静电荷会产生电场,如果电荷开始移动,它们就会产生磁场。磁场也是由磁铁产生的,磁铁是一种永久性磁铁,会产生称为磁力的力,这种磁力会使肉眼看不见磁力线,但是某些实验表明,磁铁会在磁力线周围产生磁力线,例如,在一张纸下面放一块磁铁,然后将铁屑放在纸上,将会观察到铁屑在纸上形成了一个图案,该图案看起来类似于电场线,但是磁场线,这些线形成一个闭环,在磁体外部,它们从北极传播到南极,在磁体内部,它们从南极传播到北极。
磁铁和磁场
磁铁是具有产生磁力的能力的材料,磁力会产生磁力线,磁场力能够吸引和排斥其他铁磁材料,例如铁,镍等。
磁场是一个矢量量(它既有大小又有方向),磁场的方向是从北极到南极。磁场线始终形成闭合曲线,强度由磁场线的紧密程度决定,当磁场线靠近磁性材料时,磁场线彼此靠近;而当磁场线远离磁场时,磁场线彼此远离。材料。

电流的磁效应
当电流流过磁性材料时,会产生磁场,如果将针放在材料附近,则在提供电荷(移动电荷)时,针会偏转。磁性材料所施加的力的面积称为磁场。
磁场性质:
- 磁场强度与它们产生的磁力线的密度成正比。
- 磁场线永不交叉。
- 磁场将始终具有闭合和连续的环路。
载流直导体产生的磁场线
由直的载流导体产生的磁场线为同心圆形式,取决于电流的方向,磁场线也会改变其方向。可以通过右手拇指法则或麦克斯韦的开瓶器法则来确定磁力线的方向。

同心磁场线通过直导体承载电流
右手拇指法则:
根据右手拇指法则,如果将右手拇指放在移动电流的方向上,则手指的方向表示磁场线的方向;类似地,如果将拇指放在磁场方向上线,则电流的方向由卷曲的手指的方向显示。
麦克斯韦的开瓶器规则:
根据麦克斯韦(Marswell)的Corkscrew规则,螺钉可以分辨出磁力线的方向。如果螺钉向前移动,则旋转方向表示磁场线的方向,而螺钉的移动方向表示电流的方向,反之亦然。
电流通过圆环产生的磁力线
磁场线将产生与在带电流的直导体中相同的图案,这意味着磁场线本质上是同心的,但是根据电流的方向,磁场线的方向将是同心的。改变。例如,在一个圆环中,想象两个地方,根据右手拇指法则,一个地方电流向上,一个地方电流向下,在第一种情况下,磁力线本质上必须是逆时针方向,并且在第二种情况下,磁力线本质上必须是顺时针方向。

电磁线圈中的电流引起的磁力线
螺线管是一种螺旋线圈,在提供电流时会变成电磁体,形成北极和南极,由于电荷的移动,它会产生磁场线。螺线管产生的磁力线看起来与简单的条形磁铁产生的磁力线相似。
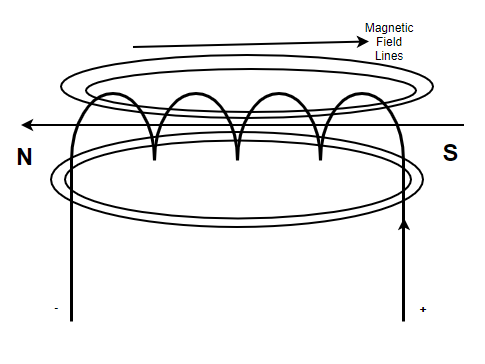
电磁铁
电磁体是由于电流移动和流过而形成的一种磁体,它是一种临时磁体,通常被看作是包裹在软铁芯上的线圈(例如螺线管)。
电磁体的特性:
- 电磁铁不是永久磁铁,它们本质上是暂时的。
- 可以通过改变电流来改变磁力的强度。
- 电磁体由软铁芯制成。
Note: When current is applied on a ferromagnetic material to produce magnetic field lines, the magnetic force is dependent on the number of magnetic dipole aligned, The amount of current applied is directly proportional to the number of dipoles alignment and the amount of magnetic force can be altered. However, it can only be done up to some point, till the point where saturation reaches and no dipoles can further be available for alignment.
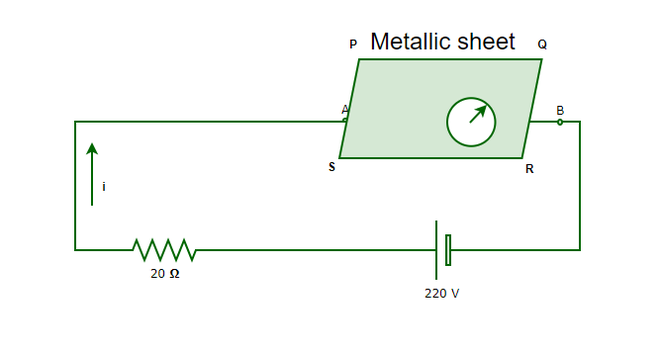
施加在置于磁场中的载流导体上的力
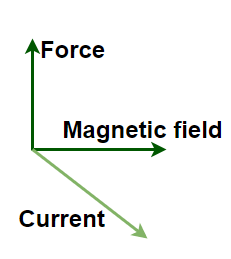
想象一下,将一根导线(导体)放在磁铁下面,并使电流流过该导线,由于磁场中的电荷不断移动,向导体施加了一定的力,使其沿某个方向移动,这种现象由下式给出:迈克尔·法拉第。导体上的力的方向由弗莱明的左手定则确定。
弗莱明的左手法则:
根据弗莱明的左手法则,力的方向可以借助左手的拇指,食指和中指来确定。拇指代表力,食指显示磁力线的方向,中指显示电流的方向。因此,如果中指和食指分别保持在电流线和磁场线的方向上,则拇指将代表在载流导体上产生的力的方向。
样题
问题1:为什么磁力线从不相交?
回答:
It is one of the properties of Magnetic field lines that they never intersect each other, if they do so, the intersection point of magnetic field lines will show two different directions which is not possible for the field lines as they follow one direction.
问题2:为什么磁力线的密度会变化?
回答:
Magnetic field lines can vary in density because the field lines start near the magnet, and then they go further away and as they go further away from the magnet, the effect of magnetic force gradually decreases and stops after a point, since the force is decreasing, the density of the magnetic field lines also tend to decrease.
问题3:弗莱明左手法则有哪些应用?
回答:
Fleming’s left-hand rule is applied in Electric motors (DC motors, induction motors, etc). The basic concept is that the induced current produces force on the conductor which helps in creating motion.
问题4:永磁体和电磁体有什么区别?
回答:
A Permanent magnet is made up of Hard material, The magnetic field is produced due to magnetization and once the magnetization is lost, the magnet ceases to show magnetic properties since the magnetic dipoles cannot be changed further.
An electromagnet is made up of Soft material, The magnetic field is produced by applying current through it. Once the current stops, the magnetism stops but again develops after applying current again, The dipoles aligned in an electromagnet can be altered again and again.
问题5:写下磁场线的属性。
回答:
Properties of magnetic field lines
- The magnetic field lines decide the strength of the magnetic field, denser the field lines, stronger the magnetic field.
- They always form closed and continuous loops.
- Magnetic field lines never cross each other, since they do not have two directions.