系统中有两个单链表。由于某些编程错误,链接列表之一的末端节点链接到第二个列表,从而形成了一个倒置的Y形列表。编写程序以获取两个链接列表合并的点。
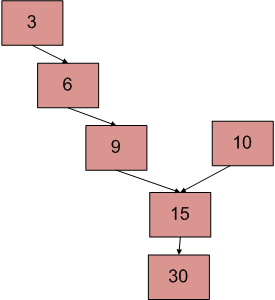
上图显示了一个以15为交点的两个链表的示例。
方法:可以观察到,遍历第一个链表然后从第二个链表的头到交点的节点数等于遍历第二个链表然后从第一个链表的头涉及的节点数。第一个列表到交点。考虑上面给出的示例,开始遍历两个链接列表,并分别使用两个指针curr1和curr2指向给定链接列表的头部。
- 如果curr1!= null,则将其更新以指向下一个节点,否则将其更新以指向第二个列表的第一个节点。
- 如果curr2!= null,则将其更新为指向下一个节点,否则将其更新为指向第一个列表的第一个节点。
- 当curr1不等于curr2时,重复上述步骤。
现在,两个指针curr1和curr2将指向同一节点,即合并点。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Link list node
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
};
// Function to get the intersection point
// of the given linked lists
int getIntersectionNode(Node* head1, Node* head2)
{
Node *curr1 = head1, *curr2 = head2;
// While both the pointers are not equal
while (curr1 != curr2) {
// If the first pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the second linked list
if (curr1 == NULL) {
curr1 = head2;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else {
curr1 = curr1->next;
}
// If the second pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the first linked list
if (curr2 == NULL) {
curr2 = head1;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else {
curr2 = curr2->next;
}
}
// Return the intersection node
return curr1->data;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
/*
Create two linked lists
1st Linked list is 3->6->9->15->30
2nd Linked list is 10->15->30
15 is the intersection point
*/
Node* newNode;
Node* head1 = new Node();
head1->data = 10;
Node* head2 = new Node();
head2->data = 3;
newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = 6;
head2->next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = 9;
head2->next->next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = 15;
head1->next = newNode;
head2->next->next->next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = 30;
head1->next->next = newNode;
head1->next->next->next = NULL;
// Print the intersection node
cout << getIntersectionNode(head1, head2);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
// Link list node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
};
// Function to get the intersection point
// of the given linked lists
static int getIntersectionNode(Node head1, Node head2)
{
Node curr1 = head1, curr2 = head2;
// While both the pointers are not equal
while (curr1 != curr2)
{
// If the first pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the second linked list
if (curr1 == null)
{
curr1 = head2;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else
{
curr1 = curr1.next;
}
// If the second pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the first linked list
if (curr2 == null)
{
curr2 = head1;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else
{
curr2 = curr2.next;
}
}
// Return the intersection node
return curr1.data;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/*
Create two linked lists
1st Linked list is 3.6.9.15.30
2nd Linked list is 10.15.30
15 is the intersection point
*/
Node newNode;
Node head1 = new Node();
head1.data = 10;
Node head2 = new Node();
head2.data = 3;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 6;
head2.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 9;
head2.next.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 15;
head1.next = newNode;
head2.next.next.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 30;
head1.next.next = newNode;
head1.next.next.next = null;
// Print the intersection node
System.out.print(getIntersectionNode(head1, head2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Link list node
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.data = 0
self.next = None
# Function to get the intersection point
# of the given linked lists
def getIntersectionNode( head1, head2):
curr1 = head1
curr2 = head2
# While both the pointers are not equal
while (curr1 != curr2):
# If the first pointer is None then
# set it to point to the head of
# the second linked list
if (curr1 == None) :
curr1 = head2
# Else point it to the next node
else:
curr1 = curr1.next
# If the second pointer is None then
# set it to point to the head of
# the first linked list
if (curr2 == None):
curr2 = head1
# Else point it to the next node
else:
curr2 = curr2.next
# Return the intersection node
return curr1.data
# Driver code
# Create two linked lists
# 1st Linked list is 3.6.9.15.30
# 2nd Linked list is 10.15.30
# 15 is the intersection point
newNode = None
head1 = Node()
head1.data = 10
head2 = Node()
head2.data = 3
newNode = Node()
newNode.data = 6
head2.next = newNode
newNode = Node()
newNode.data = 9
head2.next.next = newNode
newNode = Node()
newNode.data = 15
head1.next = newNode
head2.next.next.next = newNode
newNode = Node()
newNode.data = 30
head1.next.next = newNode
head1.next.next.next = None
# Print the intersection node
print( getIntersectionNode(head1, head2))
# This code is contributed by Arnab KunduC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Link list node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
};
// Function to get the intersection point
// of the given linked lists
static int getIntersectionNode(Node head1,
Node head2)
{
Node curr1 = head1, curr2 = head2;
// While both the pointers are not equal
while (curr1 != curr2)
{
// If the first pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the second linked list
if (curr1 == null)
{
curr1 = head2;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else
{
curr1 = curr1.next;
}
// If the second pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the first linked list
if (curr2 == null)
{
curr2 = head1;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else
{
curr2 = curr2.next;
}
}
// Return the intersection node
return curr1.data;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/*
Create two linked lists
1st Linked list is 3.6.9.15.30
2nd Linked list is 10.15.30
15 is the intersection point
*/
Node newNode;
Node head1 = new Node();
head1.data = 10;
Node head2 = new Node();
head2.data = 3;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 6;
head2.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 9;
head2.next.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 15;
head1.next = newNode;
head2.next.next.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 30;
head1.next.next = newNode;
head1.next.next.next = null;
// Print the intersection node
Console.Write(getIntersectionNode(head1, head2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji输出:
15
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。