关键点
随着函数复杂性的增加,我们从它们的图形中看到越来越复杂的行为,并且越来越难以绘制图形。他们的图表中有很多高峰和低谷。找出这些谷和峰的位置变得至关重要,峰被称为最大值,谷被称为最小值。每个图中可以有多个最大值和最小值。这些波峰和波谷使我们能够在一个区间内找到函数的最小值和最大值。我们使用导数来找到这些临界点的位置。
最大和最小点
假设我们有一个函数f(x),这个函数的图表如下所示。该函数的最大值和最小值是该函数图中存在的峰和谷。例如,我们可以在图中看到,在 x = b 和 x = a 处,它是一个波谷,因此它是一个最小值,同样 x = a 是一个最大值。可以有不止一个最大值和最小值。函数的最小值称为全局最小值,类似地,函数的最大值称为全局最大值。所有其他最大值和最小值称为局部最大值和局部最小值。

让我们看看最大值和最小值的正式定义。
Let’ say f is a function defined in the interval I, Then,
- f is said to have a maximum value in I, if there exists a point c in I such that f(c) > f(x), for all x∈ I.
- f is said to have a minimum value in I, if there exists a point c in I such that f(c) < f(x), for all x∈ I.
- f is said to have an extreme value in I if there exists a point c in I such that f (c) is either a maximum value or a minimum value of f in I.
示例:从下图中 f(x) = |x| 中找出函数f(x) 的最小值和最大值。

解决方案:
In the graph for the given function f(x),
At x = 0, f(x) = 0 and for all x∈ R except x = 0, f(x) > 0.
Thus, minimum value of the function is x = 0.
Maximum value of the function is infinite.
笔记:
A function that is monotonically increasing or decreasing has its minima and maxima at the ends of the corresponding interval. For example, the line in the figure below is increasing monotonically. The maxima and minima of the interval are at the ends of the interval.

The functions which have more than one minima and maxima have some local minima and local maxima and global maxima and minima. The figure below has more than one minima and maxima. We call them local minimum and local maximum.

对于实值函数f 和 f 域中的内部点 c。然后,
1. 如果存在 a h > 0 ,则 c 称为局部最大值点,这样,
对于 (c – h, c + h) 中的所有 x,f(c) > f(x)
点 c 处的值 f(c) 称为局部最大值。
2. 如果存在h > 0 ,则 c 称为局部最小值点,这样,
对于 (c – h, c + h) 中的所有 x,f(c) < f(x)
点 c 处的值 f(c) 称为局部最小值。
一阶导数测试
现在让我们看看如何确定最小值和最大值的点。下图显示了两个函数的最小值和最大值。请注意,在局部最小值和最大值处,切线的斜率为零。
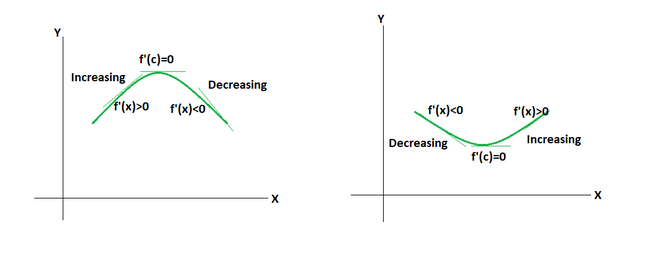
下面的规则帮助我们找出下面函数中最大值和最小值之间的区别。
For a function f defined in the open interval I, let c be a critical point c in I. Then,
1. Point c is called local maxima. If f'(x) changes sign from positive to negative as x increases through c, i.e, if f'(x) > 0 at every point close to and left of c, and f'(x) < 0 at every point close to and right of c and f'(x) < 0 at every point close to and to the right of c.
2. Point c is called local minima. If f ′(x) changes sign from negative to positive as x increases through c, i.e., if f ′(x) < 0 at every point close to and to the left of c, and f ′(x) > 0 at every point close to and to the right of c.
3. The point is a point of inflection if f ′(x) does not change sign as x increases through c, then c is neither a point of local maxima nor a point of local minima.
This test is called first derivative test.
二阶导数测试
该测试还用于检查临界点处的局部最小值或最大值。这通常比一阶导数测试更容易应用。
For a function f defined in the open interval I, let c be a critical point c in I. Assuming the function f is twice differentiable at point c,
1. x = c is local maxima if f'(x) = 0 and f”(x) < 0.
2. x = c is local minima, if f'(x) = 0 and f”(x) > 0.
3. This test fails if f'(c) = 0 and f”(c) = 0.
For the third case, we go back to the first derivative test and check.
让我们看看这些概念上的一些问题。
示例问题
问题 1:找出以下函数f(x) = x 4 – x 2的临界点。
解决方案:
For the function f(x) = x4 – x2. We know that critical points are the points where f'(x) =0
f'(x) = 4x3 – 2x
⇒ f'(x) = 0
⇒ 4x3 – 2x= 0
⇒ x(4x2 – 2) = 0
The roots of this equation are,
x = 0, x = ![]()
Thus, the critical points are, x = 0, ![]()
问题 2:找出以下函数f(x) =x 3 + 3x 2 + 3x 的临界点。
解决方案:
For the function f(x) = x3 + 3x2 + 3. We know that critical points are the points where f'(x) =0
f'(x) = 3x2 + 6x + 3
⇒ f'(x) = 0
⇒ 3x2 + 6x + 3= 0
⇒ 3(x2 + 2x + 1) = 0
⇒ 3(x + 1)2 = 0
The roots of this equation are,
x = -1
Thus, the critical points are, x = -1.
问题 3:找出以下函数的相对最大值和最小值,
f(x) = x 3 – 3x 2 + 3
解决方案:
We need to first find the critical points,
f'(x) = 3x2 – 6x
⇒ f'(x) = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 6x= 0
⇒ 3x(x – 2) = 0
⇒ 3x(x – 2) = 0
The roots of this equation are,
x = 0 and x = 2.
Thus, the critical points are, x = 0 and 2.
Now we need to check whether these are maxima or minima. We can use the second derivative test.
f”(x) =6x – 6
At x = 0, f”(x) < 0. Thus, x = 0 is a local maxima.
At x = 2, f”(x) > 0. Thus, x = 2 is a local minima.
问题4:找出以下函数在区间[0,4]内的相对最大值和最小值,
f(x) = 3x + 3
解决方案:
We need to first find the critical points,
f'(x) = 3
⇒ f'(x) = 3
Notice that this function has a constant derivative which is positive. That means that this function is constantly increasing in nature. This is a monotonically increasing function.
From the property mentioned above, the monotonically increasing functions have their maxima and minima at the boundary of the interval. Thus, in the interval [0,4], f(x) is monotonically increasing. So, it’s minima lies at x = 0 and maxima at x = 4.
问题 5:找出以下函数f(x) =sinx 的临界点。
解决方案:
For the function f(x) = sin(x). We know that critical points are the points where f'(x) =0
f'(x) = cos(x)
⇒ f'(x) = 0
⇒ cos(x)= 0
The roots of this equation are,
x = ![]()
Thus, the critical points are, x = ![]()