排列排列是元素的排列。 n个元素的排列可以用数字1、2…n的排列顺序表示。例如。 5、1、4、2、3
循环符号排列可以表示为排列循环的组成。置换周期是置换中彼此交换位置的一组元素。
例如
P = { 5, 1, 4, 2, 3 }:
Here, 5 goes to 1, 1 goes to 2 and so on (according to their indices position):
5 -> 1
1 -> 2
2 -> 4
4 -> 3
3 -> 5
Thus it can be represented as a single cycle: (5, 1, 2, 4, 3).
Now consider the permutation: {5, 1, 4, 3, 2}. Here
5 -> 1
1 -> 2
2 -> 5 this closes 1 cycle.
The other cycle is
4 -> 3
3 -> 4
In cycle notation it will be represented as (5, 1, 2) (4, 3).
换位
现在,所有循环都可以分解为2个循环(换位)的组合。置换中的换位数量很重要,因为它给出了从标识排列中获得此特定排列所需的2个元素交换的最少数目:1、2、3,…n。这样的2个周期的数量的奇偶性表示排列是偶数还是奇数。
例如
The cycle (5, 1, 2, 4, 3) can be written as (5, 3)(5, 4)(5, 2)(5, 1). 4 transpositions (even).
Similarly,
(5, 1, 2) -> (5, 2)(5, 1)
(5, 1, 2)(4, 3) -> (5, 2)(5, 1)(4, 3). 3 transpositions (odd).
It is clear from the examples that the number of transpositions from a cycle = length of the cycle – 1.
问题
给定n个数字P 1 ,P 2 ,P 3 ,…P n的排列。计算其中的换位数量。
例子:
Input: 5 1 4 3 2
Output: 3 方法:排列可以很容易地表示为有向图,其中连接的组件数给出了循环数。并且(每个成分的大小– 1)给出了该循环的转座数。
排列示例:{ 5,1,4,3,2 }->(5,1,2)(4,3)
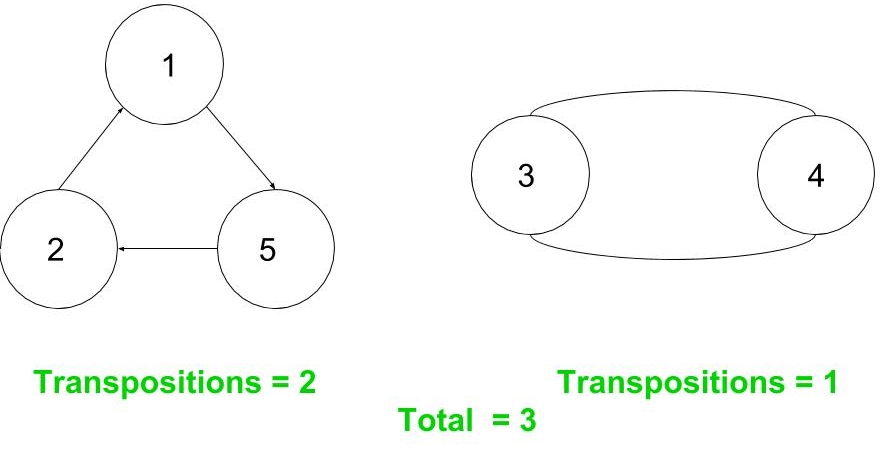
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// CPP Program to find the number of
// transpositions in a permutation
#include
using namespace std;
#define N 1000001
int visited[N];
// This array stores which element goes to which position
int goesTo[N];
// For eg. in { 5, 1, 4, 3, 2 }
// goesTo[1] = 2
// goesTo[2] = 5
// goesTo[3] = 4
// goesTo[4] = 3
// goesTo[5] = 1
// This function returns the size of a component cycle
int dfs(int i)
{
// If it is already visited
if (visited[i] == 1)
return 0;
visited[i] = 1;
int x = dfs(goesTo[i]);
return (x + 1);
}
// This functio returns the number
// of transpositions in the permutation
int noOfTranspositions(int P[], int n)
{
// Initializing visited[] array
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
visited[i] = 0;
// building the goesTo[] array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
goesTo[P[i]] = i + 1;
int transpositions = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
int ans = dfs(i);
transpositions += ans - 1;
}
}
return transpositions;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int permutation[] = { 5, 1, 4, 3, 2 };
int n = sizeof(permutation) / sizeof(permutation[0]);
cout << noOfTranspositions(permutation, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java Program to find the number of
// transpositions in a permutation
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int N = 1000001;
static int visited[] = new int[N];
// This array stores which element
// goes to which position
static int goesTo[]= new int[N];
// For eg. in { 5, 1, 4, 3, 2 }
// goesTo[1] = 2
// goesTo[2] = 5
// goesTo[3] = 4
// goesTo[4] = 3
// goesTo[5] = 1
// This function returns the size
// of a component cycle
static int dfs(int i)
{
// If it is already visited
if (visited[i] == 1)
return 0;
visited[i] = 1;
int x = dfs(goesTo[i]);
return (x + 1);
}
// This functio returns the number
// of transpositions in the
// permutation
static int noOfTranspositions(int P[],
int n)
{
// Initializing visited[] array
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
visited[i] = 0;
// building the goesTo[] array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
goesTo[P[i]] = i + 1;
int transpositions = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
int ans = dfs(i);
transpositions += ans - 1;
}
}
return transpositions;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int permutation[] = { 5, 1, 4, 3, 2 };
int n = permutation.length ;
System.out.println(
noOfTranspositions(permutation, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.Python3
# Python Program to find the number of
# transpositions in a permutation
N = 1000001
visited = [0] * N;
# This array stores which element goes to which position
goesTo = [0] * N;
# For eg. in { 5, 1, 4, 3, 2 }
# goesTo[1] = 2
# goesTo[2] = 5
# goesTo[3] = 4
# goesTo[4] = 3
# goesTo[5] = 1
# This function returns the size of a component cycle
def dfs(i) :
# If it is already visited
if (visited[i] == 1) :
return 0;
visited[i] = 1;
x = dfs(goesTo[i]);
return (x + 1);
# This functio returns the number
# of transpositions in the permutation
def noOfTranspositions(P, n) :
# Initializing visited[] array
for i in range(1, n + 1) :
visited[i] = 0;
# building the goesTo[] array
for i in range(n) :
goesTo[P[i]] = i + 1;
transpositions = 0;
for i in range(1, n + 1) :
if (visited[i] == 0) :
ans = dfs(i);
transpositions += ans - 1;
return transpositions;
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
permutation = [ 5, 1, 4, 3, 2 ];
n = len(permutation);
print(noOfTranspositions(permutation, n));
# This code is contributed by AnkitRai01C#
// C# Program to find the number of
// transpositions in a permutation
using System;
class GFG {
static int N = 1000001;
static int []visited = new int[N];
// This array stores which element
// goes to which position
static int []goesTo= new int[N];
// For eg. in { 5, 1, 4, 3, 2 }
// goesTo[1] = 2
// goesTo[2] = 5
// goesTo[3] = 4
// goesTo[4] = 3
// goesTo[5] = 1
// This function returns the size
// of a component cycle
static int dfs(int i)
{
// If it is already visited
if (visited[i] == 1)
return 0;
visited[i] = 1;
int x = dfs(goesTo[i]);
return (x + 1);
}
// This functio returns the number
// of transpositions in the
// permutation
static int noOfTranspositions(int []P,
int n)
{
// Initializing visited[] array
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
visited[i] = 0;
// building the goesTo[] array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
goesTo[P[i]] = i + 1;
int transpositions = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
int ans = dfs(i);
transpositions += ans - 1;
}
}
return transpositions;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main ()
{
int []permutation = { 5, 1, 4, 3, 2 };
int n = permutation.Length ;
Console.WriteLine(
noOfTranspositions(permutation, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.Javascript
输出:
3时间复杂度: O(n)
辅助空间: O(n)