给定一个具有N个顶点和一个整数K 的有向无权图。任务是为每对顶点(u, v)找到长度为K的路径数。路径不必很简单,即可以在单个路径中多次访问顶点和边。
该图表示为邻接矩阵,其中值G[i][j] = 1表示从顶点i到顶点j存在边,而G[i][j] = 0表示从i到j没有边。
例子:
Input: K = 2,
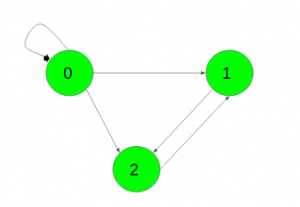
Output:
1 2 2
0 1 0
0 0 1
Number of paths from 0 to 0 of length k is 1({0->0->0})
Number of paths from 0 to 1 of length k are 2({0->0->1}, {0->2->1})
Number of paths from 0 to 2 of length k are 2({0->0->2}, {0->1->2})
Number of paths from 1 to 1 of length k is 1({1->2->1})
Number of paths from 2 to 2 of length k is 1({2->1->2})
Input: K = 3,
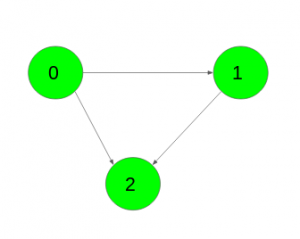
Output:
1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
Number of paths from 0 to 0 of length k is 1({0->1->2->0})
Number of paths from 1 to 1 of length k is 1({1->2->0->1})
Number of paths from 2 to 2 of length k is 1({2->1->0->2})
先决条件:矩阵求幂、矩阵乘法
方法:很明显,对于k = 1的情况,给定的邻接矩阵是问题的答案。它包含每对顶点之间长度为1的路径数。
让我们假设某些k的答案是Mat k而k + 1的答案是Mat k + 1 。
Mat k + 1 [i][j] = ∑ p = 1 N Mat k [i][p]*G[p][j]
很容易看出,该公式只计算矩阵Mat k和G的乘积,即Mat k + 1 = Mat k * G
因此,问题的解可以表示为Mat k = G * G * … * G(k 次) = G k
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
#define N 3
// Function to multiply two matrices
void multiply(int a[][N], int b[][N], int res[][N])
{
int mul[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
mul[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
mul[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
}
}
// Storing the multiplication result in res[][]
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
res[i][j] = mul[i][j];
}
// Function to compute G raised to the power n
void power(int G[N][N], int res[N][N], int n)
{
// Base condition
if (n == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
res[i][j] = G[i][j];
return;
}
// Recursion call for first half
power(G, res, n / 2);
// Multiply two halves
multiply(res, res, res);
// If n is odd
if (n % 2 != 0)
multiply(res, G, res);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int G[N][N] = { { 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 0 } };
int k = 2, res[N][N];
power(G, res, k);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
cout << res[i][j] << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
// This Code is improved by cidacoder Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
static int N = 3;
// Function to multiply two matrices
static void multiply(int a[][], int b[][], int res[][])
{
int [][]mul = new int[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
mul[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
mul[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
}
}
// Storing the multiplication result in res[][]
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
res[i][j] = mul[i][j];
}
// Function to compute G raised to the power n
static void power(int G[][], int res[][], int n)
{
// Base condition
if (n == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
res[i][j] = G[i][j];
return;
}
// Recursion call for first half
power(G, res, n / 2);
multiply(res, res, res);
// If n is odd
if (n % 2 != 0)
multiply(res, G, res);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int G[][] = { { 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 0 } };
int k = 2;
int [][]res = new int[N][N];
power(G, res, k);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
System.out.print(res[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println("");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
// This Code is improved by cidacoderPython3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
import numpy as np
N = 3
# Function to multiply two matrices
def multiply(a, b, res) :
mul = np.zeros((N,N));
for i in range(N) :
for j in range(N) :
mul[i][j] = 0;
for k in range(N) :
mul[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
# Storing the multiplication result in res[][]
for i in range(N) :
for j in range(N) :
res[i][j] = mul[i][j];
# Function to compute G raised to the power n
def power(G, res, n) :
# Base condition
if (n == 1) :
for i in range(N) :
for j in range(N) :
res[i][j] = G[i][j];
return;
# Recursion call for first half
power(G, res, n // 2);
# Multiply two halves
multiply(res, res, res);
# If n is odd
if (n % 2 != 0) :
multiply(res, G, res);
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
G = [
[ 1, 1, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 1, 0 ]
];
k = 2;
res = np.zeros((N,N));
power(G, res, k);
for i in range(N) :
for j in range(N) :
print(res[i][j],end = " ");
print()
# This code is contributed by AnkitRai01
# This Code is improved by cidacoderC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int N = 3;
// Function to multiply two matrices
static void multiply(int [,]a, int [,]b, int [,]res)
{
int [,]mul = new int[N,N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
mul[i,j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
mul[i,j] += a[i,k] * b[k,j];
}
}
// Storing the multiplication result in res[][]
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
res[i,j] = mul[i,j];
}
// Function to compute G raised to the power n
static void power(int [,]G, int [,]res, int n)
{
// Base condition
if (n == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
res[i,j] = G[i,j];
return;
}
// Recursion call for first half
power(G, res, n / 2);
// Multiply two halves
multiply(res, res, res);
// If n is odd
if (n % 2 != 0)
multiply(res, G, res);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int [,]G = { { 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 0 } };
int k = 2;
int [,]res = new int[N,N];
power(G, res, k);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
Console.Write(res[i,j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine("");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67..
// This code is improved by cidacoderJavascript
1 2 2
0 1 0
0 0 1时间复杂度——
由于我们必须将邻接矩阵乘以 log(k) 次(使用矩阵求幂),因此算法的时间复杂度为O((|V|^3)*log(k)) ,其中 V 是顶点数, k 是路径的长度。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。