给定一个具有N个节点和M个边的加权无向连通图。一些节点被标记为良好。任务是找到两个不同的良好节点之间的最短距离。
注意:在以下示例中,标记为黄色的节点被认为是良好的节点。
例子:
Input :
Output : 7
Explanation :
Pairs of Good Nodes and distance between them are:
(1 to 3) -> distance: 7,
(3 to 5) -> distance: 9,
(1 to 5) -> distance: 16,
out of which 7 is the minimum.
Input :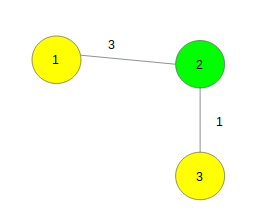
Output : 4方法:让我们首先考虑一种算法来解决给定问题的一个简单版本,其中所有边的权重为1。
- 从这里选择一个随机的好节点并执行BFS,并在第一级停止说
 其中包含另一个好节点。
其中包含另一个好节点。 - 我们知道,任何两个好节点之间的最小距离不能超过s 。因此,我们再次随机选择了一个之前未取的好节点,然后再次执行BFS。如果找不到s距离内的任何特殊节点,我们将终止搜索。如果这样做,那么我们将更新s的值,并对其他随机取的特殊节点重复该过程。
当权重为多个时,我们可以应用类似的算法。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to find the shortest pairwise
// distance between any two different good nodes.
#include
using namespace std;
#define N 100005
const int MAXI = 99999999;
// Function to add edges
void add_edge(vector > gr[], int x,
int y, int weight)
{
gr[x].push_back({ y, weight });
gr[y].push_back({ x, weight });
}
// Function to find the shortest
// distance between any pair of
// two different good nodes
int minDistance(vector > gr[], int n,
int dist[], int vis[], int a[], int k)
{
// Keeps minimum element on top
priority_queue, vector >,
greater > > q;
// To keep required answer
int ans = MAXI;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// If it is not good vertex
if (!a[i])
continue;
// Keep all vertices not visited
// and distance as MAXI
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
dist[j] = MAXI;
vis[j] = 0;
}
// Distance from ith vertex to ith is zero
dist[i] = 0;
// Make queue empty
while (!q.empty())
q.pop();
// Push the ith vertex
q.push({ 0, i });
// Count the good vertices
int good = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
// Take the top element
int v = q.top().second;
// Remove it
q.pop();
// If it is already visited
if (vis[v])
continue;
vis[v] = 1;
// Count good vertices
good += a[v];
// If distance from vth vertex
// is greater than ans
if (dist[v] > ans)
break;
// If two good vertices are found
if (good == 2 and a[v]) {
ans = min(ans, dist[v]);
break;
}
// Go to all adjacent vertices
for (int j = 0; j < gr[v].size(); j++) {
int to = gr[v][j].first;
int weight = gr[v][j].second;
// if distance is less
if (dist[v] + weight < dist[to]) {
dist[to] = dist[v] + weight;
q.push({ dist[to], to });
}
}
}
}
// Return the required answer
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Number of vertices and edges
int n = 5, m = 5;
vector > gr[N];
// Function call to add edges
add_edge(gr, 1, 2, 3);
add_edge(gr, 1, 2, 3);
add_edge(gr, 2, 3, 4);
add_edge(gr, 3, 4, 1);
add_edge(gr, 4, 5, 8);
// Number of good nodes
int k = 3;
int a[N], vis[N], dist[N];
// To keep good vertices
a[1] = a[3] = a[5] = 1;
cout << minDistance(gr, n, dist, vis, a, k);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find the shortest pairwise
// distance between any two different good nodes.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class GFG{
static class Pair
{
int first, second;
public Pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
public Pair()
{}
}
static final int N = 100005;
static final int MAXI = 99999999;
// Function to add edges
static void add_edge(ArrayList gr[],
int x, int y, int weight)
{
gr[x].add(new Pair(y, weight));
gr[y].add(new Pair(x, weight));
}
// Function to find the shortest
// distance between any pair of
// two different good nodes
static int minDistance(ArrayList gr[], int n,
int dist[], int vis[],
int a[], int k)
{
// Keeps minimum element on top
PriorityQueue q = new PriorityQueue<>(
new Comparator()
{
public int compare(Pair p1, Pair p2)
{
if (p1.first == p2.first)
{
return p1.second - p2.second;
}
return p1.first - p2.first;
}
});
// To keep required answer
int ans = MAXI;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// If it is not good vertex
if (a[i] == 0)
continue;
// Keep all vertices not visited
// and distance as MAXI
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
dist[j] = MAXI;
vis[j] = 0;
}
// Distance from ith vertex
// to ith is zero
dist[i] = 0;
// Make queue empty
while (!q.isEmpty())
q.poll();
// Push the ith vertex
q.add(new Pair(0, i));
// Count the good vertices
int good = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
// Take the top element
int v = q.peek().second;
// Remove it
q.poll();
// If it is already visited
if (vis[v] != 0)
continue;
vis[v] = 1;
// Count good vertices
good += a[v];
// If distance from vth vertex
// is greater than ans
if (dist[v] > ans)
break;
// If two good vertices are found
if (good == 2 && a[v] != 0)
{
ans = Math.min(ans, dist[v]);
break;
}
// Go to all adjacent vertices
for(int j = 0; j < gr[v].size(); j++)
{
int to = gr[v].get(j).first;
int weight = gr[v].get(j).second;
// If distance is less
if (dist[v] + weight < dist[to])
{
dist[to] = dist[v] + weight;
q.add(new Pair(dist[to], to));
}
}
}
}
// Return the required answer
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Number of vertices and edges
int n = 5, m = 5;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ArrayList[] gr = new ArrayList[N];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
gr[i] = new ArrayList();
}
// Function call to add edges
add_edge(gr, 1, 2, 3);
add_edge(gr, 1, 2, 3);
add_edge(gr, 2, 3, 4);
add_edge(gr, 3, 4, 1);
add_edge(gr, 4, 5, 8);
// Number of good nodes
int k = 3;
int[] a = new int[N],
vis = new int[N],
dist = new int[N];
// To keep good vertices
a[1] = a[3] = a[5] = 1;
System.out.println(minDistance(
gr, n, dist, vis, a, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552 输出:
7如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。