给定两个由正值节点组成的大小为N和M 的链表,它们有一个共同的交点,任务是找到两个链表合并的交点。
例子:
Input: L1: 3 → 6 → 9 → 15 → 30, L2: 10 → 15 → 30
Output: 15
Explanation:
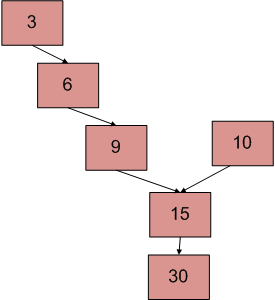
From the above image, the intersection point of the two linked lists is 15.
Input: L1: 1 → 2 → 3, L2: 4 → 5 → 1 → 2 → 3
Output: 1
方法:思想是遍历第一个链表,将每个节点的值乘以-1,从而使它们为负。然后,遍历第二个链表,打印第一个值为负的节点的值。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 遍历第一个链表L1并将每个节点的值乘以-1 。
- 现在,遍历第二个链表L2 ,如果存在任何具有负值的节点,则打印该节点值的绝对值作为链表的结果交集并跳出循环。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a node
// of a Linked List
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
// Constructor
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
// Function to find the intersection
// point of the two Linked Lists
Node* intersectingNode(Node* headA,
Node* headB)
{
// Traverse the first linked list
// and multiply all values by -1
Node* a = headA;
while (a) {
// Update a -> data
a->data *= -1;
// Update a
a = a->next;
}
// Traverse the second Linked List
// and find the value of the first
// node having negative value
Node* b = headB;
while (b) {
// Intersection point
if (b->data < 0)
break;
// Update b
b = b->next;
}
return b;
}
// Function to create linked lists
void formLinkList(Node*& head1,
Node*& head2)
{
// Linked List L1
head1 = new Node(3);
head1->next = new Node(6);
head1->next->next = new Node(9);
head1->next->next->next = new Node(15);
head1->next->next->next->next = new Node(30);
// Linked List L2
head2 = new Node(10);
head2->next = head1->next->next->next;
return;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* head1;
Node* head2;
formLinkList(head1, head2);
cout << abs(intersectingNode(head1,
head2)
->data);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
static Node head1 = null;
static Node head2 = null;
// Structure of a node
// of a Linked List
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
// Function to find the intersection
// point of the two Linked Lists
static Node intersectingNode(Node headA, Node headB)
{
// Traverse the first linked list
// and multiply all values by -1
Node a = headA;
while (a != null)
{
// Update a -> data
a.data *= -1;
// Update a
a = a.next;
}
// Traverse the second Linked List
// and find the value of the first
// node having negative value
Node b = headB;
while (b != null)
{
// Intersection point
if (b.data < 0)
break;
// Update b
b = b.next;
}
return b;
}
// Function to create linked lists
static void formLinkList()
{
// Linked List L1
head1 = new Node(3);
head1.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next = new Node(9);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(15);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(30);
// Linked List L2
head2 = new Node(10);
head2.next = head1.next.next.next;
return;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
formLinkList();
System.out.println(Math.abs(
intersectingNode(head1, head2).data));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L V.Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Structure of a node
# of a Linked List
class Node:
def __init__(self, d):
self.data = d
self.next = None
# Function to find the intersection
# point of the two Linked Lists
def intersectingNode(headA, headB):
# Traverse the first linked list
# and multiply all values by -1
a = headA
while (a):
# Update a . data
a.data *= -1
# Update a
a = a.next
# Traverse the second Linked List
# and find the value of the first
# node having negative value
b = headB
while (b):
# Intersection point
if (b.data < 0):
break
# Update b
b = b.next
return b
# Function to create linked lists
def formLinkList(head1, head2):
# Linked List L1
head1 = Node(3)
head1.next = Node(6)
head1.next.next = Node(9)
head1.next.next.next = Node(15)
head1.next.next.next.next = Node(30)
# Linked List L2
head2 = Node(10)
head2.next = head1.next.next.next
return head1, head2
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
head1, head2 = formLinkList(None, None)
print(abs(intersectingNode(head1, head2).data))
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29输出:
15时间复杂度: O(N + M)
辅助空间: O(1)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live