什么是结构?
结构是C / C++中用户定义的数据类型。结构创建一个数据类型,该数据类型可用于将可能不同类型的项目分组为单个类型。
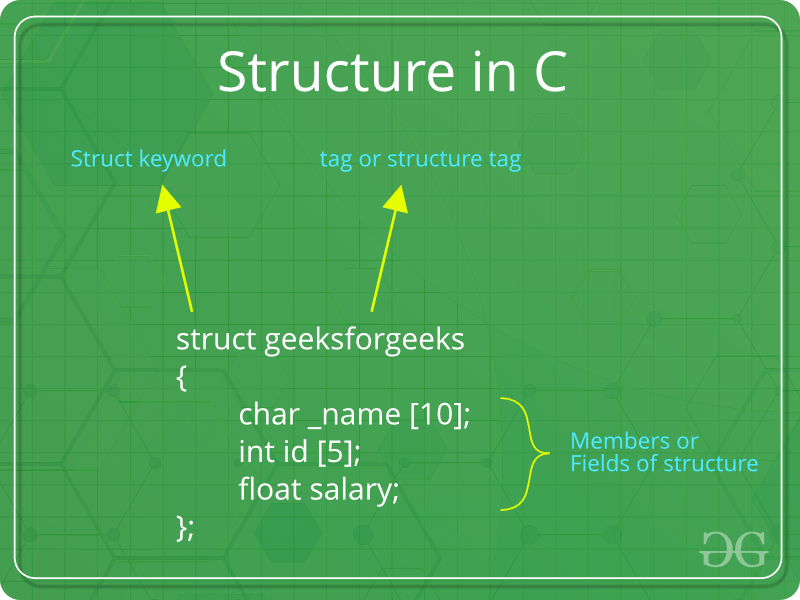
如何建立结构?
‘struct’关键字用于创建结构。以下是一个示例。
struct address
{
char name[50];
char street[100];
char city[50];
char state[20];
int pin;
};
如何声明结构变量?
结构变量既可以用结构声明来声明,也可以像基本类型一样声明为单独的声明。
// A variable declaration with structure declaration.
struct Point
{
int x, y;
} p1; // The variable p1 is declared with 'Point'
// A variable declaration like basic data types
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
int main()
{
struct Point p1; // The variable p1 is declared like a normal variable
}
注意:在C++中,在声明变量之前,struct关键字是可选的。在C语言中,它是强制性的。
如何初始化结构成员?
结构成员不能使用声明进行初始化。例如,以下C程序编译失败。
struct Point
{
int x = 0; // COMPILER ERROR: cannot initialize members here
int y = 0; // COMPILER ERROR: cannot initialize members here
};
出现上述错误的原因很简单,当声明数据类型时,不会为其分配任何内存。仅在创建变量时才分配内存。
可以使用花括号“ {}”来初始化结构成员。例如,以下是有效的初始化。
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
int main()
{
// A valid initialization. member x gets value 0 and y
// gets value 1. The order of declaration is followed.
struct Point p1 = {0, 1};
}
如何访问结构元素?
使用dot(。)运算符可以访问结构成员。
#include
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
int main()
{
struct Point p1 = {0, 1};
// Accessing members of point p1
p1.x = 20;
printf ("x = %d, y = %d", p1.x, p1.y);
return 0;
}
输出:
x = 20, y = 1
什么是初始化?
指定的初始化允许以任何顺序初始化结构成员。此功能已在C99标准中添加。
#include
struct Point
{
int x, y, z;
};
int main()
{
// Examples of initialization using designated initialization
struct Point p1 = {.y = 0, .z = 1, .x = 2};
struct Point p2 = {.x = 20};
printf ("x = %d, y = %d, z = %d\n", p1.x, p1.y, p1.z);
printf ("x = %d", p2.x);
return 0;
}
输出:
x = 2, y = 0, z = 1
x = 20
此功能在C++中不可用,仅在C中可用。
什么是结构数组?
像其他原始数据类型一样,我们可以创建结构数组。
#include
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
int main()
{
// Create an array of structures
struct Point arr[10];
// Access array members
arr[0].x = 10;
arr[0].y = 20;
printf("%d %d", arr[0].x, arr[0].y);
return 0;
}
输出:
10 20
什么是结构指针?
像原始类型一样,我们可以拥有指向结构的指针。如果我们有一个指向结构的指针,则可以使用箭头(->)运算符来访问成员。
#include
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
int main()
{
struct Point p1 = {1, 2};
// p2 is a pointer to structure p1
struct Point *p2 = &p1;
// Accessing structure members using structure pointer
printf("%d %d", p2->x, p2->y);
return 0;
}
输出:
1 2
什么是结构成员对齐?
参见https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/structure-member-alignment-padding-and-data-packing/
C结构的局限性
用C语言,结构提供了一种将不同类型的数据打包在一起的方法。结构是处理一组逻辑上相关的数据项的有用工具。但是,C结构具有一些局限性。
struct number
{
float x;
};
int main()
{
struct number n1,n2,n3;
n1.x=4;
n2.x=3;
n3=n1+n2;
return 0;
}
/*Output:
prog.c: In function 'main':
prog.c:10:7: error:
invalid operands to binary + (have 'struct number' and 'struct number')
n3=n1+n2;
*/
相关文章:C结构与C++结构
想要从精选的最佳视频中学习和练习问题,请查看《基础知识到高级C的C基础课程》。