影响重力加速度的因素
把东西拿在手里,然后扔掉。当你把它从你的手中松开时,它的速度为零。它的速度随着它的下降而上升。它飞得越远,它飞得越快。这听起来像是加速。
另一方面,加速不仅仅意味着上升速度。拿起同一个物体,垂直抛向空中。它会在上升的过程中减速,直到它停下来并改变方向。加速也可以描述为速度的降低。然而,加速度不仅仅是高度的变化。
拿起你受虐的物体并给它最后一次发射。这一次,将它水平抛,看看水平速度如何随着垂直速度的降低而增加。这种方向的变化通常称为加速度,因为加速度是速度随时间的变化率,而速度是一个向量。这两种情况下的加速度都是由重力引起的。由于重力正在将物体向下拖动,因此它正在加速。即使是直立的物体也在下落——它离开你身边的那一刻就开始下落。如果不是这样,它会一直远离你。这是由于重力引起的加速度。
现在,让我们先讨论一些基础知识,然后再了解影响重力加速度的因素。
什么是重力?
这个宇宙中所有实体或物质之间的普遍吸引力也被称为引力。它可以被认为是把所有事情都拉到一起的驱动力。重力是根据它对自由下落物体的加速度或运动来衡量的。在地球表面,重力加速度的值约为9.8 m/s 2 。因此,物体每自由落体一秒钟,它的速度就会增加大约 9.8 m/s 2 。
Some important that one must learn before going on further are:
- There exist a direct correlation between mass and gravity, that is, mass is directly proportional to gravity. The heavier the object, the greater the intensity of pull. For instance, stars and sun, have greater gravity.
- Direct relation also exists between the mass of the object and gravity, that is increase in mass leads to increase in the pull due to gravity.
- Gravity is also inversely proportional to the distance between two objects.
重力加速度
地球用一种称为万有引力或重力的力将位于其表面的任何粒子拉向其中心。当力作用在物体上时,会产生加速度,在万有引力的情况下,这种由重力引起的加速度称为重力加速度
重力加速度,通常用符号' g '表示,是宇宙中任何物体由于重力而获得的加速度。
重力加速度的 SI 单位是m/s 2 。
SI系统中g的值为9.806 ms -2 。 CGS系统中g的值为980 cm s -2 。
g的量纲公式是[M 0 L 1 T -2 ] 。
它有大小,也有方向。因此它是一个向量。
重力加速度公式的推导
在地球表面附近,重力加速度大致恒定。但是,在离地球很远的地方,或者在其他行星或卫星周围,它是变化的。重力加速度取决于以下项:
- 身体的质量,
- 距质心的距离,
- 常数 G 即万有引力常数。
Let’s consider an object of mass m, on which the acceleration due to gravity g is acting, now suppose F is the force acting on it and is given by:
F = mg ……(1)
where F is the force acting on the object,
g is the acceleration due to gravity and
m is the mass of the object.
According to the universal law of gravitation, the attractive gravitational force is given as:
F = (G × m × M) / (r+h)2
where F is the force between two objects,
G is the universal gravitational constant (6.67 × 10-11 Nm2 / kg2),
M is the mass of the earth,
r is the radius of the earth, and
h is the height at which the body is from the surface of the earth.
Since the height is negligibly small compared to the radius of the earth, so the last equation can be rewritten as:
F = (G × m × M) / r2 ……(2)
Lets equate equation (1) and (2) and solve to evaluate the expression for g as:
mg = (G × m × M) / r2
g = GM / r2
Hence, the formula of acceleration due to gravity is evaluated as shown above.
影响重力加速度的因素
g主要受以下四个因素影响:
- 地球的形状。
- 地球的自转运动。
- 地球表面以上的高度。
- 地球表面以下的深度。
g由于地球形状的变化
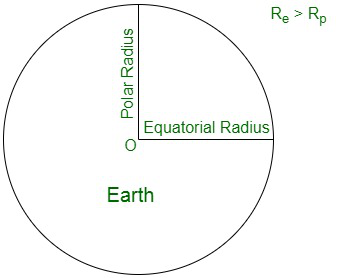
地球不是完美的球形,而是一个扁球体。地球的极半径(两极附近的半径)比赤道半径(赤道附近)小 21 公里。根据推导出的公式,重力加速度与地球半径的平方成反比
![]()
其中,g e和 g p是假定在赤道和两极的重力加速度,R e和 R p分别是赤道和两极附近的地球半径。
由上式可以很容易地推导出重力加速度在两极处较大,在赤道处较小,即 g e < g p 。因此,当一个人从赤道移动到两极时,重力加速度会增加。
地球的自转运动。
让我们假设,ω 是地球绕自身轴自转的角速度,那么在纬度为 λ 的地方的重力加速度表示为
g′ = g – Rω² cos² λ
此处,两极处的 λ 为 90°,赤道处的 λ 为 0°。
g' = g

因此,地球在两极绕着它自己的轴自转没有影响。
在赤道,
λ = 0° 和 g' = g – Rω²
g 的值在赤道处最小。
如果地球停止绕自己的轴自转,那么 g 在两极处将保持不变,但在赤道处增加 Rω²。
因此,我们可以得出结论;
在赤道,重力加速度最小。
在极点,θ=90°
重力加速度在两极处最大。
地球表面以上的高度
假设在距离地球表面高度为“h”的地方,质量“m”受到地球引力的影响。由于万有引力作用在物体上的力是;
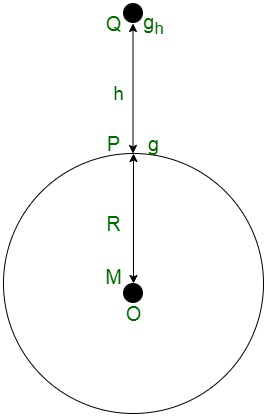
距离地球表面高度“h”处的重力加速度
……..(一世)
这里,
M是地球的质量
R是地球的半径。
在某个高度由于重力引起的加速度由“h”给出
所以,
……(ii)
那么,地球表面的重力加速度由下式表示;
………..(iii)
将等式 (iii) 和 (ii) 相除后,我们将得到,
![]() …………(四)
…………(四)
很明显,g 的值随着物体高度的增加而减小。因此,在离地球无限远的地方,g 的值变为零。
地球表面以下的深度。
地球表面的重力加速度由下式给出
![]()
认为是地球物质的密度
据我们所知
质量 = 体积 × 密度
……。(一世)
因此,如果我们将 (i) 的值放入 g 中,我们将得到
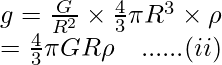

另外,让我们假设身体被带到地球表面以下的深度“d”。那么地球表面以下深度'd'处的重力加速度g d显示为:
……..(iii)
现在,将等式(iii)除以(ii),我们将得到
这里,方程(iv)是地球表面以下深度“d”处重力加速度的表达式。
从等式(iv)我们知道,当我们进入地球时,重力加速度会减小。
在地心 d = R,
因此,地心处的重力加速度为 0。
示例问题
问题 1:在距地球表面多高处,重力加速度值减小到其在地球表面上的值的九分之一?
解决方案:
From the formula
gh = 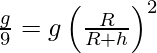
Here gh = acceleration due to gravity at height ‘h’
g = acceleration due to gravity
R = radius of the earth
Thus,
From the problem
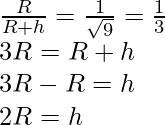
Hence,
At twice the height of the radius of the Earth value of acceleration due to gravity is reduced to one by ninth of its value on the surface of the earth.
问题 2. 如果地球的半径在保持质量不变的情况下减少 2%,重力加速度将如何变化?
解决方案:
As we know that
Where,
g = acceleration due to gravity
R = radius of the Earth
M = mass of the Earth
If R is decreased by 2% it will become
Therefore,
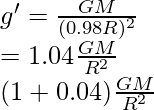
Therefore,
g’ increases by 0.04 therefore increases by 4%.
问题 3。在距地球表面多高的地方,“g”的值将减少其在地球表面的值的 19%。
解决方案:
g’ = 81% of g
g’ =
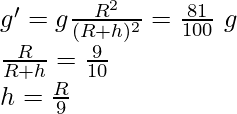
Therefore,
At the height of from the Earth surface the value of ‘g’ will be reduced to 19% of its value at the surface of earth.
问题 4. 木星表面的重力加速度是地球表面的几倍?
(使用以下数据:m Earth = 5.98 × 10 24 kg,r Earth = 6.4 × 10 6 m,m Jupiter = 1.9 × 10 27 kg,r Jupiter = 6.99 × 10 7 m)
解决方案:
To solve this example we will need to find the ratio of acceleration due to gravity of Jupiter to acceleration due to gravity of Earth
![]()
By the relation;
![]()
Here,
m = mass of planet
r = radius of planet

Thus, the acceleration due to gravity on Jupiter surface is 2.66 times more than that of Earth’s surface.
问题 5. 解释重力加速度随着高度的增加而增加或减少?
解决方案:
As we know that acceleration due to gravity at the depth of h is shown as;
![]()
Here,
Re = Radius of the Earth
g = Acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Earth
Thus, we can clearly see that from the equation that acceleration due to gravity increases with decrease in height and decreases with increase in height.
问题 6. 解释重力加速度与地球质量和物体质量无关?
解决方案:
As we know that acceleration due to gravity of body of mass m is shown as;
![]()
Here,
G = Is the universal gravitational constant
M = Mass of the Earth
R = Radius of the Earth
Thus, we can clearly see here that acceleration due to gravity is independent of the mass.
问题 7. 解释重力加速度随着深度的增加而增加或减少?
解决方案:
As we know that acceleration due to gravity is shown as;
![]()
Thus, here we can clearly see that the acceleration due to gravity increases with decrease in depth and decreases with increase in depth.