有几种形式可以用来表示二维坐标平面上的直线方程,从几种形式中可以选择三种主要形式:点-斜率形式,斜率截取形式以及常规形式或标准形式。普通形式或标准形式是线性方程,其中方程的阶次为1。
标准形式方程式
标准形式的等式为
Ax + By + C = 0
或者
Ax + By = C
在此,A,B和C是实常数,并且A和B的值不能同时为零。因此,可以说,A和B同时不为零的Ax + By + C = 0形式的方程称为直线标准方程的一般方程。标准方程的图形始终是直的。
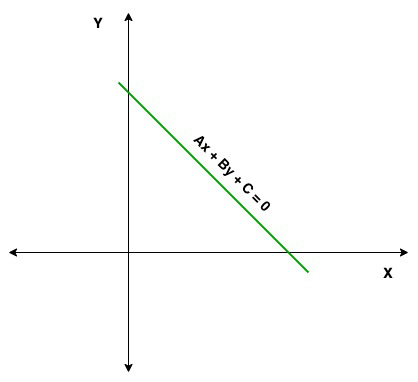
如果A = 0的值,则该线的方程为y = -C / B且该线为水平,即平行于x轴;如果B = 0,则该线的方程为x = -C / A,并且该线是垂直的,表示平行于y轴。
例如:
2x + 4y + 3 = 0
4x – 6y = -34
Both the equations are in the standard form
3x = -3y – 2
3y = 2(x + 1)
Both the given equations are not in the standard form
标准表格的类型
方程的标准形式可以表示为三种不同形式:
斜率截距形式:我们知道斜率截距形式的方程为y = mx + c。现在我们看到如何以斜率截距形式表示一般方程,即Ax + By + C = 0。
因此,如果B≠0的值,则一般等式即Ax + By + C = 0可以写成:
![]() -(1)
-(1)
现在,将方程式(1)与斜率截距形式进行比较,即y = mx + c,我们得到
m = -A / B,c = -C / B
因此,Ax + By + C = 0的斜率为-A / B,y轴截距为-C / B。
例子:
问题1.找到给定方程2x + 5y + 1 = 0的斜率和y轴截距。
解决方案:
Given: equation of line = 2x + 5y + 1 = 0
Find: slope and y-intercept
So the given equation can be written as
y = (-1 – 2x)/5
y = -2x/5 – 1/5 -(1)
As we know that the slope-intercept form is
y = mx + c -(2)
On comparing eq(1) and (2) we get
m = -2/5 and c = -1/5
Hence, the slope is -2/5 and y-intercept is -1/5
问题2.找到给定方程3x + 6y – 9 = 0的斜率和y轴截距。
解决方案:
Given: equation of line = 3x + 6y – 9 = 0
Find: slope and y-intercept
So the given equation can be written as
y = (9 – 6x)/3
y = -2x + 3 -(1)
As we know that the slope-intercept form is
y = mx + c -(2)
On comparing eq(1) and (2) we get
m = -2 and c = 3
Hence, the slope is -2 and y-intercept is 3
截距形式:我们知道方程的截距形式为![]() 。现在我们来看看如何以截距形式表示一般方程,即Ax + By + C = 0。
。现在我们来看看如何以截距形式表示一般方程,即Ax + By + C = 0。
因此,如果C≠0,那么一般等式即Ax + By + C = 0可以表示为:
![]() -(1)
-(1)
现在,将等式(1)与截距形式进行比较,即![]() ,我们得到
,我们得到
a = -C / A和b = -C / B
因此,x截距为-C / A,y截距为-C / B。并且如果C的值为0,则通用方程为Ax + By = 0,这意味着该线穿过原点,因此其截距为零。
例子:
问题1.找到给定方程4x + 8y + 2 = 0的x和y截距。
解决方案:
Given: 4x + 8y + 2 = 0.
Find: x and y-intercept
So the given equation can be written as
![]() -(1)
-(1)
As we know that the Intercept Form is
![]() -(2)
-(2)
On comparing eq(1) and (2) we get
a = -2/4 = -1/2
b = -2/8 = -1/4
So the x-intercept is -1/2 and y-intercept is -1/4
问题2.找到给定方程12x – 4y – 2 = 0的x和y截距。
解决方案:
Given: 12x – 4y – 2 = 0
Find: x and y-intercept
So the given equation can be written as
![]() -(1)
-(1)
As we know that the Intercept Form is
![]() -(2)
-(2)
On comparing eq(1) and (2) we get
a = 2/12 = 1/6
b = -2/4 = -1/2
So the x-intercept is 1/6 and y-intercept is -1/2
范式:我们知道方程的截距形式为xcosω+ysinω= p。现在我们来看看如何以一般形式表示一般方程,即Ax + By + C = 0。
因此,让我们考虑正态形式为等式Ax + By + C = 0的直线的xcosω+ysinω= p。
所以, ![]()
cosω= -Ap / C和sinω= -Bp / C
我们知道
罪2(ω)+ COS 2(ω)= 1 – (1)
因此,将所有这些值放在等式(1)中,我们得到
(-Ap / C) 2 +(-Bp / C) 2 = 1
![]()
![]()
所以, ![]()
因此,一般方程的范式为xcosω+ysinω= p。
例子:
问题1.将给定的方程式转换为标准形式2x – 2y – 6 = 0。
解决方案:
Given: 2x – 2y – 6 = 0
Divide the given equation
√(2)2 + (-2)2 = √4 + 4 = √8 = 2√2
So, 2x/2√2 – 2y/2√2 = 6/2√2
x/√2 – y/√2 = 3/√2 (1)
As we know that the Intercept Form is
xcosω + ysinω = p -(2)
On comparing eq(1) and (2) we get
cosω = 1/√2
sinω = -1/√2
So, xcos45° + ysin225° = 3/√2
问题2。找到p和ω的值,等式为x + y + 3 = 0。
解决方案:
Given: x + y + 3 = 0
Divide the given equation
√(1)2 + (1)2 = √2
So, x/√2 + y/√2 = -3/√2 (1)
As we know that the Intercept Form is
xcosω + ysinω = p -(2)
On comparing eq(1) and (2) we get
cosω = 1/√2
sinω = 1/√2
xcos45° + ysin45° = -3/√2
Hence, p = -3/√2 and ω = 45°
绘制线性方程式:5x + 2y = 20
要创建线性方程5x + 2y = 20的图形,我们需要找到x轴和y轴的坐标。
步骤1:因此,我们求解y:
5x + 2y = 20-(1)
两侧减-5x
5x – 5x + 2y = 20 – 5x
2y = 20 – 5x-(2)
现在将方程式(2)除以2,我们得到
2 / 2y =(20 – 5x)/ 2
y = 10 – 5x / 2-(3)
现在,我们将方程式(3)布置为斜率截距形式,即y = mx + b
y = -5x / 2 + 10
现在,方程式(m)的斜率为-5 / 2,y轴截距(b)为10。
步骤2 :现在我们创建一个表以查找要点:
| x | y = 10 – 5x/2 | Points |
| 0 | y = 10-5(0)/2 | (0, 10) |
| 2 | y = 10 – 5(2)/2 | (2, 5) |
| 4 | y = 10 – 5(4)/2 | (4, 0) |
步骤3:找到点后,在图形上绘制x轴和y轴,并在图形上绘制所有这些坐标。
步骤4:现在通过连接点画一条直线,这里的直线代表给定的线性方程。

如何将斜率截距转换为标准形式?
让我们借助示例讨论如何将斜率截距转换为标准形式。
我们有一个方程y = 3 / 5x + 2/9。现在,我们将给定的方程式转换为标准形式。这里,给定的方程可写在斜截的形式,即,表达式y = mx + c和我们必须在标准形式给定的方程即AX + + C = 0转换。
因此,给定的方程式在两边都乘以45,因为45可以被5和9整除
45y = 45(3x / 5)+ 45(2/9)
45y = 9(3x)+ 5(2)
45y = 21x + 10
或21x – 45y + 10 = 0
因此,方程y = 3 / 5x + 2/9的标准形式为21x – 45y + 10 = 0。