在跳伞过程中,当跳伞运动员从飞机上跳下来时,下降的速度突然增加,这是由于重力引起的加速度以及吸引人体的力(即重力)引起的。另外,当跳伞者打开降落伞时,降落伞会抵抗重力并降低速度,从而使人安全着陆。还观察到,当球沿向上方向运动时,其速度要比其下降时低。这完全是由于重力而产生的加速度。
地心引力
物体对地球的吸引力称为重力或重力。宇宙中的每个物体,无论大小,都会对其他物体施加力,因此,这种力称为万有引力。
例如:在地球表面上的任何两本书或任何两个物体之间作用的力。
此外,重力也被定义为以质量吸引两个物体的任何力。此外,这种引力之所以具有吸引力,是因为它总是试图将质量拉在一起,并且因为它是一种吸引力,所以它从未将它们推开。此外,包括您在内的每个物体都被整个宇宙中所有其他物体所吸引,这被称为牛顿万有引力定律或万有引力公式。
It is stated as:
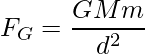
where, FG is the Gravitational constant,
G is the Gravitational Constant \left(6.67\times10^{-11}\text{N}\cdot\text{m}^2/\text{kg}^2\right),
d is the distance between the two masses,
M and m are the masses of the two objects in contact.
The SI unit of the Gravitational force is Newton (N).
重力加速度
当物体掉落到地球上时,由于地球的重力,其加速度会发生变化。将该加速度称为重力引起的加速度。这是物体由于重力而获得的加速度。
由于重力(g)引起的加速度的SI单位为m /s² 。
由于重力引起的加速度具有大小和方向。因此,它是一个向量。
海平面在地球表面的标准值为9.8 m /s² 。
从数学上讲,由于重力而产生的加速度与物体的质量成正比,与与质心的距离成反比,因此给出:
![]()
或者
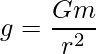
其中,G是引力常数,
m是身体的质量,
r是距中心的距离。
推导重力加速度公式
According to the second law of motion:
F = ma
But, in case of a free-falling body, the force is equal to the product of the mass of the body and acceleration due to gravity.
F = mg ……(1)
But, according to the universal law of gravitation:
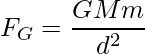 ……(2)
……(2)
Now, from the equation (1) and (2),
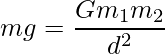
Consider for an ideal case the object is placed near to earth therefore the distance between earth and object will be radius of earth, so replace d with r and rearranging the above expression for g as:
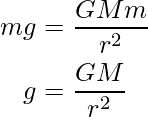
计算重力引起的加速度
The acceleration due to gravity is stated as:
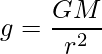
Here, substitute 6.67 × 10-11 Nm2 kg-2 for G, 6 × 1024 kg for M and 6.4 × 106 m for r in the above expression to calculate g at the surface of Earth.
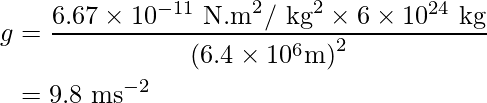
由于重力影响加速度的因素
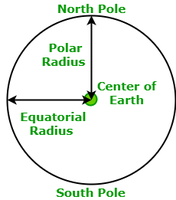
- 地球的形状:众所周知,地球的形状不是球形,而是相当椭圆形的,因此重力在不同的地方会有所不同。由于地球的半径在极点处最小,因此在地球极处的吸引力最大,约为9.82 m / s 2。由于地球的半径在赤道处最大,而地球赤道的引力最小,约为9.78 m / s 2
- 高度:当物体远离地球表面时,吸引力会随着地球与物体之间距离的增加而减小。
- 深度:将物体放入地球表面时,由于重力而产生的加速度变小。
深度D对g的影响
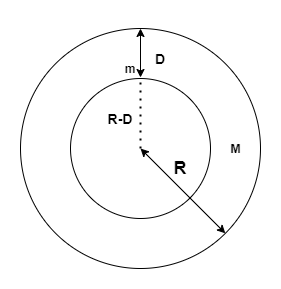
考虑质量为M的地球内部深度为D的质量为m的物体。
就密度而言,由于重力作用在地球表面产生的加速度为:
g = 4/3 xπρx RG
在深度D
g D = 4/3 xπρx(RD)G
将两个方程相除,我们得到
g d = gxπρx(RD)
Now two cases can be possible:
Case 1: If depth D is equal to the radius of the earth i.e. D = R, then:
gd = 0
Case 2: If depth D = 0, i.e. the object is at the surface of earth, then
gd = g
高度h对g的影响
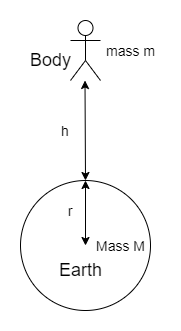
如果将物体放置在某个高度h,则d的值将变为(r + h),因此,
g h = GM /(r + h) 2
= GM / r 2 (1 + h / r) 2
=(GM / r 2 )/(1 + h / r) 2
= g /(1 + h / r) 2 (因为g = GM / r 2 )
当h远小于地球半径时,高度h处的g值由下式给出:
g h = g /(1 – 2h / r)
样本问题
这是基于上面讨论的主题而解决的一些问题。
Problem 1: A body is placed at a height of 2 x 106 m from the earth’s surface having a mass of 20 kg. Find the acceleration due to the gravity of the body?
Solution:
Given that,
The height of the body, h is 2 x 106 m.
The mass of the body, m is 20 kg.
By the formula for g at a height h is:
gh = g / (1+h/r)2
Here, g is the acceleration due to gravity, h is the height and r is the radius of the Earth.
Substitute 2 x 106 m for h, 9.8 ms-2 for g and 6.4 x 106 m for r in the above expression to calculate gh.
gh = 9.8 /(1+(2×106 / 6×106))
= 7.35 ms-2
Hence, the acceleration due to the gravity of the body at height h is 7.35 ms-2.
Problem 2: A body of mass m is placed on the earth and then on the moon. Find the ratio of acceleration due to gravity on earth w.r.t. to the moon? (mass of earth = 5.98 x 1024 Kg, mass of moon = 7.36 x 1022 Kg, radius of earth = 6.37 x 106 m, radius of moon = 1.74 x 106 m).
Solution:
The acceleration due to gravity is:
g=GM/r2
Here, G is the Gradational constant. M is the mass and r is the radius of the Earth.
The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is:
ge = G x Me/re2 ……(1)
The acceleration due to gravity on Moon is:
gm = G x Mm/rm2 ……(2)
Divide equation (1) by equation (2) as:
ge/gm = (Me x rm2)/(Mm x re2)
Substitute the given values in the above expression, to calculate the ratio of acceleration due to gravity on earth w.r.t. to the moon.
ge/gm = 6.062 ≈ 6
Hence, the ratio of acceleration due to gravity on earth w.r.t. to the moon is equal to 6:1.
Problem 3: A body is placed inside the earth at a depth d=1.5 x 106 m. Find the acceleration due to the gravity of the body? Take the density of earth 5515 kg/m3.
Solution:
The acceleration due to gravity in terms of density is:
g=4/3 x πρ x RG
Here, ρ is the density, R is the radius and G is the gravitational constant.
And, at depth d is:
gd = 4/3 x πρ x (R-d)G
= 4/3 x 5515 x (6 x 106 – 1.5 x 106) x 6.67 x 10-11
= 0.206 m/s2
Hence, the acceleration due to the gravity of the body is equal to 0.206 m/s2.
Problem 4: What will be the decrease in the value of g as a body moves a distance of R/2 above the earth’s surface?
Solution:
The acceleration due to gravity at a height h is:
gh = g / (1+h/R)2
Now, it is given that: h = R/2.
Therefore, the above expression becomes:
gh = g/(1+R/2R)2
= g/ (3/2)2
= 4/9 x g
Hence, the values of g decreases by 4/9 times.
Problem 5: A planet has a radius and mass are half those of the earth. Find the acceleration due to gravity on the planet?
Solution:
Given that,
The radius of the planet, rp = 2r.
The mass of the planet, Mp = 2M
The formula to calculate the acceleration due to gravity of the planet,
gp = GMp / rp2
= (2GM) / (2r)2
= (1/2) GM/r
= 1/2 x g (Since, g=GM/r2 )
Hence, the acceleration due to gravity on the planet is half times the acceleration due to gravity on earth.