给定具有N个顶点和M个边且没有自环或多个边的无向图。任务是将给定的无向图转换为有向图,以使路径的长度不大于1。如果可以制作这样的图,则在M行中打印两个以空格分隔的整数u和v,其中u, v分别表示源顶点和目标顶点。如果不可能,则打印-1。
例子:
Input:
Output:
1 2
1 3
1 4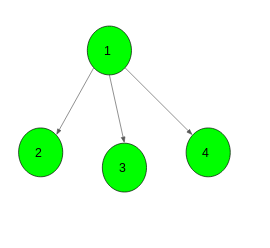
Input: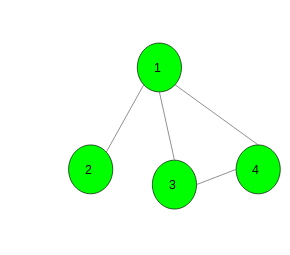
Output: -1
For the given graph it is not possible to get a directed graph
such that there is no path of length greater than 1
方法:假设图形包含一个奇数长度的循环。这意味着此循环的某些两个连续边将以相同的方式定向,并将形成长度为2的路径。那么答案是-1。
并且如果该图不包含奇数长度的循环。然后是二分的。让我们给它上色,看看我们得到了什么。我们在左侧有一些顶点,在右侧有一些顶点,并且所有边缘都连接来自不同部分的顶点。让我们调整所有边缘的方向,使其从左到右。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
#define N 100005
// To store the graph
vector gr[N];
// To store colour of each vertex
int colour[N];
// To store edges
vector > edges;
// To check graph is bipartite or not
bool bip;
// Function to add edges
void add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].push_back(y);
gr[y].push_back(x);
edges.push_back(make_pair(x, y));
}
// Function to check given graph
// is bipartite or not
void dfs(int x, int col)
{
// colour the vertex x
colour[x] = col;
// For all it's child vertices
for (auto i : gr[x]) {
// If still not visited
if (colour[i] == -1)
dfs(i, col ^ 1);
// If visited and having
// same colour as parent
else if (colour[i] == col)
bip = false;
}
}
// Function to convert the undirected
// graph into the directed graph such that
// there is no path of length greater than 1
void Directed_Graph(int n, int m)
{
// Initially each vertex has no colour
memset(colour, -1, sizeof colour);
// Suppose bipartite is possible
bip = true;
// Call bipartite function
dfs(1, 1);
// If bipartite is not possible
if (!bip) {
cout << -1;
return;
}
// If bipartite is possible
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
// Make an edge from vertex having
// colour 1 to colour 0
if (colour[edges[i].first] == 0)
swap(edges[i].first, edges[i].second);
cout << edges[i].first << " "
<< edges[i].second << endl;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 4, m = 3;
// Add edges
add_edge(1, 2);
add_edge(1, 3);
add_edge(1, 4);
// Function call
Directed_Graph(n, m);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static int N = 100005;
// To store the graph
static Vector []gr = new Vector[N];
// To store colour of each vertex
static int []colour = new int[N];
// To store edges
static Vector edges = new Vector<>();
// To check graph is bipartite or not
static boolean bip;
// Function to add edges
static void add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].add(y);
gr[y].add(x);
edges.add(new pair(x, y));
}
// Function to check given graph
// is bipartite or not
static void dfs(int x, int col)
{
// colour the vertex x
colour[x] = col;
// For all it's child vertices
for (Integer i : gr[x])
{
// If still not visited
if (colour[i] == -1)
dfs(i, col ^ 1);
// If visited and having
// same colour as parent
else if (colour[i] == col)
bip = false;
}
}
// Function to convert the undirected
// graph into the directed graph such that
// there is no path of length greater than 1
static void Directed_Graph(int n, int m)
{
// Initially each vertex has no colour
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
colour[i] = -1;
// Suppose bipartite is possible
bip = true;
// Call bipartite function
dfs(1, 1);
// If bipartite is not possible
if (!bip)
{
System.out.print(-1);
return;
}
// If bipartite is possible
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
// Make an edge from vertex having
// colour 1 to colour 0
if (colour[edges.get(i).first] == 0)
{
Collections.swap(edges, edges.get(i).first,
edges.get(i).second);
}
System.out.println(edges.get(i).first + " " +
edges.get(i).second);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4, m = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
gr[i] = new Vector<>();
// Add edges
add_edge(1, 2);
add_edge(1, 3);
add_edge(1, 4);
// Function call
Directed_Graph(n, m);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
N = 100005
# To store the graph
gr = [[] for i in range(N)]
# To store colour of each vertex
colour = [-1] * N
# To store edges
edges = []
# To check graph is bipartite or not
bip = True
# Function to add edges
def add_edge(x, y):
gr[x].append(y)
gr[y].append(x)
edges.append((x, y))
# Function to check given graph
# is bipartite or not
def dfs(x, col):
# colour the vertex x
colour[x] = col
global bip
# For all it's child vertices
for i in gr[x]:
# If still not visited
if colour[i] == -1:
dfs(i, col ^ 1)
# If visited and having
# same colour as parent
elif colour[i] == col:
bip = False
# Function to convert the undirected
# graph into the directed graph such that
# there is no path of length greater than 1
def Directed_Graph(n, m):
# Call bipartite function
dfs(1, 1)
# If bipartite is not possible
if not bip:
print(-1)
return
# If bipartite is possible
for i in range(0, m):
# Make an edge from vertex
# having colour 1 to colour 0
if colour[edges[i][0]] == 0:
edges[i][0], edges[i][1] = edges[i][1], edges[i][0]
print(edges[i][0], edges[i][1])
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
n, m = 4, 3
# Add edges
add_edge(1, 2)
add_edge(1, 3)
add_edge(1, 4)
# Function call
Directed_Graph(n, m)
# This code is contributed by Rituraj JainC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
class pair
{
public int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static int N = 100005;
// To store the graph
static List []gr = new List[N];
// To store colour of each vertex
static int []colour = new int[N];
// To store edges
static List edges = new List();
// To check graph is bipartite or not
static Boolean bip;
// Function to add edges
static void add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].Add(y);
gr[y].Add(x);
edges.Add(new pair(x, y));
}
// Function to check given graph
// is bipartite or not
static void dfs(int x, int col)
{
// colour the vertex x
colour[x] = col;
// For all it's child vertices
foreach (int i in gr[x])
{
// If still not visited
if (colour[i] == -1)
dfs(i, col ^ 1);
// If visited and having
// same colour as parent
else if (colour[i] == col)
bip = false;
}
}
// Function to convert the undirected
// graph into the directed graph such that
// there is no path of length greater than 1
static void Directed_Graph(int n, int m)
{
// Initially each vertex has no colour
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
colour[i] = -1;
// Suppose bipartite is possible
bip = true;
// Call bipartite function
dfs(1, 1);
// If bipartite is not possible
if (!bip)
{
Console.Write(-1);
return;
}
// If bipartite is possible
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
// Make an edge from vertex having
// colour 1 to colour 0
if (colour[edges[i].first] == 0)
{
var v = edges[i].first;
edges[i].first = edges[i].second;
edges[i].second = v;
}
Console.WriteLine(edges[i].first + " " +
edges[i].second);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4, m = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
gr[i] = new List();
// Add edges
add_edge(1, 2);
add_edge(1, 3);
add_edge(1, 4);
// Function call
Directed_Graph(n, m);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji 输出:
1 2
1 3
1 4
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。