使用 BFS 打印从给定源到目的地的所有路径
给定一个有向图,一个源顶点“src”和一个目标顶点“dst”,打印从给定“src”到“dst”的所有路径。
考虑以下有向图。设 src 为 2,dst 为 3。从 2 到 3 有 3 条不同的路径。
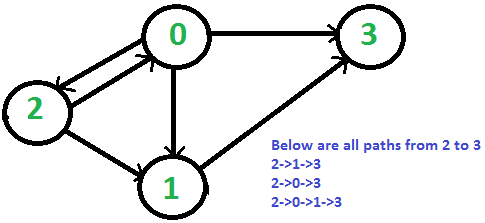
我们已经讨论过使用 DFS 打印从给定源到目的地的所有路径。
以下是基于 BFS 的解决方案。
算法 :
create a queue which will store path(s) of type vector
initialise the queue with first path starting from src
Now run a loop till queue is not empty
get the frontmost path from queue
check if the lastnode of this path is destination
if true then print the path
run a loop for all the vertices connected to the
current vertex i.e. lastnode extracted from path
if the vertex is not visited in current path
a) create a new path from earlier path and
append this vertex
b) insert this new path to queueC++
// C++ program to print all paths of source to
// destination in given graph
#include
using namespace std;
// utility function for printing
// the found path in graph
void printpath(vector& path)
{
int size = path.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << path[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// utility function to check if current
// vertex is already present in path
int isNotVisited(int x, vector& path)
{
int size = path.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (path[i] == x)
return 0;
return 1;
}
// utility function for finding paths in graph
// from source to destination
void findpaths(vector >&g, int src,
int dst, int v)
{
// create a queue which stores
// the paths
queue > q;
// path vector to store the current path
vector path;
path.push_back(src);
q.push(path);
while (!q.empty()) {
path = q.front();
q.pop();
int last = path[path.size() - 1];
// if last vertex is the desired destination
// then print the path
if (last == dst)
printpath(path);
// traverse to all the nodes connected to
// current vertex and push new path to queue
for (int i = 0; i < g[last].size(); i++) {
if (isNotVisited(g[last][i], path)) {
vector newpath(path);
newpath.push_back(g[last][i]);
q.push(newpath);
}
}
}
}
// driver program
int main()
{
vector > g;
// number of vertices
int v = 4;
g.resize(4);
// construct a graph
g[0].push_back(3);
g[0].push_back(1);
g[0].push_back(2);
g[1].push_back(3);
g[2].push_back(0);
g[2].push_back(1);
int src = 2, dst = 3;
cout << "path from src " << src
<< " to dst " << dst << " are \n";
// function for finding the paths
findpaths(g, src, dst, v);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to print all paths of source to
// destination in given graph
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Graph{
// utility function for printing
// the found path in graph
private static void printPath(List path)
{
int size = path.size();
for(Integer v : path)
{
System.out.print(v + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Utility function to check if current
// vertex is already present in path
private static boolean isNotVisited(int x,
List path)
{
int size = path.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (path.get(i) == x)
return false;
return true;
}
// Utility function for finding paths in graph
// from source to destination
private static void findpaths(List > g,
int src, int dst, int v)
{
// Create a queue which stores
// the paths
Queue > queue = new LinkedList<>();
// Path vector to store the current path
List path = new ArrayList<>();
path.add(src);
queue.offer(path);
while (!queue.isEmpty())
{
path = queue.poll();
int last = path.get(path.size() - 1);
// If last vertex is the desired destination
// then print the path
if (last == dst)
{
printPath(path);
}
// Traverse to all the nodes connected to
// current vertex and push new path to queue
List lastNode = g.get(last);
for(int i = 0; i < lastNode.size(); i++)
{
if (isNotVisited(lastNode.get(i), path))
{
List newpath = new ArrayList<>(path);
newpath.add(lastNode.get(i));
queue.offer(newpath);
}
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List > g = new ArrayList<>();
int v = 4;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
g.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
// Construct a graph
g.get(0).add(3);
g.get(0).add(1);
g.get(0).add(2);
g.get(1).add(3);
g.get(2).add(0);
g.get(2).add(1);
int src = 2, dst = 3;
System.out.println("path from src " + src +
" to dst " + dst + " are ");
// Function for finding the paths
findpaths(g, src, dst, v);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rajatsri94 Python3
# Python3 program to print all paths of
# source to destination in given graph
from typing import List
from collections import deque
# Utility function for printing
# the found path in graph
def printpath(path: List[int]) -> None:
size = len(path)
for i in range(size):
print(path[i], end = " ")
print()
# Utility function to check if current
# vertex is already present in path
def isNotVisited(x: int, path: List[int]) -> int:
size = len(path)
for i in range(size):
if (path[i] == x):
return 0
return 1
# Utility function for finding paths in graph
# from source to destination
def findpaths(g: List[List[int]], src: int,
dst: int, v: int) -> None:
# Create a queue which stores
# the paths
q = deque()
# Path vector to store the current path
path = []
path.append(src)
q.append(path.copy())
while q:
path = q.popleft()
last = path[len(path) - 1]
# If last vertex is the desired destination
# then print the path
if (last == dst):
printpath(path)
# Traverse to all the nodes connected to
# current vertex and push new path to queue
for i in range(len(g[last])):
if (isNotVisited(g[last][i], path)):
newpath = path.copy()
newpath.append(g[last][i])
q.append(newpath)
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Number of vertices
v = 4
g = [[] for _ in range(4)]
# Construct a graph
g[0].append(3)
g[0].append(1)
g[0].append(2)
g[1].append(3)
g[2].append(0)
g[2].append(1)
src = 2
dst = 3
print("path from src {} to dst {} are".format(
src, dst))
# Function for finding the paths
findpaths(g, src, dst, v)
# This code is contributed by sanjeev2552C#
// C# program to print all paths of source to
// destination in given graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Graph{
// utility function for printing
// the found path in graph
static void printPath(List path)
{
int size = path.Count;
foreach(int v in path)
{
Console.Write(v + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Utility function to check if current
// vertex is already present in path
static bool isNotVisited(int x, List path)
{
int size = path.Count;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (path[i] == x)
return false;
return true;
}
// Utility function for finding paths in graph
// from source to destination
private static void findpaths(List > g,
int src, int dst, int v)
{
// Create a queue which stores
// the paths
Queue > queue = new Queue>();
// Path vector to store the current path
List path = new List();
path.Add(src);
queue.Enqueue(path);
while (queue.Count!=0)
{
path = queue.Dequeue();
int last = path[path.Count - 1];
// If last vertex is the desired destination
// then print the path
if (last == dst)
{
printPath(path);
}
// Traverse to all the nodes connected to
// current vertex and push new path to queue
List lastNode = g[last];
for(int i = 0; i < lastNode.Count; i++)
{
if (isNotVisited(lastNode[i], path))
{
List newpath = new List(path);
newpath.Add(lastNode[i]);
queue.Enqueue(newpath);
}
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
List > g = new List>();
int v = 4;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
g.Add(new List());
}
// Construct a graph
g[0].Add(3);
g[0].Add(1);
g[0].Add(2);
g[1].Add(3);
g[2].Add(0);
g[2].Add(1);
int src = 2, dst = 3;
Console.WriteLine("path from src " + src +
" to dst " + dst + " are ");
// Function for finding the paths
findpaths(g, src, dst, v);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput 输出:
path from src 2 to dst 3 are
2 0 3
2 1 3
2 0 1 3