
def bfs(adj: List[List[int]],
parent: List[List[int]], n: int,
start: int) -> None:
# dist will contain shortest distance
# from start to every other vertex
dist = [maxsize for _ in range(n)]
q = deque()
# Insert source vertex in queue and make
# its parent -1 and distance 0
q.append(start)
parent[start] = [-1]
dist[start] = 0
# Untill Queue is empty
while q:
u = q[0]
q.popleft()
for v in adj[u]:
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + 1):
# A shorter distance is found
# So erase all the previous parents
# and insert new parent u in parent[v]
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1
q.append(v)
parent[v].clear()
parent[v].append(u)
elif (dist[v] == dist[u] + 1):
# Another candidate parent for
# shortes path found
parent[v].append(u)
# Function which prints all the paths
# from start to end
def print_paths(adj: List[List[int]], n: int,
start: int, end: int) -> None:
paths = []
path = []
parent = [[] for _ in range(n)]
# Function call to bfs
bfs(adj, parent, n, start)
# Function call to find_paths
find_paths(paths, path, parent, n, end)
for v in paths:
# Since paths contain each
# path in reverse order,
# so reverse it
v = reversed(v)
# Print node for the current path
for u in v:
print(u, end = " ")
print()
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Number of vertices
n = 6
# array of vectors is used
# to store the graph
# in the form of an adjacency list
adj = [[] for _ in range(n)]
# Given Graph
add_edge(adj, 0, 1)
add_edge(adj, 0, 2)
add_edge(adj, 1, 3)
add_edge(adj, 1, 4)
add_edge(adj, 2, 3)
add_edge(adj, 3, 5)
add_edge(adj, 4, 5)
# Given source and destination
src = 0
dest = n - 1
# Function Call
print_paths(adj, n, src, dest)
# This code is contributed by sanjeev2552输出:
0 1 3 5
0 2 3 5
0 1 4 5时间复杂度: O(V + E) ,其中V是顶点数,E是边数。
辅助空间: O(V) ,其中V是顶点数。