用于查找两个链表的交点的Python程序
一个系统中有两个单链表。由于一些编程错误,其中一个链表的结束节点链接到了第二个链表,形成了一个倒 Y 形链表。编写一个程序来获取两个链表合并的点。
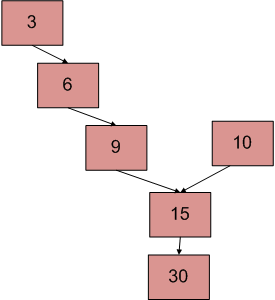
上图显示了一个示例,其中两个链表具有 15 个作为交点。
方法1(只需使用两个循环):
使用 2 个嵌套的 for 循环。外部循环将针对第一个列表的每个节点,内部循环将针对第二个列表。在内部循环中,检查第二个链表的任何节点是否与第一个链表的当前节点相同。此方法的时间复杂度为 O(M * N),其中 m 和 n 是两个列表中的节点数。
方法2(标记访问节点):
该解决方案需要修改基本的链表数据结构。每个节点都有一个已访问标志。遍历第一个链表并不断标记访问过的节点。现在遍历第二个链表,如果再次看到访问过的节点,则有一个交点,返回相交的节点。此解决方案在O(m+n)中有效,但需要每个节点的附加信息。不需要修改基本数据结构的该解决方案的变体可以使用散列来实现。遍历第一个链表并将访问节点的地址存储在哈希中。现在遍历第二个链表,如果您看到哈希中已经存在的地址,则返回相交节点。
方法3(使用节点数的差异):
- 获取第一个列表中的节点数,设 count 为 c1。
- 获取第二个列表中的节点数,设 count 为 c2。
- 获得计数的差异d = abs(c1 – c2)
- 现在遍历从第一个节点到 d 个节点的更大列表,以便从这里开始两个列表的节点数相等
- 然后我们可以并行遍历这两个列表,直到遇到一个公共节点。 (注意,获取普通节点是通过比较节点的地址来完成的)
下图是上述方法的试运行:

以下是上述方法的实现:
Python3
# Python program to implement
# the above approach
# Defining a node for LinkedList
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
def getIntersectionNode(head1, head2):
# Finding the total number of elements
# in head1 LinkedList
c1=getCount(head1)
# Finding the total number of elements
# in head2 LinkedList
c2=getCount(head2)
# Traverse the bigger node by 'd' so that
# from that node onwards, both LinkedList
# would be having same number of nodes and
# we can traverse them together.
if c1 > c2:
d = c1 - c2
return _getIntersectionNode(d, head1,
head2)
else:
d = c2 - c1
return _getIntersectionNode(d, head2,
head1)
def _getIntersectionNode(d, head1, head2):
current1 = head1
current2 = head2
for i in range(d):
if current1 is None:
return -1
current1 = current1.next
while current1 is not None and current2 is not None:
# Instead of values, we need to check
# if there addresses are same because
# there can be a case where value is
# same but that value is not an
# intersecting point.
if current1 is current2:
# or current2.data (the value
# would be same)
return current1.data
current1 = current1.next
current2 = current2.next
# Incase, we are not able to find
# our intersecting point.
return -1
# Function to get the count of a LinkedList
def getCount(node):
cur=node
count=0
while cur is not None:
count+=1
cur=cur.next
return count
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Creating two LinkedList
# 1st one: 3->6->9->15->30
# 2nd one: 10->15->30
# We can see that 15 would be
# our intersection point
# Defining the common node
common = Node(15)
#Defining the first LinkedList
head1 = Node(3)
head1.next = Node(6)
head1.next.next = Node(9)
head1.next.next.next = common
head1.next.next.next.next = Node(30)
# Defining the second LinkedList
head2 = Node(10)
head2.next = common
head2.next.next = Node(30)
print("The node of intersection is ",
getIntersectionNode(head1,head2))
# This code is contributed by Ansh Gupta.输出:
The node of intersection is 15时间复杂度: O(m+n)
辅助空间: O(1)
方法4(在第一个列表中画圈):
感谢Saravanan Man提供以下解决方案。
1.遍历第一个链表(计数元素),制作一个循环链表。 (记住最后一个节点,以便我们以后可以打破圆圈)。
2. 现在将问题视为在第二个链表中找到循环。所以问题就解决了。
3. 由于我们已经知道循环的长度(第一个链表的大小),我们可以遍历第二个链表中的许多节点,然后从第二个链表的开头开始另一个指针。我们必须遍历直到它们相等,这就是所需的交点。
4. 从链表中删除圆圈。
时间复杂度: O(m+n)
辅助空间: O(1)
方法5(反转第一个列表并制作方程式):
感谢Saravanan Mani提供这种方法。
1) Let X be the length of the first linked list until intersection point.
Let Y be the length of the second linked list until the intersection point.
Let Z be the length of the linked list from the intersection point to End of
the linked list including the intersection node.
We Have
X + Z = C1;
Y + Z = C2;
2) Reverse first linked list.
3) Traverse Second linked list. Let C3 be the length of second list - 1.
Now we have
X + Y = C3
We have 3 linear equations. By solving them, we get
X = (C1 + C3 – C2)/2;
Y = (C2 + C3 – C1)/2;
Z = (C1 + C2 – C3)/2;
WE GOT THE INTERSECTION POINT.
4) Reverse first linked list.优点:没有指针比较。
缺点:修改链表(倒排表)。
时间复杂度: O(m+n)
辅助空间: O(1)
方法6(遍历两个列表并比较最后一个节点的地址):该方法仅用于检测是否存在交叉点。 (感谢 NeoTheSaviour 的建议)
1) Traverse list 1, store the last node address
2) Traverse list 2, store the last node address.
3) If nodes stored in 1 and 2 are same then they are intersecting.该方法的时间复杂度为O(m+n),使用的辅助空间为O(1)
有关详细信息,请参阅关于编写函数以获取两个链表的交点的完整文章!