载流导体产生的磁场
在物理学中,磁铁是一种能产生磁场的材料,该磁场会吸引或排斥其他磁性材料。磁铁总是被极化的,有北极和南极,这两个极总是在一起,不能孤立,当我们自由悬挂一块磁铁时,磁北极将指向地球的地理北极。
磁铁存在于冰箱、收音机和立体声耳机、音频和录像带播放器、儿童玩具以及打印机硬盘和软盘中。现在,在我们进入由载流回路和螺线管引起的磁场之前,让我们先了解一些基本术语,如磁场、磁力线和螺线管:
磁场
磁场是由磁偶极子和移动电荷形成的力场,它对周围的其他移动电荷和磁偶极子施加力。
磁场是存在于磁铁、电流或移动电场附近并且可以观察到磁力的矢量场。与称为自旋的基本量子特性对齐的基本粒子的移动电荷和固有磁矩会产生磁场。
由于它既有大小又有方向,所以磁场是一个矢量。
它用符号B表示。
磁场N s/C或特斯拉 (T)的 SI 单位。
磁场线
- 磁力线是磁铁周围的假想线,它们是连续的闭环。任何给定点的场线的切线表示该时刻总磁场的方向。
- 由于磁铁是偶极的,磁力线必须有始有终。因此,它从北极开始,在条形磁铁外部终止于南极,并在磁铁内部从南极移动到北极。
- 磁力线的接近程度表明磁场的相对强度,即更近的线表明磁场更强,反之亦然。靠近磁铁磁极的密集磁力线显示出更大的强度。
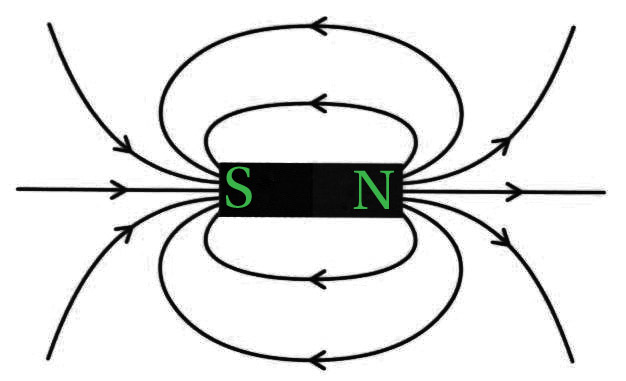
条形磁铁的磁力线
磁场线的特性
- 永远不会跨越磁场边界。
- 场线的深度显示场的力量。
- 磁场线通常是闭环。
- 磁力线通常起源于或开始于北极并终止于南极。
如何通过载流导体找到磁场的方向?
当电流通过直通载流导体时,会在其周围产生磁场。在载流导体的每个点上,场线都是同心圆的形式。我们可以找到磁场的方向,相对于通过直导体的电流方向可以用右手拇指规则来描述,也称为麦克斯韦开瓶器规则。
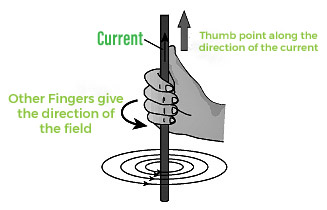
右手拇指法则
这条规则规定:“如果右手握住通电导体,保持拇指伸直,如果电流的方向是拇指的方向,那么其他手指缠绕的方向将显示出导体的方向。磁场。'
电流通过圆形回路产生的磁场
右手拇指规则可用于圆形导线以及它包括小的直线段。导线上的每一个点都会产生一个磁场,当我们远离导线时,它周围的磁场会越来越大,当我们到达圆环的中心时,这些圆的弧线会呈现为一条直线线
磁场和线圈匝数
磁场的大小与线圈匝数的增加相加。如果线圈有“n”圈,则在线圈单圈的情况下,磁场的大小将是磁场的“n”倍。
The strength of the magnetic field at the center of the loop (coil) depends on:
- The radius of the coil: The strength of the magnetic field is inversely proportional to the radius of the coil. If the radius increases, the magnetic strength at the center decreases
- The number of turns in the coil: As the number of turns in the coil increase, the magnetic strength at the center increases, because the current in each circular turn is having the same direction, thus, the field due to each turn adds up.
- The strength of the current flowing in the coil: As the strength of the current increases, the strength of three magnetic fields also increases.
什么是螺线管?
螺线管是由许多圆形绝缘铜线绕成圆柱形的线圈。载流螺线管产生与条形磁铁相似的磁场模式。螺线管的一端充当北极,另一端充当南极。
电磁阀中的电流产生的磁场
螺线管内部的磁场线是平行的,类似于条形磁铁,这表明在螺线管内部所有点的磁场都是相同的。螺线管产生的磁场类似于条形磁铁。磁场的强度与匝数和电流大小成正比。
通过在螺线管内部产生强磁场,磁性材料可以被磁化。通过在螺线管内产生磁场而形成的磁体称为电磁体。
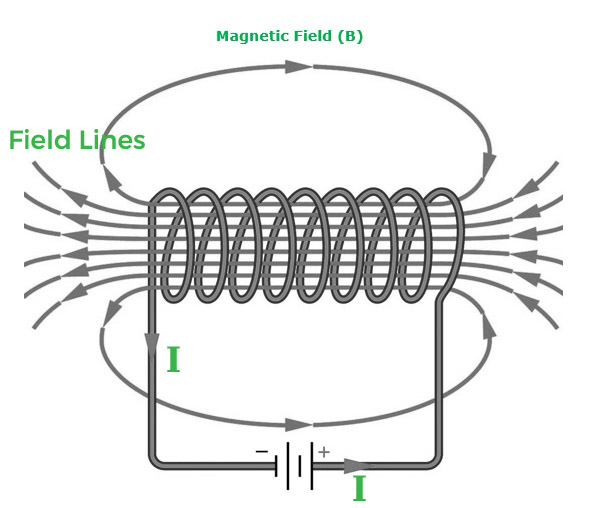
螺线管的场线
示例问题
问题 1:解释由于以下原因对载流圆形线圈中某点产生的磁场的影响:
(i) 增加流过它的电流量,
(ii) 点到线圈的距离增加,
(iii) 增加线圈的匝数。
解决方案:
(i) The magnetic field produced by current carrying circular coil is directly proportional to the current flowing through the coil. Therefore, with increase in the magnitude of magnetic field the current flowing through the coil will increase.
(ii) Magnitude of magnetic field at a point in a current carrying coil is inversely proportional to the distance. Hence, with increase in distance the magnetic field will decrease.
(iii) The magnetic field produced depends on directly to the current flowing through the circular coil. If number of turns of coil increases then the current flowing in a coil also increases and hence the magnetic field will increase with increase in number of turns.
问题 2:螺线管如何像磁铁一样工作?
解决方案:
Since solenoid has iron core with insulated copper wire around it, therefore it behaves like magnet. When a current is flowing through the solenoid, magnetic field is produced around it. And the field produced is similar to the magnetic field of a bar magnet.
问题 3:定义右手拇指规则?
解决方案:
This rule states that ‘If a current carrying conductor is held by right hand, keeping the thumb straight and if the direction of electric current is in the direction of thumb, then the direction of wrapping of other fingers will show the direction of magnetic field.’
问题4:为什么两条磁力线不能相交?
解决方案:
All Field lines follow their own path to reach from the North Pole to the South Pole. Two magnetic field lines do not intersect each other because if there was point of intersection, then there would be two tangents for a single point which means that the magnetic field has two directions, which is not possible.
问题5:什么是磁场线?列出这些线条的两个特征。
解决方案:
The lines drawn around the magnetic field of any magnet is known as magnetic field lines which are also be used to determine the direction of the magnetic field.
Properties of magnetic lines of force:
- Outside the magnet the field lines originates from north pole and ends at the South Pole.
- The magnetic field lines are continuous closed loop.